Abstract
Background: LIGHT (Homologous to lymphotoxins, shows inducible expression, and competes with herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D for herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM)/tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related 2, HVEM-L, TNFSF14, or CD258) is a member of TNF superfamily. It is expressed as a homotrimer on activated T cells and also on immune dendritic cells, and has three receptors such as HVEM, LT-¥â receptor (LT-¥âR) and decoy receptor 3 (DcR3). So far, three receptors with distinct cellular expression patterns are described to interact with LIGHT. Follicular DCs and stromal cells bind LIGHT through LT-¥âR. We monitored the effects of LIGHT on human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs).
Methods: At first, we checked negative and positive differentiation markers of BM-MSCs. After rhLIGHT treatment, we monitored cell count, viability, proliferation, and cell cycle distribution. Also, PDGF and TGF¥â production by rhLIGHT were examined by ELISA, and biological mechanism were checked by immunoblotting through the rhLIGHT treatment.
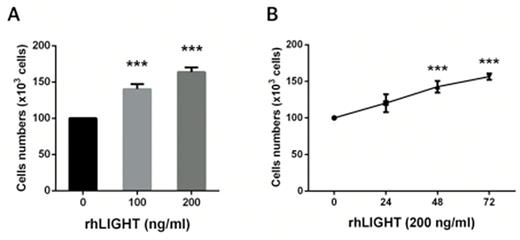
Results: FACS analysis result showed that LT-¥âR receptor is expressed in human BM-MSCs, but not HVEM indicating that LIGHT binds only LT-¥âR in human BM-MSCs. (Fig. 1A/B). rhLIGHT and LT-¥âR interaction increased cell numbers in BM-MSCs using an inverted microscope for cell number changes. Cell numbers by rhLIGHT enhanced dose-dependently and time-dependently (Fig. 2 A/B). Cell viability and the expression of p-AKT, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL by rhLIGHT were significantly increased in BM-MSCs and rhLIGHT-induced IkB-¥á degradation activated NF-kB signal (Fig. 3A/B). rhLIGHT increased cell proliferation by increasing S/G2/M phase in BM-MSCs (Fig. 3C and 4D). And cell cycle regulatory proteins were enhanced by rhLIGHT in BM-MSC including cyclin B1, D1, D3, E, and cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 1 and 2 while CDK inhibitor, p27 was decreased by rhLIGHT treatment (Fig. 3E). Moreover, rhLIGHT-induced PDGF and TGF¥â production by STAT3 and smad3 activation accelerated BM-MSCs proliferation. And we also confirmed differentiation potential of rhLIGHT on BM-MSCs by the staining for adipogenesis (Oil Red O staining), chondrogenesis (Alcian blue staining) and Osteogenesis (Alizarin red Staining).
Conclusion: LIGHT and LT-¥âR interaction increases survival and proliferation of human BM-MSCs by activation of survival proteins, anti-apoptotic proteins, CDKs and cyclins. Moreover, LIGHT-induced STAT-3 and smad-3 activation causes PDGF and TGF-¥â production, and they enhance LIGHT signals in human BM-MSCs. We proposed the pathway of LIGHT and LT-¥âR interaction in human BM-MSCs. Therefore, LIGHT may play an important role for therapy of stem cells, and contribute to modification of MSCs.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal