Abstract

Background
Children with Down syndrome (DS) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) are shown to have increased therapy-related morbidity and mortality. Hence, therapy modifications and/or dose-reductions are common treatment strategies for this patient (pt) population. Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) ALL Consortium protocols have used same risk-stratified treatment for children with and without DS and ALL.
Aim:
To define the toxicity profile and outcome of children with DS and de novo ALL treated on DFCI ALL Consortium therapy protocols 00-001 and 05-001 using therapy identical to non-DS patients.
Methods:
Demographic, clinical and outcome data of DS and non-DS patients enrolled on the DFCI ALL protocols 00-001 (2000-2004) and 05-001 (2005-2011) were analyzed. Risk categorization and protocol therapy have previously been described (J Clin Oncol 2013; 31:1202-10; Lancet Oncol 2015;16:1677-90). On both protocols, DS ALL pts were treated identically to non-DS pts without any dose reduction or modification, except for the option for DS ALL pts to receive 3 doses of leucovorin after IT methotrexate. Fisher's exact test was used to compare toxicities in the DS and non-DS pts and Gray test was used to compare the cumulative incidence of fracture and osteonecrosis. Overall survival (OS) was defined as time from registration to death. Event-free survival (EFS) was defined as time from registration to first event (defined as induction failure, relapse, second malignant neoplasm (SMN) or death due to any cause). Induction failure and induction death were included as events at time zero. Disease-free survival (DFS) was defined as time from complete remission (CR) to relapse, SMN or death. Pts without an event were censored at the last known follow-up. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival estimation and Greenwood's formula for calculation of 95% confidence interval (CI) of survival estimates. Outcome of DS patients was also examined using Ponte di Legno (PdL) risk group [Low risk (LR) was defined as age at diagnosis ≤ 6 yr. and white cell count < 10X109/L and, remainder as high risk (HR)].(Blood 2014;123:70-7). Two-sided p values <0.05 were considered significant.
Results:
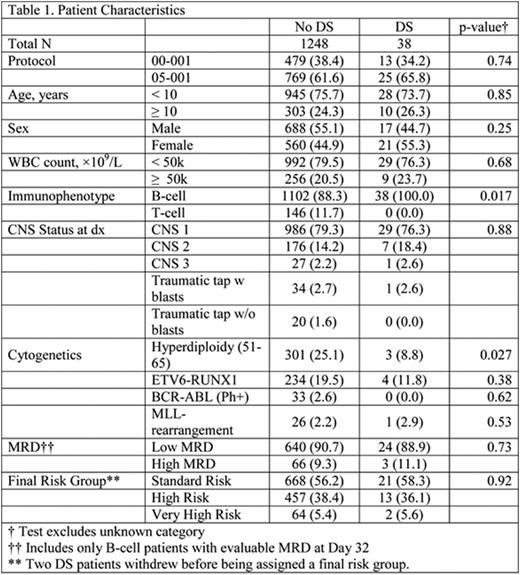
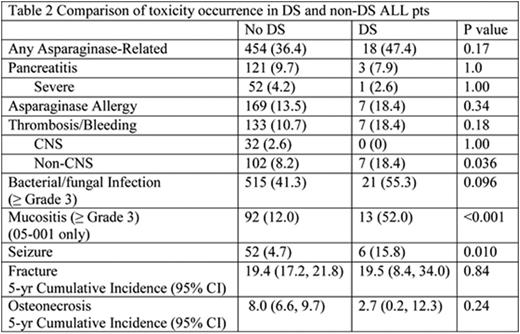
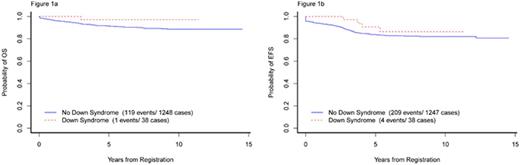
Of 1286 eligible pts aged 1-18 yrs. with de novo ALL enrolled on protocols 00-001 and 05-001, 38 (3%) had DS. There was no difference in demographic or presenting clinical features between DS and non-DS ALL pts except immunophenotype (absence of T-ALL in DS vs 11.7% in non-DS, p=0.017) and presence of high hyperdiploidy (51-65 chromosomes) (8.8% in DS vs 25.1% in non-DS, p=0.027) (Table 1). Two DS-ALL pts withdrew from the study after achieving CR. There was no difference in the CR rates (DS: 100% vs non-DS: 95.2%, p=0.47) or proportion of pts with low end of induction minimal residual disease (MRD) between DS and non-DS groups (p=0.73). Toxicities were comparable except DS pts had significantly higher rates of ≥Grade 3 mucositis (data available for protocol 05-001 only) (DS: 52.0% vs. non-DS: 12.0%, p<0.001), non-CNS thrombosis/bleed (18.4% vs. 8.2%; p=0.036), and seizure (15.8% vs. 4.7%, p=0.010). DS pts also had marginally higher rate of bacterial and fungal infections (55.3% vs. 41.3%, p=0.096) (Table 2). All 38 DS pts achieved a CR and there were 4 relapses with 1 death due to disease. There were no treatment-related deaths in DS-ALL pts. With a median follow-up of 6.2 yrs. the 5-yr EFS, DFS, and OS of DS pts were similar to non-DS pts (90.7% [81.1-100.0] vs. 83.7% [81.7-85.9]; 90.7% [81.1-100.0] vs. 87.4% [85.5-89.3]; 97.1% [91.8-100.0] vs. 91.4% [89.8-93.0]), with the 95% CI overlapping for each comparison (Figures 1a and 1b). There was no difference in outcomes of DS-ALL PdL LR pts (n=13) compared to PdL HR pts (n=25) (5-yr EFS 90.0% [73.2-100.0]. vs. 91.0% [79.9-100.0]; 5-yr OS 100.0% [100.0-100.0] vs. 95.8% [88.2-100.0]).
Conclusion:
DS pts treated on DFCI ALL Consortium protocols without dose reduction or modifications achieved similar outcomes to non-DS pts. DS pts had a higher frequency of mucositis, infection, and seizures, but did not experience any treatment-related deaths. Other than a higher risk of thrombotic complications, they did not develop excessive toxicity to asparaginase. The low rates of relapse and toxicity-related mortality support the approach of unified therapy protocol for DS and non-DS ALL pts with emphasis on supportive care interventions to prevent toxicities.
Overall and event free survival
Asselin:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Sigma Tau Pharamceuticals: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal