Abstract
Introduction:The myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are clonal disorders characterized by cytopenias and abnormal hematopoiesis. Though there are reports of perturbations in the hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) and the mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) as well as other elements of the bone marrow (BM) niche in an instructive or permissive manner leading to the genesis of ineffective hematopoiesis in this condition, most studies have evaluated single elements. Here we demonstrate altered HSC, MSC and the vascular niche elements in patients with MDS - Refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia (RCMD).
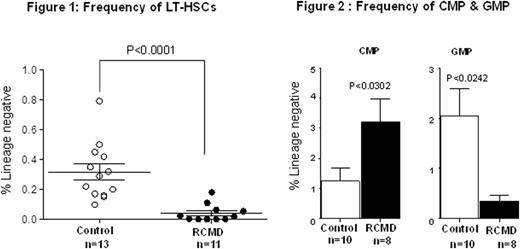
Methods and results: Bone marrow aspirates from patients with RCMD (n=12, mean age 54.33±14.51 years) were compared with those from age-matched controls (n=18, mean age 47.78±18.60 years) who had a 'normal' marrow obtained for other diagnostic purposes. Cytogenetic analysis showed abnormal karyotypes in seven patients and normal karyotypes in five. The abnormalities seen were as follows: deletion 7q/monosomy 7 (four patients), deletion 5q (three patients), loss of Y (two patients), monosomy 5, deletion 20q (one each), complex karyotypes (four patients). Phenotypic enumeration of HSPCs revealed a marked decrease in the frequency of highly purified HSCs (Lin-CD34+CD38-CD90+CD45RA-) in RCMD (0.04135±0.01748%, n=11) when compared to controls (0.3168±0.05266%, n=13, p<0.0001) (Figure 1). Patients with RCMD also had increased common myeloid progenitors (CMP) (3.221 ± 0.7478%, n=8) compared to control (1.243±0.4463%, n=10, p<0.0302) and loss of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (GMP) (0.4863±0.1638%, n=8) compared to controls (2.047±0.5422%, n=10, p<0.0242) (Figure 2).
Assessment of the frequency of de novo MSCs (CD31-CD45/CD71- population) expressing CD271 and/or CD146, indicating the more primitive population, in total nucleated cells showed increased CD271+CD146-MSCs (0.632±0.2, n=5) compared to controls (0.2000±0.05158, n=6, p<0.0401) as also the CD271+CD146+ MSCs (0.2900±0.09803, n=5) in RCMD patients when compared to controls (0.02861±0.01354, n=6, p<0.0172) (Figure 3). We also evaluated in vitro cultured MSCs (P4) in these patients. CD271+CD146+ MSCs within total cultured MSCs were higher (0.1900±0.06429%, n=3) than in controls (0.0040±0.0040%, n=3, p<0.0447). RCMD MSCs had significantly lower proliferation index (32±3.7%, n=3) compared to controls (60±9.2%, n=3, p<0.0479). Cell cycle analysis of MSC showed significantly lower numbers in G0 in RCMD (0.1567 ± 0.07881 %, n=3) compared to control (0.6400 ± 0.1007 %, n=3; p<0.0194). Apoptosis was much higher in RCMD MSCs (2.700±0.8007%, n=3) compared to controls (0.03633±0.01802%, n=3, P<0.0292). No significant differences in expression profile of stem cell maintenance related cytokines and growth factors (CXCL12a, SCF, VEGF, ANGPT and LIF ) or components of Notch (Notch1, Notch3, Jagged-1, Delta like-1 and Hes1) and Wnt (Dkk1 and Dkk-2) pathways were found between RCMD and control MSCs within the limited numbers evaluated. Interestingly, unlike controls, immunofluorescence imaging of bone marrow trephine from MDS-RCMD revealed CD271+CD146+ MSCs co-localized with sinusoids and in direct contact with CD34+ (<5% blast) HSC/progenitor cells (HSPCs).
Conclusion: Our data shows that in patients with MDS-RCMD, both qualitative and quantitative abnormalities exist in the HSC, HSPC and niche elements. We also show that the cytopenia could be related to decreased numbers of primitive HSCs and a differentiation arrest at the CMP stage. Primitive MSCs are reduced, and those that exist show poorer proliferative and survival features. Further studies are needed to understand the cause and effect relationship of these changes.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal