Background: Ibrutinib, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, was approved by FDA for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety data from randomized controlled trials (RCT) of ibrutinib-based therapy in patients with CLL or SLL.
Methods: PubMed, ASH, and ASCO databases (2008-2016) were searched for randomized control trials of ibrutinib therapy (either single-agent or combination) for chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma through June 30, 2016. Study endpoints included overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and adverse events (AE). Pooled hazard ratios (HR) for survival outcomes and relative risks (RR) for dichotomous data with 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated with a random effect model using MedCalc.
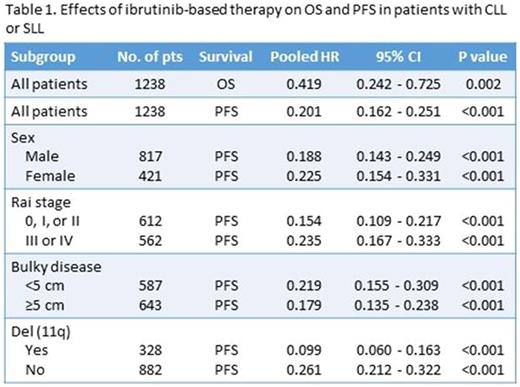
Results: Four randomized controlled trials (RESONATE-1, RESONATE-2, HELIOS, and CLL12) were identified, but CLL12 trial was excluded from this study since the efficacy data were not available at the time of this meta-analysis. Pooled data from the 3 RCTs (1238 patients) showed that ibrutinib-based therapy improved overall survival (HR 0.419; 95% CI 0.242-0.725, P = 0.002) and progression-free survival (HR 0.201; 95% CI 0.162-0.251, P < 0.001) compared to regimens without ibrutinib. Subgroup analysis showed that the PFS benefits were independent of sex (male: HR 0.188, 95% CI 0.143-0.249, P < 0.001; female: HR 0.225, 95% CI 0.154-0.331, P < 0.001), Rai stage (0-II: HR 0.154, 95% CI 0.109-0.217, P < 0.001; III-IV: HR 0.235, 95% CI 0.167-0.333, P < 0.001), bulky disease (<5 cm: HR 0.219, 95% CI 0.155-0.309, P < 0.001; ≥5 cm: HR 0.179, 95% CI 0.135-0.238, P < 0.001) or chromosome 11q deletion (positive: HR 0.099, 95% CI 0.060-0.163, P < 0.001; negative: HR 0.261, 95% CI 0.212-0.322, P < 0.001). Ibrutinib-based therapy significantly increased the risk of developing all-grade diarrhea (RR = 2.135, 95% CI = 1.437-3.174, p < 0.001), pyrexia (RR = 1.265, 95% CI = 1.011-1.583, p = 0.040), and arthralgia (RR = 1.863, 95% CI = 1.101-3.152, p = 0.020), but not anemia (RR = 0.955, 95% CI = 0.694-1.313, p = 0.777), neutropenia (RR = 1.048, 95% CI = 0.760-1.446, p = 0.774), fatigue (RR = 0.897, 95% CI = 0.746-1.078, p = 0.247), or nausea (RR = 0.951, 95% CI = 0.600-1.506, p = 0.829).
Conclusions: Ibrutinib-based therapy significantly improves OS and PFS (independent of sex, Rai stage, bulky disease or chromosome 11q deletion) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma, but increases the risks of all-grade adverse events including diarrhea, pyrexia, and arthralgia.
Chang:Johnson and Johnson: Other: Stock; Amgen: Other: Research; Boehringer Ingelheim: Other: Research. Goldberg:Neostem: Equity Ownership; Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis: Speakers Bureau; COTA Inc: Employment; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal