Abstract
Background: A substantial number of pts with CML-CP achieve a sustained deep molecular response on long-term tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. For these pts, TFR (ie, discontinuation of therapy without experiencing a loss of response) is becoming the goal of treatment. Prior studies have shown the feasibility of TFR in carefully selected pts. This phase 2 study investigates TFR in pts who achieved MR4.5 (BCR-ABL1 ≤ 0.0032% on the International Scale [IS]) on second-line nilotinib following a switch from imatinib.
Methods: Pts with CML-CP who achieved a major molecular response (MMR; BCR-ABL1IS ≤ 0.1%) but not MR4.5 after ≥ 1 year of frontline imatinib treatment were enrolled and switched to nilotinib (300 mg twice daily) for a monitoring phase lasting up to 2 years. Pts who achieved a confirmed MR4.5 during the monitoring phase entered a 2-year consolidation phase, and those with no confirmed loss of MR4 (BCR-ABL1IS ≤ 0.01%) during the consolidation phase were eligible to stop nilotinib and enter the TFR phase. Pts with molecular relapse, defined as confirmed loss of MMR (2 consecutive samples within ≈ 4 weeks) during TFR, entered a reinitiation phase to resume nilotinib treatment. The primary endpoint of the study is the molecular relapse-free rate at 6 months after stopping treatment.
Results: A total of 59 pts were enrolled; the median age was 54 years (range, 26-74 years), 66% were male, and 56% had low Sokal risk scores. Pts had a median BCR-ABL1IS level of 0.03% at baseline. Prior therapy included chemotherapy (54%), immunotherapy (3%), and targeted therapy (58%); all pts received prior imatinib (median [range] duration, 64 [13.5-168] months). By the data cutoff date (April 28, 2017), all pts had either achieved confirmed MR4.5 and entered the consolidation phase (n = 41; 69%) or discontinued from the study during the monitoring phase (n = 18; 31%). Of the 41 pts who entered the consolidation phase, 17 entered TFR by the data cutoff. Overall, 31 pts remained on study at the data cutoff date (consolidation phase, n = 17; TFR phase, n = 7; reinitiation phase, n = 7).
Median time to confirmed MR4.5 was 298 days (range, 43-757 days), and median duration of first MR4.5 in the consolidation phase was 321 days (range, 29-820 days). All 17 pts who entered TFR had MR4.5 at the start of the TFR phase. By the data cutoff date, 7 of these 17 pts remained in the TFR phase, 1 had discontinued from the study while in TFR, and 9 had experienced molecular relapse and entered the reinitiation phase; the median duration of follow-up in the TFR phase was 102 days (range, 3-492 days). Among evaluable pts at 3, 6, and 12 months after entering the TFR phase, 2 of 11 (18.2%), 2 of 3 (66.7%), and 1 of 1 (100%), respectively, had MR4.5; 7 of 11 (63.6%), 3 of 3 (100%), and 1 of 1 (100%), respectively, had at least MMR. Of the 9 pts who entered the reinitiation phase, the median time to molecular relapse was 96 days (range, 63-246 days). The median follow-up time in the reinitiation phase for these 9 pts was 59 days (range, 37-631 days), and 3 pts reachieved a confirmed MR4.5 by the data cutoff.
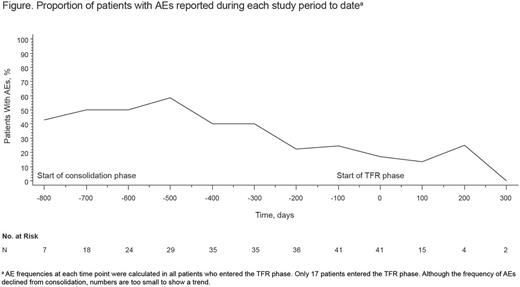
The most common adverse events (AEs) during nilotinib treatment included fatigue (reported in 37% of pts in the monitoring and consolidation phases combined), constipation (27%), rash (25%), headache (22%), abdominal pain (20%), pruritus (19%), nausea (17%), increased lipase (17%), weight decrease (17%), pain in extremity (17%), and diarrhea (15%); in most cases, these AEs were mainly grade 1/2. Five pts (9%) discontinued from the study due to AEs. The percentage of pts with ≥ 1 AE was higher in the monitoring (97%) than in the consolidation phase (54%). Among pts who entered the TFR phase, the incidence of AEs appeared to decrease after stopping treatment (Figure).
Conclusion: The majority (69%) of pts were able to achieve a confirmed MR4.5 following switch from imatinib to nilotinib. Nilotinib treatment was well tolerated and the safety profile was generally consistent with that in previous studies, with few pts discontinuing due to AEs. The achievement of sustained deep molecular responses and the rate and duration of TFR continue to be evaluated. Because the achievement of sustained deep response is crucial for TFR, the achievement of deeper responses with nilotinib may serve to enhance the effectiveness and durability of TFR; however, only a small number of pts have entered the TFR phase of this study thus far and, therefore, these preliminary TFR results should be interpreted with caution.
Ritchie: Astellas Pharma: Other: Research funding to my institution; Pfizer: Consultancy, Other: Research funding to my institution; Celgene: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Research funding to my institution, and travel, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: Research funding to my institution; NS Pharma: Other: Research funding to my institution. Pinilla-Ibarz: BMS: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; ARIAD: Consultancy, Honoraria. Deininger: Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, CTI BioPharma Corp, Gilead, Incyte, Novartis, Pfizer, Celgene, Blue Print, Galena: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy; Gilead: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy. Erba: Celgene: Consultancy, Other: Chair, Scientific Steering Committee , Speakers Bureau; Incyte: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; MacroGen: Consultancy; Ono: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy; Millennium/Takeda: Consultancy, Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; Agios: Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; Juno: Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; Astellas: Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; Celator: Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; Janssen: Other: all research support paid to University of Alabama, Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Other: Chair, Data and Safety Monitoring Committee. Radich: Novartis: Consultancy, Other: lab contracts for bid and service assays; Amgen: Consultancy; Ariad: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Gilliad: Consultancy. Savona: Karyopharm: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Astex: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sunesis: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Dautaj: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Employment. Purkayastha: Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Employment. Habucky: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Employment. Mauro: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal