Abstract
Introduction: Patients with AML and MDS who are age 60 or above represent a discrete group of patients with a different disease biology compared to younger patients. These patients are often not offered allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) as a curative intent because of concern of increased nonrelapse mortality (NRM) and poor overall survival (OS). Hence, the information on transplant outcomes among this population is very limited. Recently with the use of better supportive care measures and reduced intensity preparative regimens, patients greater than 60 are often recommended to proceed to transplant. This study evaluates our single center experience of allogeneic transplantation in patients with MDS and AML aged 60 and older.
Patients and Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 60 years or older consecutive patients with AML and MDS who underwent allogeneic HSCT between January 2005 and December 2014. The primary objectives of our study were to determine NRM, relapse, relapse free survival (RFS) and OS at 1 year following transplant. The secondary objectives were to estimate cumulative incidence of acute (aGVHD) and chronic GVHD (cGVHD) at 1 year, length of stay and readmission rate in the first 100 days following transplant.
Results: Between January 2005 and December 2014, 159 patients underwent allogeneic HSCT with the median age of 64 (range, 60-75) years and median follow-up duration for OS of 3.34 (95% CI, 2.51-3.87) years. Increasing number of patients were transplanted in recent years, i.e., 67% patients between 2010-2014 compared to 33% between 2005-2009. One hundred three patients (65%) had AML and 56 patients (35%) had MDS. Forty-nine patients (31%) received full intensity regimen and 110 patients (69%) received reduced intensity regimen. Fifty-two patients (33%) underwent allogeneic related transplant and 107 patients (67%) had allogeneic unrelated transplant. Thymoglobulin based GVHD prophylaxis was given in 77 patients (48%) whereas non-thymoglobulin based GVHD prophylaxis was given in 82 patients (52%). The median day to neutrophil and platelet engraftment was 11 (range, 7-22) days and 16 (range, 0-675) days, respectively. Graft failure occurred in 3 patients. At 1-year follow-up, the cumulative incidence of grade II-IV aGVHD was 39.7% (95% CI, 32.0-47.2%), grade III-IV aGVHD was 20.8% (95% CI, 14.9-27.5%) and cGVHD was 54.1% (95% CI, 46.0-61.5%). The cumulative incidence of chronic extensive GVHD was 39.8% (95% CI, 32.1-47.4%). Blood stream infection, cytomegalovirus reactivation, Epstein-Barr virus reactivation, C. difficile diarrhea occurred in 44%, 35%, 22% and 26% of patients, respectively. At 1-year follow-up, NRM was 25.3% (95% CI, 18.8-32.3%), RFS was 53.3% (95% CI, 46.1-61.7%), relapse rate was 21.4% (95% CI, 15.4-28.1%) and OS was 56.4% (95% CI, 49.2-54.7%). The median day of hospitalization following transplant was 26 (range, 19-112) days and almost half (52%) of patients were readmitted in the first 100 days following transplant. Leukemia recurrence was the most common cause of death. Multivariable analysis demonstrated high disease risk index to be the independent predictor of poor RFS, OS and higher relapse rate (p<0.03), whereas non-thymoglobulin based GVHD prophylaxis, higher comorbidity index (≥3) and MDS were found to be associated with higher NRM (p<0.03). Most importantly, age did not shown to have any effect on relapse rate, OS, RFS, or NRM.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that allogeneic HSCT is well tolerated and had acceptable NRM, and OS among this group. Hence, older age alone should not be considered a contraindication to HSCT.
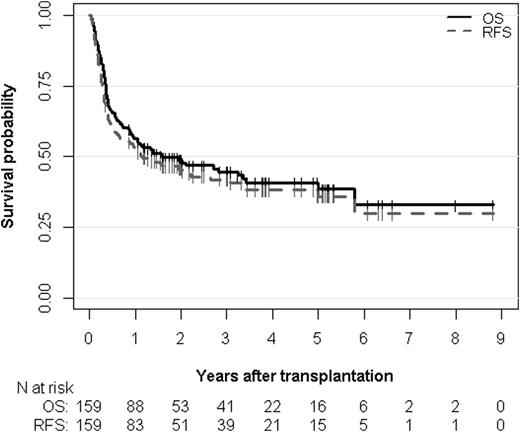
Overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) estimates. The median OS is 1.60 years (95% CI, 0.94 to 5.00 years) and the median RFS is 1.15 years (95% CI, 0.63 to 3.07 years). The median follow-up time of OS and RFS are 3.34 years (95% CI, 2.51 to 3.87 years) and 3.25 years (95% CI, 2.51 to 3.87 years), respectively.
Overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) estimates. The median OS is 1.60 years (95% CI, 0.94 to 5.00 years) and the median RFS is 1.15 years (95% CI, 0.63 to 3.07 years). The median follow-up time of OS and RFS are 3.34 years (95% CI, 2.51 to 3.87 years) and 3.25 years (95% CI, 2.51 to 3.87 years), respectively.
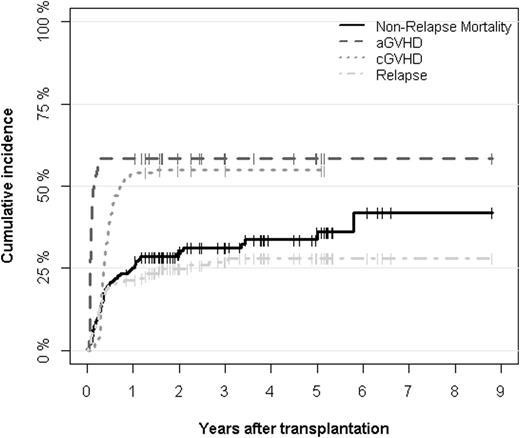
Cumulative incidences of aGVHD, cGVHD, relapse and non-relapse mortality after transplantation.
Cumulative incidences of aGVHD, cGVHD, relapse and non-relapse mortality after transplantation.
Deol:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal