Abstract
Background: Engraftment syndrome (ES) has been observed post autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (ASCT) in patients with multiple myeloma (MM), and may require treatment with immunosuppressive therapies and prolonged hospitalization. Risk factors for the development of ES have not been clearly defined, with conflicting reports as to the role of CD34+ cell dose and pre-ASCT therapy. Defining risk factors could lead to the development of strategies to mitigate the risk of ES.
Methods : A cohort of 496 patients who received 596 ASCT for MM between January 2005 and December 2015 was reviewed. ES was defined as a combination of at least 2 symptoms not attributed to other causes including non-infectious fever, diarrhea, skin rash, pulmonary infiltrates or hepatic dysfunction starting from 3 days prior to 10 days post-engraftment. Potential risk factors for the development of ES were analyzed, including age, pre-ASCT therapy, mobilization regimen, pre-ASCT dialysis or radiation therapy, number of CD34+ cells infused, time from diagnosis to transplantation, and disease status at the time of transplantation. Pre-ASCT therapies included lenalidomide (Len), bortezomid (Bor) and Carfilzomib (Car). High risk disease (HRD) was defined as t(14;16), t(14;20), del 17p, t(4;14) or 1q gain by FISH, del 13q, monosomy 13 or hypodiploidy by standard cytogenetics, or high risk signature gene expression profiling. Kaplan Meier and Cox proportional hazard methods were employed.
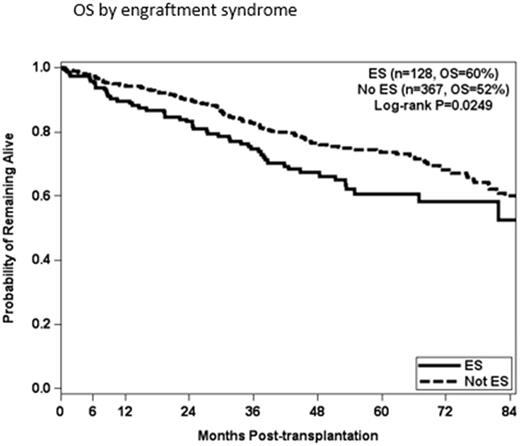
Results: The median age at ASCT was 61 years (range 39-84) and 58% were male. There were 153 incidents of ES by defined criteria, with 123 patients requiring corticosteroids, 6 patients requiring the addition of tacrolimus, and one patient death attributed to ES. Pre-ASCT radiation therapy, time from diagnosis to transplantation and disease status at the time of transplantation were not significantly associated with the development of ES. Patients who received Len (p=0.8840), Bor (p=0.2458), Len and Bor combination (0.6907), or Car (p=0.6818) did not have increased risk of ES. Cyclophosphamide (Cy) for mobilization resulted in higher collection of CD34+ cells, but was not significantly associated with the risk of ES (p=0.6095). The median CD34+ cell dose infused for patients with ES was 5.22 x 10e6/kg versus 5.91 x 10e6/kg for patients without ES. Higher doses of CD34+ cells infused were protective against ES (P=0.0030). Patients with HRD had a significantly higher risk for developing ES, vs patients with standard risk disease (P=0.0041). Patients age 60 and older at the time of ASCT were more likely to develop ES (p=0.0249), and the incidence of ES increased with age up to age 75 . OS by univariate analysis was worse for patients who experienced ES (p=0.0.49). In multivariate analysis, stratified by number of transplants, patients with ES had lower overall survival than patients without ES (p=0.0179) when accounting for HRD, progression and response at ASCT.
Conclusions: Pre-ASCT chemotherapy with Bor, Car and/or Len has no effect on the incidence of ES. Stem cell mobilization regimen did not impact the incidence of ES, but higher CD34+ cell doses are protective against ES. Patients without ES have improved overall survival. Older patients are at greater risk for ES, and the risk increases along the age continuum up to age 75. Infusing higher doses of CD34+ cells could be a strategy to mitigate the risk of ES in older patients.
McKiernan: Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Siegel: Merck: Consultancy; Celgene, Takeda, Amgen Inc, Novartis and BMS: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Vesole: Takeda: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Skarbnik: Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Other: Ad board, Speakers Bureau. Biran: Celgene, Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau. Richter: Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Pecora: COTA: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties; Caladrius Biosciences: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Goy: Genentech: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics / J&J: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal