Abstract
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is one of the most prevalent childhood cancers worldwide. Although the 5-year event-free survival rate of ALL patients have been improved to about 80% in latest years, there are approximately 15% of ALL cases in China remained to be poorly responsive to chemotherapy treatments, and therefore manifested in poor prognosis. Daunorubicin (DNR) is a key agent (Fig.1), as a chemical can cause DNA damages, in the formula for the treatments of ALL patients, the drug resistance to DNR will directly contributed to the failing of treatments and poor prognosis. In clinic, there is an urgent need for the development of assays that can be used for the prediction of DNR resistance, especially the involvement of visual indicators. Coilin is a major scaffold and marker protein of the functional nuclear structure - Cajal body (CB). We found that DNR was able to induce vast nucleolar accumulation of coilin in ALL leukemia cell lines of RS4;11 and Reh. Such accumulation of coilin was dose-dependently correlated to the increase of drug concentrations (Fig.2). At the molecular level, we also observed that the expression levels of coilin increased based on treatment of DNR(Fig.3B), while the expression levels of p27 protein was much lower in DNR insensitive cells with less significant changes of Coilin-indicated CB morphology as compared to the sensitive cells (Fig.3A). The over-expression of Coilin inhibited p27 expression and coilin knock-down increased the expression of p27(Fig.3 C,D). Our study suggested that coilin could be considered as a visual maker for the detection of daunorubicin resistance in ALL cells, and the mechanism possibly involved the regulation of drug sensitivity -related protein p27 through Cajal body -mediated RNA processing, during which coilin is an important participator with crucial functions.
Results
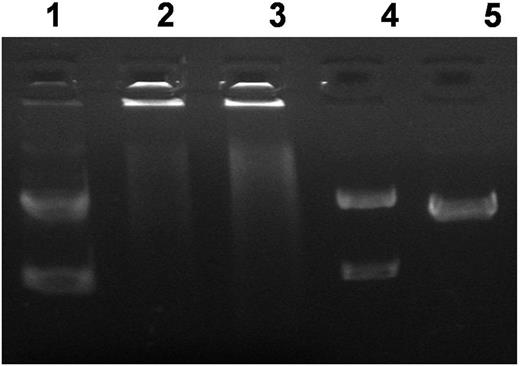
1.Daunorubicin inhibits topoisomerase II activity
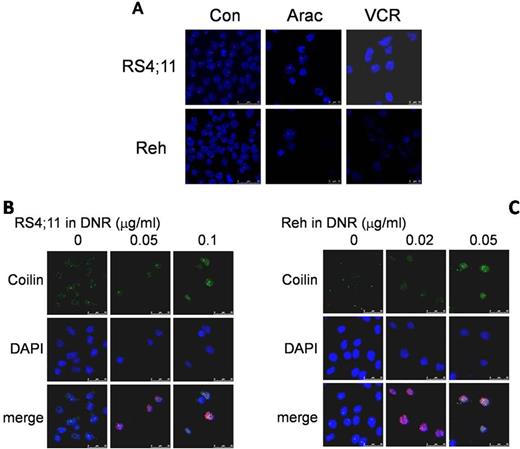
2.Daunorubicin(DNR)-induced DNA damage triggers the nucleolar accumulation of coilin
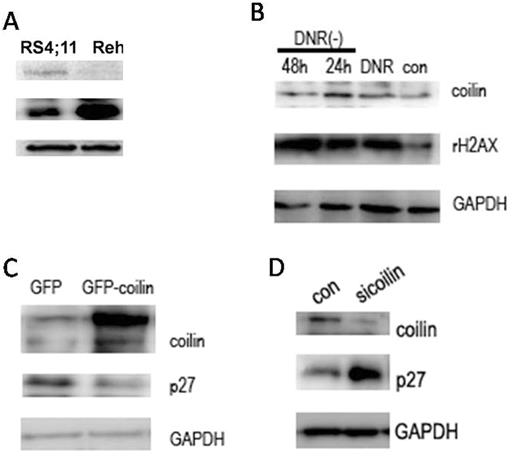
3.Coilin inhibit the expression of p27 and may play a role in the drug resistance of leukemia through p27
Daunorubicin (DNR) as a drug for leukemia treatment. Inhibition on topoisomerase II activity with DNR. Decatenated kDNA was incubated with nuclear extracts from Reh treated with DNR (0, 0.02 and 0.05 mg/ml) and compared with linearized kDNA.
Daunorubicin (DNR) as a drug for leukemia treatment. Inhibition on topoisomerase II activity with DNR. Decatenated kDNA was incubated with nuclear extracts from Reh treated with DNR (0, 0.02 and 0.05 mg/ml) and compared with linearized kDNA.
Daunorubicin (DNR) induced accumulation of Coilin. (A) Morphology of Cajal bodies in RS4;11 or Reh in native and conditions treated with Ara c or VCR. Dose-dependent coilin accumulation was observed in RS4;11 cells (B) treated with increasing concentrations of DNR (0, 0.05 and 0.1 m g/ml) or in Reh cells (C) treated with DNR of 0, 0.02 and 0.05 mg/ml.
Daunorubicin (DNR) induced accumulation of Coilin. (A) Morphology of Cajal bodies in RS4;11 or Reh in native and conditions treated with Ara c or VCR. Dose-dependent coilin accumulation was observed in RS4;11 cells (B) treated with increasing concentrations of DNR (0, 0.05 and 0.1 m g/ml) or in Reh cells (C) treated with DNR of 0, 0.02 and 0.05 mg/ml.
Coilin regulated the expression of p27
(A)The expression of coilin was higher in RS4;11 cells than that in Reh cells, whereas p27 had the opposite expression pattern in the two cells.(B)The level of coilin increased when cells were treated with DNR.(C,D)The over-expression of coilin inhibited p27 expression and coilin knock-down increased the expression of p27.
Coilin regulated the expression of p27
(A)The expression of coilin was higher in RS4;11 cells than that in Reh cells, whereas p27 had the opposite expression pattern in the two cells.(B)The level of coilin increased when cells were treated with DNR.(C,D)The over-expression of coilin inhibited p27 expression and coilin knock-down increased the expression of p27.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal