Key Points
fam49a is a negative regulator of PTEN.
fam49a controls T cell differentiation.
During hematopoiesis, the balance between proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis is tightly regulated in order to maintain homeostasis. Failure in these processes can ultimately lead to uncontrolled proliferation and leukemia. Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is one of the molecular pathways involved in this balance. By opposing PI3-kinases, PTEN inhibits proliferation and promotes differentiation and is thus considered a tumor suppressor. Indeed, PTEN is frequently mutated in many cancers, including leukemias. Loss of PTEN often leads to lymphoid cancers. However, little is known about the molecular events that regulate PTEN signaling during lymphopoiesis. In this study, we used zebrafish to address this. We report that N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1b (ndrg1b) rescues lymphoid differentiation after PTEN inhibition. We also show that a previously uncharacterized gene, fam49ab, inhibits T-cell differentiation, a phenotype that can be rescued by ndrg1b. We propose that ndrg1b and fam49ab are 2 new modulators of PTEN signaling that control lymphoid differentiation in the zebrafish thymus.
Introduction
During hematopoiesis, the balance between quiescence, proliferation, and differentiation is tightly regulated. Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN)1 regulates this process. PTEN dephosphorylates phosphatidyl inositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate,2 a molecule that promotes cell proliferation, survival, and motility.3 PTEN phosphatase activity is directly counteracted by phosphatidylinositol-3 kinases (PI3Ks).4 Together, PTEN and PI3Ks control the balance between cell proliferation and differentiation, which places an important role on this pathway at several checkpoints during hematopoietic processes, such as T-cell development in the thymus.5,6 Indeed, PTEN mutations or deletions have been detected in 8% to 30% of T-cell acute lymphoid leukemia (T-ALL),7,8 consistent with its role in T-cell development. Several models of PTEN inactivation have been assessed to model T-cell leukemias. Mice deficient for 1 allele of pten develop CD4+CD8− T-cell lymphoma after several weeks of development.9,10 In addition, transgenic mice expressing short hairpin RNA targeting the PTEN pathway display T-cell leukemia, initiating in thymic double-positive cells.11 Conditional inactivation of Pten in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) leads to early-onset myeloproliferative diseases and lymphoid leukemias, which is accompanied by the exhaustion of the HSC pool,12 and deletion of PTEN in CD45+ hematopoietic cells results in T-ALL.13 All these experiments point to a crucial role of PTEN in maintaining progenitor cells in a nonproliferative state.
Pten−/− mice die early during embryogenesis between 3.5 and 6.5 days postcoitum,9 which renders the study of blood cells impossible. However, zebrafish pten mutants can progress through early embryogenesis.14 Zebrafish possess 2 orthologs of the mammalian Pten gene, ptena and ptenb. When both genes are inactivated in the zebrafish, embryos develop until 5 to 6 days postfertilization (dpf).14 In these double mutants, hematopoiesis occurs normally until 48 hours postfertilization (hpf): the primitive blood waves are unaffected, and HSCs develop normally from the aortic hemogenic endothelium between 30 and 48 hpf. However, whereas early hematopoietic precursors can colonize the thymus, these mutants show abnormal thymocyte development in that thymic immigrants cannot differentiate into rag1-positive thymocytes.15
In this study, we analyzed the potential of NDRG proteins to mediate the PTEN pathway. First, we found that zebrafish ndrg1b could rescue pten loss of function, resulting in the normal development of thymocytes. To uncover the signaling pathway responsible for this rescue, we searched for proteins predicted to interact with NDRG on publically available databases. One such protein is the highly conserved FAM49A. Upon overexpression in zebrafish, fam49a abolished T-cell differentiation similar to that in pten double-mutant embryos. However, enforced expression of ndrg1b antagonized this effect. We thus propose that Fam49a is a new negative regulator of Pten, through inhibition of Ndrg proteins.
Materials and methods
Zebrafish husbandry
Zebrafish strains were maintained and bred according to the University of Geneva procedures and authorizations from the local veterinary authorities. All experiments were performed using wild-type (WT) AB*, and the following transgenic lines: Tg(rag2:loxP-DsRed2-loxP-Has.KRAS_G12D), referred to as rag2:DsRed,16 and Tg(Ikaros:eGFP), referred to as Ikaros:eGFP,17 Tg(kdrl:CREs898; βActinSw:DsRedsd5).18
Whole-mount in situ hybridization
mRNA injections and inhibitor treatment
For each gene, the open reading frame sequence was amplified from 48-hpf or 5-dpf zebrafish cDNA. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products were cloned into the pCS2+ vector from which messenger RNA (mRNA) was synthesized using the mMessage mMachine Kit (Life Technologies). In all experiments, 200 pg of each mRNA (unless otherwise stated) was injected into 1- to 2-cell-stage embryos. PTEN signaling was inhibited by treating embryos with 1 µM SF1670 (Sigma-Aldrich) or 1 µM VO-OHpic (Tocris) dissolved in E3 medium from 36 hpf to 4.5 dpf. PI3K was inhibited with 10 µM LY294002 (Tocris) from 3.5 to 4.5 dpf.
Morpholino injections
All morpholino oligonucleotides (MOs) were purchased from Gene Tools and are listed in supplemental Table 2. MO efficiency was tested by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from total RNA extracted from ∼20 embryos at 48 hpf using primers listed in supplemental Table 3.
Western blot
Embryos were lysed in Pierce lysis buffer (Thermo) with added protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktails (Roche) for 15 minutes on ice with mechanical disruption using a syringe and a 27-G needle. Debris was removed by centrifugation for 10 minutes at 4°C. Samples were then subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting according to standard protocols, using anti pS473-Akt (1:2000; CST) and anti-Akt (1:1000; CST) antibodies.
Flow cytometry
For each sample, 40 to 60 embryos (Rag2:DsRed or Ikaros:eGFP) were dissociated in 0.9 × phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), 0.2 mg/mL liberase (Roche) for 2 hours at 32°C with agitation, as previously described.21 Similarly, thymi were dissected from Rag2:DsRed adults and dissociated in liberase as above. Dissociated cells were washed in 0.9 × PBS + 1% fetal calf serum, filtered through 0.45-µm mesh, and stained on ice with SYTOX Red Cell Death Stain (Molecular Probes). Cells were sorted using a FACSAria II cell sorter (BD Biosciences). For cell-cycle analysis, cells were labeled with propidium iodide (Sigma) as previously described.22
Quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR
RNA was isolated using the RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and reverse transcribed into cDNA using the qScript cDNA SuperMix kit (Quanta Biosciences). Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed on a CFX connect Real-Time PCR Detection cycler (BioRad) using the KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR mastermix (KAPA Biosystems) and primers listed in supplemental Table 4. Relative expression was calculated using the 2−∆∆Ct method.23
Microscopy and immunofluorescence
Bright-field images were collected using an Olympus MVX10 microscope fitted with an Olympus SC100 camera (32× magnification). The size of the left thymus was measured using cellSens Standard v1.8.1 software (Olympus). Fluorescent images were collected on a Nikon A1r spectral confocal microscope and processed with ImageJ. Mitotic cells were detected with anti-pHistone 3 antibody (1:250; Abcam) using standard protocols after permeabilization with 1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 40 minutes. Apoptotic cells were detected by incubating live embryos in 10 µg/mL Acridine orange in E3 for 30 minutes followed by 3 × 10 minute washes in E3. Embryos were then anesthetized with Tricaine, mounted on glass bottom dishes in 0.7% agarose, and imaged.
Results
Ndrg family genes are expressed in the zebrafish thymus
To better understand the role of PTEN in early T-cell differentiation, we determined expression patterns of the components of the PTEN signaling pathway in zebrafish. Among them are members of the N-myc Downstream Regulated (NDRG) protein family. In mammals, this family comprises 4 members. In zebrafish, 6 mammalian homologs belong to this family: ndrg1a, ndrg1b, ndrg2, ndrg3a, ndrg3b, and ndrg4. WISH analysis showed that none of these family members are expressed in hemogenic or hematopoietic organs, ie, the ventral floor of the aorta and caudal hematopoietic tissue (CHT) at 33 hpf and 3.5 dpf, respectively (supplemental Figure 1A-L). However, at 4.5 dpf, expression of ndrg1b, ndrg3a, and ndrg3b can be detected in the thymus. Double WISH revealed that these genes overlapped with rag1 expression, a marker for differentiating thymocytes (Figure 1A). To confirm this expression, we made use of the rag2:dsRed and ikaros:eGFP lines, which mark differentiating thymocytes and lymphoid progenitors, respectively.16,17 DsRed+ and eGFP+ cells were purified by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) from 5-dpf embryos, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis showed expression of ndrg1b, ndrg3a, and ndrg3b in thymocytes (supplemental Figure 1M), consistent with the WISH analysis. To investigate whether ndrg expression persisted in adult thymocytes, we sorted rag2:DsRed+ cells from 3-month-old adults. qPCR analysis showed that ndrg1a, ndrg1b, ndrg2, and ndrg3a were expressed in rag2-positive thymocytes (supplemental Figure 1N).
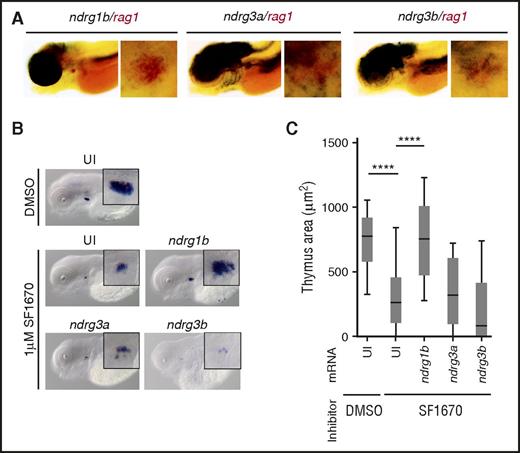
ndrg1b overexpression can restore rag1 expression in zebrafish treated with the PTEN inhibitor SF1670. (A) Double WISH in 4.5-dpf embryos showing overlapping expression of indicated ndrgs (black) and rag1 (red). (B) rag1 expression in 4.5-dpf embryos in uninjected embryos (UI) treated with DMSO or 1 µM SF1670, and in SF1670-treated embryos overexpressing indicated ndrg mRNA at 200 pg per embryo. (C) Quantification of the thymus area in (B). Graph shows 3 independent experiments combined, n = 43 to 68 embryos per condition. ****P < .0001, 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
ndrg1b overexpression can restore rag1 expression in zebrafish treated with the PTEN inhibitor SF1670. (A) Double WISH in 4.5-dpf embryos showing overlapping expression of indicated ndrgs (black) and rag1 (red). (B) rag1 expression in 4.5-dpf embryos in uninjected embryos (UI) treated with DMSO or 1 µM SF1670, and in SF1670-treated embryos overexpressing indicated ndrg mRNA at 200 pg per embryo. (C) Quantification of the thymus area in (B). Graph shows 3 independent experiments combined, n = 43 to 68 embryos per condition. ****P < .0001, 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Ndrg1b mediates PTEN signaling in the thymus
Given their thymic expression and that PTEN can upregulate their expression,24,25 ndrg genes are good candidates to mediate PTEN signaling during T-cell development. To test this hypothesis, we used an inhibitor of PTEN (SF1670)26 and observed the effect on rag1-positive cells by WISH. Initially, we confirmed that SF1670 augments pAkt levels in our experimental design, although statistical significance was not reached (supplemental Figure 2A-B). Treatment of embryos with 1 µM SF1670 from 36 hpf to 4.5 dpf resulted in significantly smaller thymus when compared with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated siblings (Figure 1B-C). These results are very similar to the previously reported reduction in rag1-positive cells in ptena−/−ptenb−/− double-mutant zebrafish.15 We then attempted to rescue this decrease in thymus size. WT embryos were injected with full-length mRNA coding for Ndrg proteins normally expressed in the embryonic thymus and treated with SF1670 from 36 hpf to 4.5 dpf. ndrg1b mRNA was able to reverse the effects of the inhibitor, whereas ndrg3a and ndrg3b could not (Figure 1B-C). SF1670 inhibits PTEN by binding the active site.26 To complement the above result, we used an alternative inhibitor, VO-OHpic, which appears to inhibit PTEN phosphatase activity even when the latter is bound to substrate, and thus, is likely to inhibit PTEN at least in part via another mechanism.27 Similarly to SF1670, treatment with 1 µM VO-OHpic elevated pAkt levels and significantly reduced the size of the thymus (supplemental Figure 2C). In contrast to SF1670, however, inhibition with VO-OHpic could be rescued by all 3 thymically expressed ndrg mRNAs (supplemental Figure 2C). Importantly, overexpression of ndrg mRNA on its own did not significantly alter rag1 expression (supplemental Figure 2D). We thus conclude that at least ndrg1b can mediate PTEN signaling during embryonic T-cell differentiation.
Fam49ab is a gene of unknown function expressed in thymocytes
To uncover potentially unknown regulators of T-cell differentiation in the thymus, we searched for proteins that could bind to NDRG1 or NDRG3, which are expressed in thymocytes. The human and mouse NDRG3 have been proposed to interact with Family with sequence similarity 49 (FAM49A), among others (data from Genemania.org). Similarly, the Caenorhabditis elegans NDRG1-4 protein ortholog, Y48G10A.3, has been reported to bind to R07G3.8, the ortholog of FAM49A in worms (data from wormbase.org). FAM49A appears as a common partner of NDRG proteins through evolution and has been highly conserved between zebrafish and human (∼84% identity; supplemental Figure 3A), which suggests that its role may be significant. We therefore decided to further investigate its function. There are 2 closely related paralogs described in the zebrafish genome: fam49a (ENSDARG00000035907) and zinc finger protein 395 (znf395) (ENSDARG00000006672) (supplemental Figure 3B). This latter annotation is likely to be a mistake, as zebrafish znf395 is most closely related to human and mouse FAM49A (supplemental Figure 3B). Moreover, phylogenetic analysis clusters zebrafish znf395 closer with human and zebrafish FAM49A proteins than with either the mammalian ZNF395 or with the 2 zebrafish paralogs, znf395a and znf395b (supplemental Figure 3C). In addition, a high degree of synteny is observed between zebrafish znf395 and human FAM49A (supplemental Figure 3D), whereas no synteny is detected between zebrafish Znf395 and human ZNF395 (data not shown). It is likely that zebrafish Znf395 is an ortholog of mammalian Fam49a, which has been misannotated. Thus, we will refer to zebrafish znf395 as fam49ab to avoid any confusion, whereas zebrafish fam49a will become fam49aa.
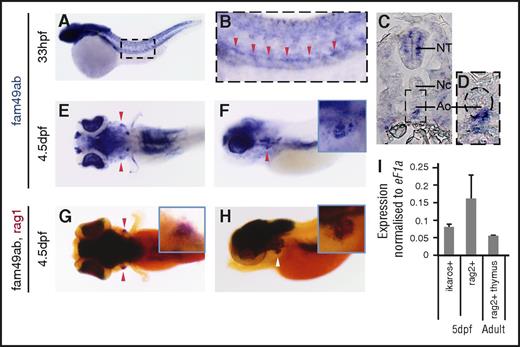
WISH analysis showed that fam49aa is expressed in the somites, the hatching gland, the eyes, and the brain in zebrafish embryos until 36 hpf (supplemental Figure 4A-B). In older embryos, expression in the brain and eyes persists until 4.5 dpf (supplemental Figure 4C-E). Because this gene is not expressed in hematopoietic organs, we did not analyze its function further. Fam49ab is initially expressed in the somites, the eyes, and the neural crest up to 26 hpf (supplemental Figure 4S-K). At 33 hpf, fam49ab is expressed in the ventral aorta (Figure 2A-D), suggesting that this transcript could be expressed by nascent HSCs.18,28 Moreover, at 4.5 dpf, fam49ab is expressed in the thymus (Figure 2E-F), as evidenced by overlapping expression of fam49ab and rag1 (Figure 2G-H). Furthermore, the presence of fam49ab in the thymus was confirmed by qRT-PCR performed on RNA isolated from ikaros:GFP+ or rag2:dsRed+ cells FACS purified from 5-dpf transgenic embryos and from rag2:dsRed+ cells from thymi dissected from adult fish (Figure 2I). We therefore decided to proceed further with the analysis of fam49ab to characterize its function.
fam49ab is expressed in hematopoietic organs in zebrafish.fam49ab expression in the aorta can be seen in (A-B) whole-mount embryo and (C-D) transverse section at 33 hpf (red arrowheads). (D) A magnification of the area is indicated, with a dotted rectangle in (C). Ao, aorta; NC, notochord; NT, neural tube. (E) Dorsal and (F) lateral views showing fam49ab expression at 4.5 dpf, and (G) dorsal and (H) lateral views showing fam49ab expression in the thymus (black staining) overlapping with rag1 expression (red staining, red and white arrowheads). (I) qRT-PCR showing fam49ab expression in ikaros+ or rag2+ thymocytes FACS sorted from 5 dpf embryos, and rag2+ cells sorted from dissected adult thymi. Graph shows 3 independent experiments combined.
fam49ab is expressed in hematopoietic organs in zebrafish.fam49ab expression in the aorta can be seen in (A-B) whole-mount embryo and (C-D) transverse section at 33 hpf (red arrowheads). (D) A magnification of the area is indicated, with a dotted rectangle in (C). Ao, aorta; NC, notochord; NT, neural tube. (E) Dorsal and (F) lateral views showing fam49ab expression at 4.5 dpf, and (G) dorsal and (H) lateral views showing fam49ab expression in the thymus (black staining) overlapping with rag1 expression (red staining, red and white arrowheads). (I) qRT-PCR showing fam49ab expression in ikaros+ or rag2+ thymocytes FACS sorted from 5 dpf embryos, and rag2+ cells sorted from dissected adult thymi. Graph shows 3 independent experiments combined.
Fam49ab overexpression mimics pten mutant phenotype
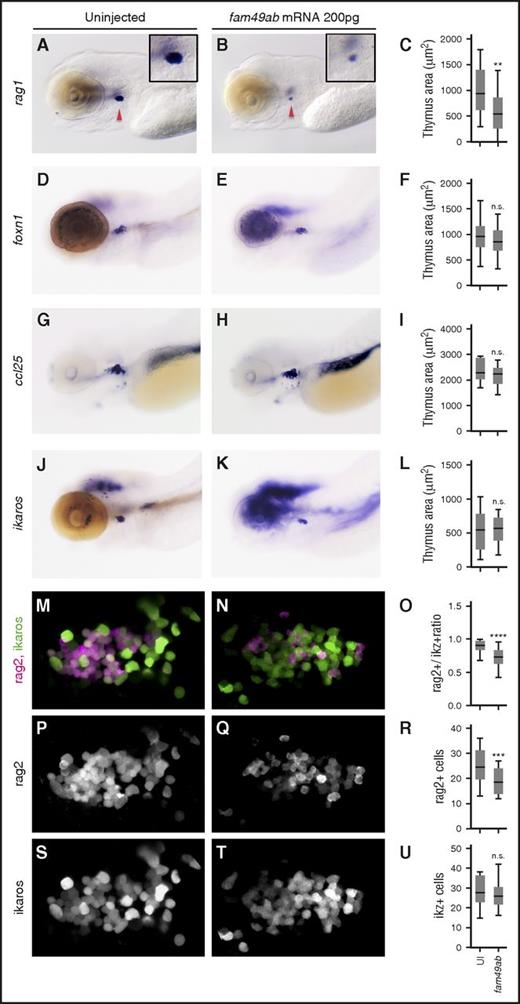
Because fam49ab is expressed in the thymus during T-cell differentiation, we investigated its impact on lymphopoiesis. Fam49ab mRNA was injected at the 1-cell stage, and embryos were fixed at 4.5 dpf. We observed a strong reduction in the number of rag1+ cells (Figure 3A-C). To determine whether other blood lineages were affected, we analyzed earlier hematopoietic events. Endothelial specification and HSC emergence were not affected by fam49ab overexpression at 33 hpf as flk1 and runx1 expression were unchanged (supplemental Figure 5A-D). cmyb expression in the CHT was also unaffected at 3 dpf (supplemental Figure 5E-F), indicating that HSC migration occurred normally,29 nor did analysis of erythroid and myeloid lineages at 3.5 and 4.5 dpf reveal any changes, as indicated by gata1 and mpx expression, respectively (supplemental Figure 5G-O). As a reduction in thymocytes could be due to a non–cell autonomous defect at the level of the thymic epithelium, we studied the expression of foxn1 and ccl25a after fam49ab gain-of-function. Expression of both genes was unaffected by fam49ab, suggesting that thymic epithelial cells were present and functional (Figure 3D-I). This result was consistent with a normal seeding of the thymus anlage, as ikaros expression was normal in fam49ab overexpressing embryos (Figure 3J-L). To determine whether fam49ab gain-of-function affects the total number of thymocytes, we overexpressed fam49ab in rag2:dsRed; ikaros:GFP double transgenic fish and imaged the thymus at 4.5 dpf (Figure 3M-N). The ratio of Rag2+ cells to Ikaros+ cells was significantly reduced in treated embryos (Figure 3O), due to a reduction in rag2+ cells (Figure 3P-R), whereas no change was observed in Ikaros+ cells (Figure 3S-U). This result suggests that fam49ab overexpression affects the differentiation of thymic seeding progenitors into rag2-expressing thymocytes, and not the thymic input. In addition, we tested whether alterations in cell proliferation or apoptosis could contribute to changes in the thymus. Because future thymic immigrants are present in the CHT at 2 dpf onwards,29 we examined 2 time points, 3.5 dpf and 4.5 dpf, and 2 locations, the thymus and the CHT. We observed no significant changes in mitosis, detected with phospho-H3 immunostaining (supplemental Figure 6), or apoptosis, detected with Acridine orange (supplemental Figure 7) in either region. Overall, these data point to a specific role of fam49ab in blocking T-cell differentiation at an early stage, in good agreement with the phenotype observed in the ptena−/−ptenb−/− double mutants.15
fam49ab overexpression inhibits thymocyte differentiation but not the arrival of early thymic progenitors. (A-C) Embryos injected with fam49ab mRNA display reduced rag1 expression at 4.5 dpf (red arrowheads); however, the expression of (D-F) ikaros, (G-I) foxn1, and (J-L) ccl25 is unchanged. (C,F,I,L) Plotted measurements of the thymus area in squared micrometers, n = 29 to 52 embryos per condition. (M-N,P-Q,S-T) Confocal images of (rag2:dsRed; ikaros:GFP) 4.5-dpf fish uninjected or injected with 200 pg of fam49ab mRNA. Images are maximum intensity projections of 5 optical sections covering a depth of field of 15 µm. (O,R,U) Ratio of rag2+ cells to ikaros+ cells, total number of rag2+ cells, and total number of ikaros+ cells, respectively. n.s., not significant. **P < .01; ***P < .001; ****P < .0001, Student t test.
fam49ab overexpression inhibits thymocyte differentiation but not the arrival of early thymic progenitors. (A-C) Embryos injected with fam49ab mRNA display reduced rag1 expression at 4.5 dpf (red arrowheads); however, the expression of (D-F) ikaros, (G-I) foxn1, and (J-L) ccl25 is unchanged. (C,F,I,L) Plotted measurements of the thymus area in squared micrometers, n = 29 to 52 embryos per condition. (M-N,P-Q,S-T) Confocal images of (rag2:dsRed; ikaros:GFP) 4.5-dpf fish uninjected or injected with 200 pg of fam49ab mRNA. Images are maximum intensity projections of 5 optical sections covering a depth of field of 15 µm. (O,R,U) Ratio of rag2+ cells to ikaros+ cells, total number of rag2+ cells, and total number of ikaros+ cells, respectively. n.s., not significant. **P < .01; ***P < .001; ****P < .0001, Student t test.
Fam49ab-induced block in T-cell differentiation is rescued by ndrg1b
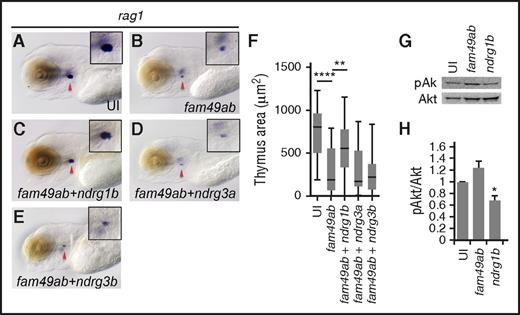
Because (1) fam49ab has been proposed to directly bind at least some NDRG proteins (in mammals and C elegans), (2) NDRG proteins can mediate PTEN signaling, and (3) fam49ab overexpression phenocopies the zebrafish pten double mutants, we hypothesized that coexpression of ndrg genes with fam49ab would rescue the reduced number of thymic rag1+ cells. Again, fam49ab overexpression resulted in reduced rag1 labeling (Figure 4A-B,F). Coinjection of ndrg1b mRNA partially but significantly rescued this phenotype (Figure 4C,F), whereas coinjection of ndrg3a or ndrg3b did not (Figure 4D-F). Because the PTEN pathway regulates the phosphorylation status of downstream Akt, we next tested whether fam49ab and ndrg1b can modulate pAkt levels. Embryos overexpressing fam49ab showed elevated levels of pAkt protein, whereas ndrg1b overexpression reduced pAkt (Figure 4G-H). These data suggest that Fam49ab is a negative regulator of the PTEN pathway, acting through Ndrg1b during T-cell differentiation.
ndrg1a and ndrg1b can rescue thymus size in fam49ab overexpressing embryos. (A-B) rag1 expression at 4.5 dpf is reduced in embryos injected with fam49ab mRNA. (C) rag1 expression is partially restored in embryos injected with fam49ab mRNA together with ndrg1b mRNA. (D-E) Coinjection of ndrg3a or ndrg3b together with fam49ab does not rescue rag1 expression. (F) Plotted thymus area measurements from 3 independent experiments combined, n = 57 to 73 embryos per condition. **P < .01; ****P < .0001, 1-way ANOVA. (G) Representative western blot of pools of embryos injected with 200 pg of indicated mRNA, lysed at 2 dpf, detecting pAkt and Akt. (H) Densitometric analysis of (G), 3 experiments combined. *P < .05, 1-way ANOVA.
ndrg1a and ndrg1b can rescue thymus size in fam49ab overexpressing embryos. (A-B) rag1 expression at 4.5 dpf is reduced in embryos injected with fam49ab mRNA. (C) rag1 expression is partially restored in embryos injected with fam49ab mRNA together with ndrg1b mRNA. (D-E) Coinjection of ndrg3a or ndrg3b together with fam49ab does not rescue rag1 expression. (F) Plotted thymus area measurements from 3 independent experiments combined, n = 57 to 73 embryos per condition. **P < .01; ****P < .0001, 1-way ANOVA. (G) Representative western blot of pools of embryos injected with 200 pg of indicated mRNA, lysed at 2 dpf, detecting pAkt and Akt. (H) Densitometric analysis of (G), 3 experiments combined. *P < .05, 1-way ANOVA.
PI3K inhibition can rescue T-cell differentiation block
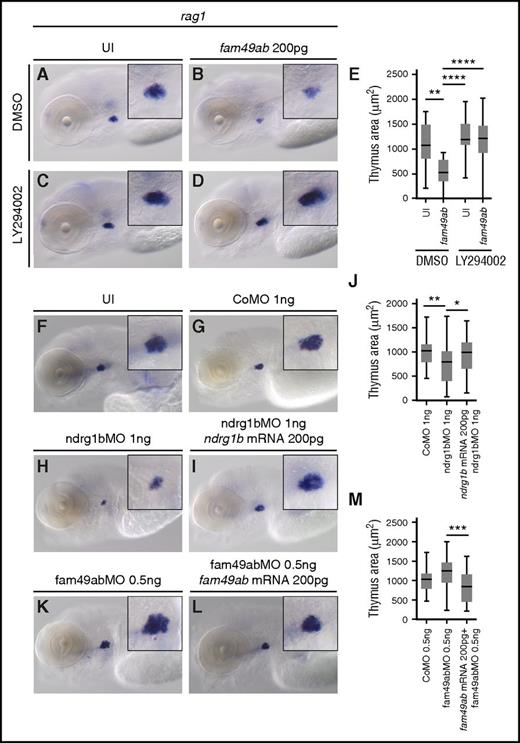
If Fam49ab inhibits PTEN signaling, as our findings suggest, then the block in T-cell differentiation should be reversed by PI3K inhibition. To test this, we treated uninjected and fam49ab overexpressing embryos with the PI3K inhibitor LY294002. Reduction in rag1 expression (Figure 5A-B,E) could indeed be rescued by PI3K inhibition (Figure 5D-E). No significant differences were observed in uninjected fish treated with DMSO or LY294002 (Figure 5A,C,E).
PI3K inhibitor rescues rag1 expression. Morpholinos against fam49ab and ndrg1b can also affect thymus size. (A-D) rag1 expression in 4.5-dpf embryos treated with DMSO or 10 µM LY294002, and either uninjected or injected with 200 pg of fam49ab mRNA. (E) Plotted thymus area measurements from 3 independent experiments combined. n = 37 to 61 embryos per condition. (F-M) rag1 expression in 4.5-dpf embryos treated with indicated MOs and MOs together with mRNAs. (J) Quantification of (G-I), 3 independent experiments combined. n = 30 to 57 embryos per condition. (M) Quantification of (G-I), 3 independent experiments combined. n = 30 to 44 embryos per condition. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001; ****P < .0001, 1-way ANOVA. CoMO, control morpholino oligonucleotide.
PI3K inhibitor rescues rag1 expression. Morpholinos against fam49ab and ndrg1b can also affect thymus size. (A-D) rag1 expression in 4.5-dpf embryos treated with DMSO or 10 µM LY294002, and either uninjected or injected with 200 pg of fam49ab mRNA. (E) Plotted thymus area measurements from 3 independent experiments combined. n = 37 to 61 embryos per condition. (F-M) rag1 expression in 4.5-dpf embryos treated with indicated MOs and MOs together with mRNAs. (J) Quantification of (G-I), 3 independent experiments combined. n = 30 to 57 embryos per condition. (M) Quantification of (G-I), 3 independent experiments combined. n = 30 to 44 embryos per condition. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001; ****P < .0001, 1-way ANOVA. CoMO, control morpholino oligonucleotide.
Inhibition of fam49ab and ndrg1b affects thymic rag1 expression
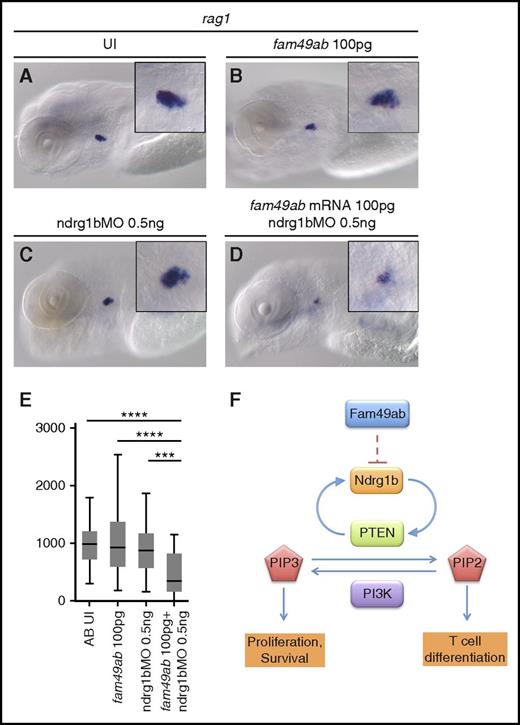
To further characterize the roles of fam49ab and members of the ndrg family, we designed morpholinos (MOs) that block RNA splicing of their respective pre-mRNAs. Because splice blocking MOs can result in either intron retention or exon exclusion, we injected a range of concentrations into groups of embryos, extracted RNA, and performed RT-PCR with primers specific to exons flanking the MO target junction (supplemental Figure 8A-D). Ndrg1b-MO appeared to result in intron retention, as the WT sequence could not be amplified from treated embryos (supplemental Figure 8A). Injection of ndrg3b and fam49ab MOs resulted in a gradual loss of WT product and the appearance of a smaller band. Sequencing of the smaller band in each case confirmed target exon deletion and direct joining of neighboring exons (supplemental Figure 8B-D). Ndrg3a-MO injection also produced a smaller band, which was confirmed by sequencing to result from exon deletion; however, reduction in WT mRNA was not apparent. Nevertheless, injection of ndrg3a-MO at 8.3 ng per embryo resulted in severe developmental and growth delay, when compared with uninjected embryos or embryos injected with control MO (supplemental Figure 8E-G). Similar defects were observed in embryos injected with 12.5 ng of ndrg3b-MO (supplemental Figure 8H). This phenotype precluded us from studying the effects of these MOs on thymus development. Injection of 1 ng of ndrg1b-MO resulted in normal embryonic morphology but reduced thymic rag1 expression (Figure 5F,H,J) when compared with control MO (Figure 5F,G,J). This effect was reversed when 200 pg of ndrg1b mRNA was injected concomitantly (Figure 5F,I-J). Injection of 5.5 ng of fam49ab-MO was embryonically lethal between 24 and 48 hpf. Upon titration of MO, we found 0.5 ng per embryo allowed for normal morphology and survival rates at 4.5 dpf. These embryos exhibited a slightly, but not significantly, enlarged thymus (Figure 5K,M). This effect was reversed when 200 pg of fam49ab mRNA was injected concomitantly (Figure 5L-M). We next performed epistasis experiments to determine whether synergy occurred between ndrg1b-MO and fam49ab mRNA. Subliminal doses of either did not significantly affect rag1 expression in the thymus (Figure 6A-C,E). However, injection of both fam49ab mRNA and ndrg1b-MO had a significant synergistic effect on rag1 expression in the thymus (Figure 6D-E). Taken together, these data indicate that Fam49ab inhibits Ndrg1b in the PTEN pathway during embryonic thymocyte development (Figure 6F), thereby directing the balance between proliferation and differentiation.
fam49ab mRNA and ndrg1b-MO display a synergistic effect on rag1 expression. (A-D) rag1 expression in 4.5-dpf embryos injected with low doses of fam49ab mRNA or ndrg1b-MO, or both of the above. (E) Plotted thymus area measurements from 3 independent experiments combined. n = 33 to 49 embryos per condition. ***P < .001; ****P < .0001, 1-way ANOVA. (F) Proposed mechanism of Fam49ab signaling: Fam49ab inhibits Ndrg1b, interrupting the positive regulation of PTEN, thereby inhibiting T-cell differentiation.
fam49ab mRNA and ndrg1b-MO display a synergistic effect on rag1 expression. (A-D) rag1 expression in 4.5-dpf embryos injected with low doses of fam49ab mRNA or ndrg1b-MO, or both of the above. (E) Plotted thymus area measurements from 3 independent experiments combined. n = 33 to 49 embryos per condition. ***P < .001; ****P < .0001, 1-way ANOVA. (F) Proposed mechanism of Fam49ab signaling: Fam49ab inhibits Ndrg1b, interrupting the positive regulation of PTEN, thereby inhibiting T-cell differentiation.
Discussion
In this study, we identified 2 new proteins that control T-cell development in zebrafish, by modulating the PTEN pathway: Ndrg1b and Fam49ab. The PTEN pathway is crucial for T-cell development. Experimental inactivation of Pten in the T-cell lineage leads to abnormal T-cell development, hyperplasia of double positive thymocytes, and eventually, the development of T-cell lymphoma.5,6,30 In the above studies, however, pten was inactivated in progenitor cells already committed to T-cell lineage, and therefore, does not allow the study of an earlier step of T-cell commitment from bone marrow progenitors. PTEN requirement at the HSC level has been addressed in the mouse, where bone marrow–specific loss of PTEN results in multiple lymphoid and myeloid leukemic–like diseases.12 In addition, loss of PTEN in CD45+ hematopoietic cells during fetal development leads to T-ALL.13 These findings place PTEN as an important regulator of proliferation of hematopoietic precursors, as well as stem cells in general.
In this study, we were interested in Ndrg genes, as they modulate the PTEN and MYCN pathways, which antagonize each other. Although MYCN can directly bind the promoter of NDRG1 and downregulate its transcription,31 it is not clear how PTEN and NDRG1 interact, whether by direct gene regulation or through regulation of its activity. However, 1 member of the NDRG protein family, NDRG2, has been shown to activate PTEN via direct protein interaction.32 We tested the capacity of Ndrg genes to rescue T-cell differentiation defect in zebrafish embryos treated with PTEN inhibitors. There are 6 NDRG orthologs in zebrafish, and only Ndrg4 has been investigated. Ndrg4 is expressed specifically in the heart and brain of zebrafish embryos, and its inactivation leads to severe heart defects.20 We found that another member of this family, ndrg1b, was able to rescue the T-cell differentiation defect induced by PTEN inhibition. PTEN and NDRG1 are known tumor suppressor genes in mammals,33 and both promote differentiation of progenitors, while inhibiting proliferation signals.34,35 We propose that ndrg1b plays a similar role during T-cell differentiation, by initiating the differentiation of immature hematopoietic progenitors into the T-cell lineage.
The worm orthologs of FAM49A and NDRG1 have been proposed to interact with each other in the yeast-2-hybrid system (thebiogrid.org and wormbase.org). Overexpression of fam49ab (previously annotated as znf395) in zebrafish produces a phenotype very similar to ptena−/−ptenb−/− double-mutant embryos.15 We thus hypothesized that Fam49ab could antagonize the Pten pathway through Ndrg1b, as both proteins can interact in the worm. Indeed, ndrg1b mRNA rescued T-cell differentiation defects induced by fam49ab overexpression. The precise role of FAM49A during T-cell commitment or differentiation remains to be understood. When human CD34+ hematopoietic precursors are transduced with a lentivirus overexpressing AF1q/MLLT11, a gene that promotes commitment to the T-cell lineage, Fam49a is one of the top target genes induced, together with other known genes involved in T-cell differentiation.36 Gene profiling showed that the expression of FAM49A decreases between the DN1 stage to the Double Positive stage (data from Immunological Genome Project37 ), correlating with our observation in zebrafish, that fam49ab could block T-cell differentiation, presumably at the DN2 stage, before rag1/2 expression.
In vertebrates, FAM49A is a protein containing a domain of unknown function, DUF1394. This domain could be necessary to interact with NDRG1 and block its activity, therefore promoting cell proliferation at the expense of differentiation by opposing PTEN and NDRG1. We were unable to show interaction between these 2 proteins, first using zebrafish transcripts in the yeast-2-hybrid system (data not shown), or by performing coimmunoprecipitation in HeLa cells, as they express both NDRG1 and FAM49A (data not shown), but we could show a synergistic effect between the gain of fam49a and the loss of ndrg1b. This result may indicate that interactions between NDRG1 and FAM49A have low affinity or are transient. In a pathway that determines the balance between proliferation and differentiation, low-affinity interactions may allow cells to respond more rapidly to upstream signals, thus keeping the signaling network dynamic.38 It will be interesting to determine the crystal structure of FAM49A, which may hint at its ability to interact with other proteins. As FAM49A could oppose PTEN, and thus promote the proliferation of progenitor cells, we also attempted to block fam49a expression in HeLa cells using small interfering RNA (siRNA). qPCR analysis of transcripts showed that Fam49a expression was reduced only after 48 hours following siRNA treatment (data not shown), indicating that the transcript is very stable. Cell cycle was unchanged between the control population and fam49a siRNA-treated cells (data not shown). Possibly, cell-cycle progression in immortalized cancer cell lines may not be responsive to fine tuning by pathways promoting differentiation. In the future, it would be worthwhile to test whether Fam49a can affect the cell cycle in HSCs. An siRNA screen performed on HeLa cells has also reported no change in distribution of cell-cycle phases following siRNA-mediated fam49a knockdown.39 However, in the same screen, the authors found that an siRNA directed against fam49b augmented the percentage of cells in G1 phase,39 therefore slowing down the cell cycle. As FAM49A and FAM49B share the same domain DUF1394, it is likely that both proteins should play a similar role, but perhaps exerting it to a differing extent in various cells.
Finally, it appears that both MYCN and FAM49A genes are neighbors in all vertebrates. As MYCN is a well-established negative regulator of NDRG1 at the transcriptional level, it is interesting to note that its direct neighbor on the chromosome would be a negative regulator of NDRG1 at the protein level. Although no evidence indicates a joint regulation of both genes, both genes are involved in cancer. Indeed, in leukemias or solid tumors where MYCN is overexpressed after gene amplification by excision, FAM49A is frequently fused to other genes.40 Although the role of these fusions is still unclear, they could play a role in the establishment or the maintenance of the tumor.
In summary, we report here that zebrafish Ndrg1b and Fam49ab antagonize each other to control the balance between proliferation and differentiation in early thymic immigrants. Our study assigned a role to Fam49a, previously a gene of unknown function. Further work shedding light on the mechanisms of action through which FAM49A controls T-cell differentiation and exerts its antagonistic effect on the NDRG1 protein could inform us on novel strategies for leukemia treatments.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all members of the Bertrand laboratory for fruitful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. The authors also thank M. Gannagé for her help with western blots and immunoprecipitation experiments, as well as M. Gotta and F. Schwager for their help with yeast-2-hybrid experiments.
J.Y.B. is endorsed by a Chair in Life Sciences funded by the Gabriella Giorgi-Cavaglieri Foundation and was also funded by the Swiss National Fund (31003A_146527 and 31003A_166515).
Authorship
Contribution: J.Y.B., R.A.L., and T.M. designed the research; R.A.L. and T.M. performed experiments. The initial work on fam49ab was performed by J.Y.B. in D.T.’s laboratory. R.A.L., D.T., T.M. and J.Y.B. wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Julien Y. Bertrand, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pathology and Immunology, CMU, University of Geneva, Rue Michel-Servet 1, 1211 Geneva 4, Switzerland; e-mail: julien.bertrand@unige.ch.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal