Abstract
Introduction
The number of MDS patients who receive allogeneic stem cell transplantation is steadily increasing. However, the main cause for treatment failure is relapse which exceeds 50%. Post transplant strategies such as novel agents (5-azacytidine, HDAC inhibitor etc.) as well as adoptive immunotherapy (e.g. DLI) are currently under investigation to reduce the risk of relapse.
Patients and methods
In order to have a valid tool for stratification in phase III studies, the CMWP of EBMT is developing a simplified "Relapse-risk score" for MDS patients. For this purpose 1638 patients with MDS who received an allogeneic stem cell transplantation from HLA-identical sibling or a matched unrelated donor between 1995 and 2012 and reported to EBMT registry were included. The median age of the patients was 54 years (range 18-76) and diagnosis were: RAR/RARS/RCDM-(RS) and RAEB. Variables which were taken into the analysis were: age, classification of MDS, donor source (HLA-identical sibling vs matched unrelated donors), acute and chronic GvHD,stem cell source (PBSC vs bone marrow), T-cell depletion , intensity of the conditioning regimen (reduced intensity vs standard myeloablative), blasts in bone marrow at time of transplant, and cytogenetic: very poor (very poor according to IPSS revised or monosomal karyotype), poor (according to IPSS-revised), and good (according to IPSS-revised) and unclassifiable. To take the different risks of relapse depending on time from transplant into account we developed 4 different prognostic models: 1) relapse between SCT and 6 months after SCT, 2) relapse between 6 and 12 months post-SCT, 3) relapse between 12 and 24 months post-SCT and 4) relapse after 24 months post-SCT.
Results
Multivariate Fine and Gray regression models were used to assess the impact of risk factors on the cumulative incidence of relapse. Disease status RAEB remains significant in all 4 models (1: HR 1.62 (95% CI 1.14-2.86), 2: HR 2.51 (95% CI 1.49-4.20), 3: HR 2.10 (95% CI 1.19-3.73), and 4: HR 2.97 (95% 1.56-5.60), whereas very poor cytogenetic was significant in model 1: HR 4.33 (95% CI 2.85-6.60), and model 3: HR 3.51 (95% CI 1.69-7.29)), poor cytogenetic only for early relapse: model 1: HR 2.19 (95% CI 1.39-3.27). RIC was significant for model 1: HR 2.04 (95% CI 1.51-2.75 and 2: HR 1.72 (95% CI 1.06-2.77), T-cell depletion for model 2: HR 1.61 (95% CI 1.02-2.56), and 3: HR 2.01 (95% CI 1.19-3.39).
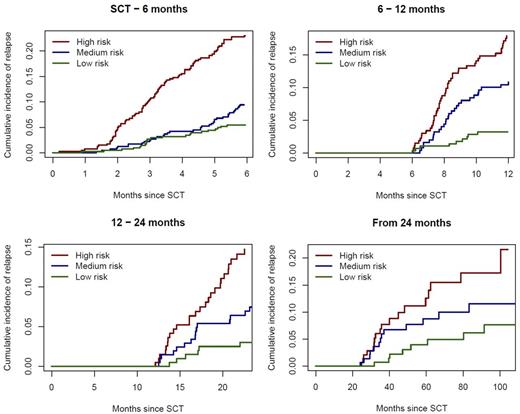
The prognostic risk scores are directly obtained by adding up the relevant log-hazard ratios, which allows dividing patients into three risk groups, low, medium, high, defined by tertiles in the study population. Cumulative incidence plots of relapse for each of the three groups are shown.
Conclusion
Relapse as most common treatment failure of allogeneic SCT in MDS can occur even after 24 months. Several risk factors influence the incidence of relapse, however while RAEB disease status influence early, intermediate and late relapse, other risk factors such as cGvHD influence only late (>24 months relapse. Therefore, these risk scores may help to stratify patients according to their risk of relapse after stem cell transplantation which can be used for stratification in further prospective trials using post transplant therapies at different time points after stem cell transplantation to reduce the risk of relapse.
Kröger:Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding. Maertens:Amgen: Consultancy; Merck Sharp & Dohme: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Schetelig:Sanofi: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal