Abstract
The international prognosis scoring system (IPSS) and the revised-IPSS were generated with data from 816 and 7,019 patients (pts) from academic centers with a median age of 69 and 71 years (y) respectively. As the median age of pts with MDS receiving care in Germany is 74.9 y and around a quarter of pts are older than 80 y, the aim was to evaluate the meaning of the IPSS and additional risk factors in the older population group.
Methods: Pts with written informed consent could be included in the online-registry. Pts were eligible if a bone marrow examination had been performed and if basic data and the quarterly course of the disease were documented. Statistical analysis: Depending on the distributions of each variable frequency tables, means (SD), medians were calculated overall and stratified by age classes. Corresponding overall tests were performed (Chi-square, Kruskal-Wallis). Time dependent survival probabilities from MDS diagnosis were estimated by Kaplan Meier curves (compared using log rank test). Multiple Cox regression models were used to investigate associations between mortality risk and baseline risk factors. Variable selection was performed in the subpopulation of elderly pts based on univariate models and models including all prespecified variables (IPSS, sex, transfusion dependent at diagnosis (Tx at d), primary or secondary MDS, comorbidities). Mortality of pts subgroups was compared and age-sex-standardized with the German population 2013 as given in the Human Mortality Database (www.mortality.org, University of California Berkeley, Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research). Standardized mortality rates (SMR) and 95%-confidence intervals were estimated.
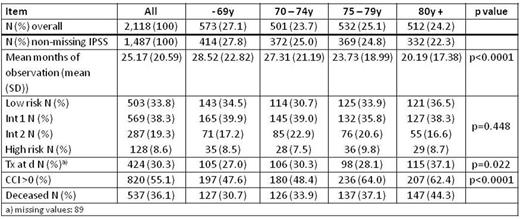
Results: Between July 2009 and March 2016 (81 months) 2,118 pts from 90 institutions, mainly outpatient practices, were documented. The median age of the 843 (39.8%) female and 1,275 (60.2%) male pts was 74.9y (min-max: 26.5 - 94.2). 631 patients were excluded from analysis due to missing IPSS risk. The duration of observation, frequencies of IPSS, Tx at d, and the Charlson comorbidity index (CCI) are given in the table.
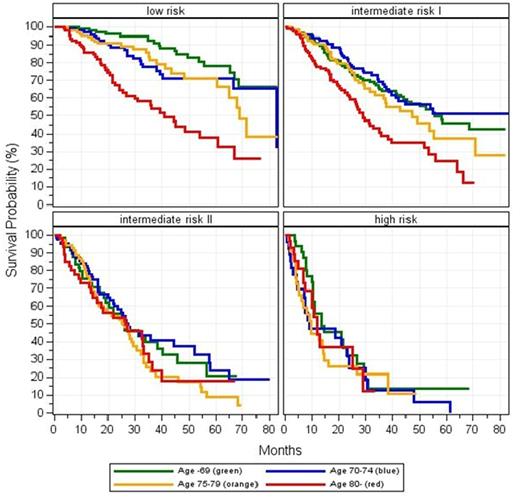
Increased age and IPSS risk were significantly associated with the risk of death. An additional interaction between age and IPSS risk was significant (p=0.0198, Cox model, lower IPSS risk in increased age).
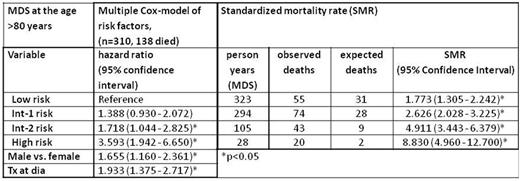
In the subgroup of elderly patients (n=332, 147 died) after variable selection, IPSS, gender and Tx at d (22 missings) were significantly associated with the risk of death. Furthermore, even in the low risk group an elevated risk was estimated (SMR 1.773) compared to the normal population in the same age class. SMRs increase with higher IPSS risk.
Analysis of comorbidities using CCI showed no significant association with mortality in the low risk group of the elderly patients (n=121, 44 died). Because of low sample sizes in the CCI subgroups the power is small, but even the survival curves did not show a clear trend (p= 0.497).
Conclusion: IPSS risk and age are significantly associated with the risk of death. In elderly pts associated risk factors were IPSS, male gender and transfusion at diagnosis. Even the diagnosis of low risk MDS has a negative impact on life expectancy.
Supported by an unrestricted grant from Celgene and Novartis.
Steinmetz:Vifor: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Haastert:X-Med: Honoraria. Tesch:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Schmitz:Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal