Abstract
Introduction: Patients (pts) with double hit lymphoma (DHL) often experience poor outcomes due to chemotherapy resistance. Accordingly, DHL pts achieving first complete remission (CR1) may undergo consolidative stem cell transplant (SCT), but the benefit of this treatment remains unclear. Here we report the results of a retrospective analysis of DHL pt outcomes based on receipt of SCT in CR1.
Methods: DHL was defined as high-grade B cell lymphoma (HGBL) with rearrangement of MYC/8q24as well as BCL2/18q21and/or BCL6/3q27 by fluorescence in situ hybridization or conventional karyotype. Pts received front-line therapy with either RCHOP or intensive induction, defined as REPOCH, RhyperCVAD or RCODOX-M/IVAC. To avoid confounding due to inclusion of pts with primary refractory or rapidly-relapsing disease who would not be eligible to receive SCT, all pts analyzed achieved CR1, defined as the absence of disease at ≥7.5 months (mo) from diagnosis. All included pts were also age ≤75 and deemed fit for SCT by the local investigator. A landmark analysis was carried out, with progression free survival (PFS) defined as the time from 7.5 mo post-diagnosis to relapse or last follow-up if in CR1 and overall survival (OS) defined as the time from 7.5 mo post-diagnosis to death or last follow-up if alive. Therapy, including SCT, was given at the discretion of the treating physician. Pts were treated from 2006-2016 and data were censored on 4/15/16.
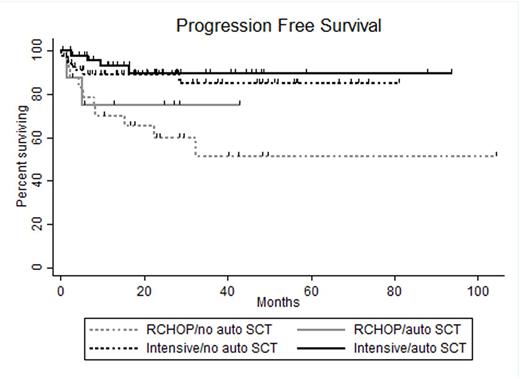
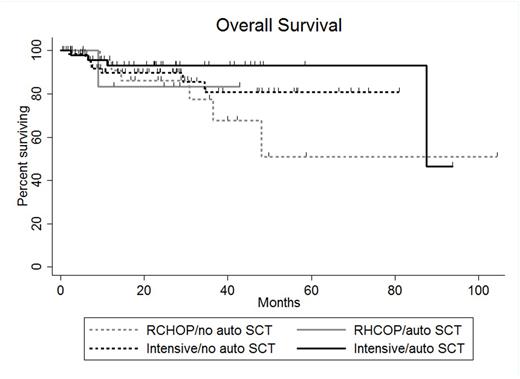
Results: A total of 163 pts treated at 17 US academic medical centers were included in this analysis. Sixty-eight pts (42%) received SCT in CR1 (SCT group) and 95 pts (58%) did not receive SCT in CR1 (no SCT group). In the SCT group, 57 pts received autologous (auto) SCT only, 10 pts allogeneic SCT only and 1pt both. Comparison of baseline clinicopathologic characteristics revealed higher frequency of male sex (p=0.05), transformed low-grade lymphoma (p<0.01) and receipt of intensive induction (p=0.03) in SCT as compared with no SCT pts. All other characteristics, including age >60 (41% vs. 51%), stage 3-4 disease (81% vs. 74%), elevated lactate dehydrogenase (65% vs. 62%), ECOG performance status >1 (24% vs. 23%), International Prognostic Index score 3-5 (65% vs. 62%) bone marrow involvement (28% vs. 29%), extranodal disease (53% vs. 54%), Ki67 expression ≥90% (50% vs. 53%), germinal center cell of origin by Hans algorithm (93% vs. 83%), presence of BCL2 rearrangement (94% vs. 85%) and receipt of CNS prophylaxis (68% vs. 56%) were similar between SCT and no SCT pts, respectively. For all pts, the median length of follow-up from the time of landmark analysis was 23.5 mo (range 0.2-104.2 mo). Thirty-six mo PFS was 87% in SCT pts and 74% in no SCT pts (p=0.21) and 36 mo OS were 89% and 80%, respectively (p=0.49). No baseline characteristic was significantly associated with 36 mo OS; however, pts treated with R-CHOP (n=33) had a significantly higher hazard ratio (HR) for relapse at 36 mo (HR 3.45 95% confidence interval 1.59-7.45, p=0.002) as compared to that of pts treated with intensive induction (n=130). Additional analysis incorporating induction regimen and receipt of auto SCT revealed 36 mo PFS and OS as follows: 51% and 77% for pts receiving RCHOP induction and no auto SCT (RCHOP-, n=25), 75% and 83% for pts receiving RCHOP induction and auto SCT (RCHOP+, n=8), 85% and 81% for pts receiving intensive induction and no auto SCT (intensive-, n=70) and 90% and 93% for pts receiving intensive induction and auto SCT(intensive+, n=49) . Comparison of survival outcomes between groups revealed that RCHOP- pts experienced inferior 36 mo PFS to that of intensive- (p=0.006) and intensive+ (p=0.002) pts. However, 36 mo PFS was similar for RCHOP+, intensive- and intensive+ pts. Additionally, 36 mo PFS was similar between RCHOP- and RCHOP+ pts as well as intensive- and intensive+ pts. No difference in 36 mo OS was detected between groups. For 24 pts who relapsed, the median OS was 8.6 mo with 3 pts achieving OS >24 mo.
Conclusion: The inferior rate of relapse at 36 mo experienced by pts treated with R-CHOP as compared to that of pts treated with intensive induction appears to be overcome by receipt of consolidative auto SCT. Neither 36 mo PFS in pts receiving intensive induction or 36 mo OS in any pt subgroup is significantly increased by receipt of consolidative auto SCT. DHL pts who relapse rarely experience prolonged OS, suggesting a need for novel therapies for these pts.
Reddy:INFINITY: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; KITE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GILEAD: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Howlett:Amgen: Honoraria; Teva: Speakers Bureau; Eisai: Honoraria; Sandoz: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria. Mato:Abbvie, Gilead Sciences, Pharmacyclics, TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Abbvie, Acerta Pharma, Gilead Sciences, ProNAi, TG Therapeutics, Theradex: Research Funding. Kaplan:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding. Petrich:AbbVie: Employment. Chavez:Janssen: Speakers Bureau. Barta:Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene, Merck, Seattle Genetics: Research Funding. Lansigan:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Teva: Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy. Calzada:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding. Cohen:Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millennium/Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Infinity: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Amengual:Acetylon Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal