Key Points
Endogenous IL-18BP is critical to prevent severe MAS on repetitive TLR9 stimulation.
IL-18BP deficiency is associated with elevated plasma levels of free IL-18 and an enhanced IFN-γ molecular signature in TLR9-induced MAS.
Abstract
The term macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) defines a severe, potentially fatal disorder characterized by overwhelming inflammation and multiorgan involvement. Interleukin-18 (IL-18) is a proinflammatory cytokine belonging to the IL-1 family, the activity of which is regulated by its endogenous inhibitor IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP). Elevated IL-18 levels have been reported in patients with MAS. Herein, we show that on repeated toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) stimulation with unmethylated cytosine guanine dinucleotide containing single-stranded DNA (CpG), IL-18BP−/− mice display severe MAS manifestations, including increased weight loss, splenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, hyperferritinemia, and bone marrow hemophagocytosis as compared with wild-type mice. Serum-free IL-18 was detected in CpG-treated IL-18BP−/− mice only. Levels of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and of IFN-γ signature genes, such as the chemokine Cxcl9 or the transcription factor CIIta, were significantly increased in IL-18BP−/− mice. Blocking IL-18 receptor signaling attenuated the severity of MAS and IFN-γ responses in IL-18BP−/− mice. Blocking IFN-γ had comparable effects to IL-18 inhibition on most MAS manifestations. Our data indicate that endogenous IL-18BP exerts a protective role in CpG-induced MAS and that IL-18, which acts upstream of IFN-γ, is involved in the severity of MAS.
Introduction
Interleukin-18 (IL-18) is a cytokine that belongs to the IL-1 family and was first discovered as an interferon-γ (IFN-γ)–inducing factor.1 IL-18 exerts proinflammatory activities and is potentially involved in the pathogenesis of a variety of inflammatory disorders.2 The biological activity of IL-18 is tightly regulated at different levels. Indeed, IL-18 is produced as a biologically inert 24-kDa propeptide that needs to be processed by caspase-1 into an 18-kDa protein to become active.3 In addition, IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP), which is constitutively present in large concentrations in the circulation in humans, binds to IL-18 with high affinity to form a complex that prevents the interaction of IL-18 with its cell surface receptors. Thus, IL-18BP acts as a natural IL-18 inhibitor that controls excessive IL-18–mediated inflammatory responses.4,5 However, in some pathological circumstances associated with excessive IL-18 production, the buffering capacities of IL-18BP can be overwhelmed, and IL-18 can be present in the circulation as uncomplexed free bioactive IL-18. Using a novel immunoassay that is able to detect specifically free IL-18, we have recently shown that circulating levels of free IL-18 are elevated in patients with adult onset Still’s disease (AOSD) in comparison with patients with other rheumatic diseases and healthy controls.6
Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) describes a set of clinicopathological manifestations that occurs in different diseases and is now classified among histiocytic disorders as hemophagocytic syndromes.7,8 Primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is the prototype of this syndrome and is associated with a genetic deficiency of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells (reviewed in Grom et al9 ). Secondary HLH appears as a complication of infections (most commonly viral), malignancies, or inflammatory diseases, such as AOSD and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA).10,11 Remarkably high circulating levels of proinflammatory cytokines are present in patients with the various forms of MAS.9 In particular, high levels of circulating IL-18 and IFN-γ have been described in MAS.12 Moreover, some authors have pointed out the relevance of elevated IL-18 levels as a risk factor for MAS in AOSD and sJIA.13,14 To examine the role of the IL-18:IL-18BP ratio in MAS, we have used an experimental model of systemic inflammation elicited by repetitive injections of the toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) ligand unmethylated cytosine guanine dinucleotide containing single-stranded DNA (CpG).15 We report herein that, after CpG injections, IL-18BP−/− mice developed a more severe form of MAS than their wild-type (WT) littermates, which was associated with the presence of circulating free IL-18, as well as higher IFN-γ production and an enhanced IFN-γ molecular signature. Blocking IL-18 receptor (IL-18R) and IFN-γ signaling markedly attenuated the severity of CpG-induced MAS in IL-18BP−/− mice.
Material and methods
Mice and treatments
Frozen C57BL/6N Il18bptm1.1(KOMP)Vlcg (IL-18BP+/−) mouse embryos, generated by the KOMP Repository (University of California, Davis, Davis, CA), were purchased and implanted into the uterus of foster females to obtain IL-18BP+/− mice, which were maintained at Charles River Laboratories (L’Arbresle, France). IL-18BP+/− mice were then bred in the conventional area of the animal facility of the University of Geneva School of Medicine (Geneva, Switzerland) to obtain IL-18BP−/− and WT cohoused littermates. Genotyping was performed on total DNA extracted from ear biopsies using 4-primer polymerase chain reaction (PCR) combining a primer pair specific for the WT allele (5′-TCTTTCTTGTAGCCCCACTGCTAGG-3′ forward; 5′-ACTAAGTGGAGCTTGGCAGGATAGG-3′ reverse, amplified product, 226 bp) and a primer pair specific for the IL-18BP−/− allele (5′-GCAGCCTCTGTTCCACATACACTTCA-3′ forward; 5′-TTGCCTTGGGGACAGTACATTAGGG-3′ reverse, amplified product, 624 bp) (Figure 1A). All experiments were approved by the Geneva cantonal authority for animal experimentation (licenses nos. GE/58/16 and GE/151/17) and performed on sex- and 7- to 13-week-old age-matched animals. A phosphorothioate CpG 1826 oligonucleotide (5′-TCCATGACGTTCCTGACGTT-3′; Eurofins Genomics GmbH, Ebersberg, Germany) was injected intraperitoneally into mice at a dose of 2.5 μg per g of body weight on days 0, 2, and 4, or once only. In some experiments, rat immunoglobulin G1 anti–IL-18R monoclonal or isotype control antibodies (Amgen Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA) or rat immunoglobulin G1 anti–IFN-γ monoclonal (clone XMG1.2) or isotype control antibodies (BioLegend, San Diego, CA) were administered intraperitoneally at 7.5 μg per gram of body weight or 500 μg per mouse, respectively, 2 hours before each CpG injection. Monitoring of mice, assessment of clinical readouts, and sample collection are described in the supplemental Methods (available on the Blood Web site).
IL-18BP−/−mice display normal growth and no spontaneous proinflammatory phenotype. (Ai) Schematic representation of WT and knockout (−/−) mouse Il18bp alleles is shown. Coding exons appear as white boxes, and noncoding exons as black boxes. Targeting vector-derived sequences in the targeted allele are shown in gray, between brackets. Triangles represent LoxP sequences. Location of primers designed for genotyping (P1 and P2 for WT allele, P3 and P4 for −/− allele) is indicated. (Aii) PCR products for the WT and targeted allele in −/−, heterozygous (+/−) and WT mice (+/+) are shown. (B) The mean body weight (± SD) of 20 male and 16 female WT littermates (+/+) and 10 male and 9 female IL-18BP−/− (−/−) mice between 3 and 12 weeks of age is reported. (Ci) White and (Cii) red blood cell counts as well as (Ciii) platelet counts are shown for naive WT littermate and IL-18BP−/− mice (n = 11). Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The number of (Di) total and CD45+ cells, (Dii) total T cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and B cells, and (Diii) conventional DCs (cDCs), plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), monocytes/macrophages (mono/macro), and neutrophils (neutro) in the spleen are shown for naive WT littermates and IL-18BP−/− female mice (n = 5, data are from 1 experiment representative of 2). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and IL-18BP−/− mice. ns, nonsignificant.
IL-18BP−/−mice display normal growth and no spontaneous proinflammatory phenotype. (Ai) Schematic representation of WT and knockout (−/−) mouse Il18bp alleles is shown. Coding exons appear as white boxes, and noncoding exons as black boxes. Targeting vector-derived sequences in the targeted allele are shown in gray, between brackets. Triangles represent LoxP sequences. Location of primers designed for genotyping (P1 and P2 for WT allele, P3 and P4 for −/− allele) is indicated. (Aii) PCR products for the WT and targeted allele in −/−, heterozygous (+/−) and WT mice (+/+) are shown. (B) The mean body weight (± SD) of 20 male and 16 female WT littermates (+/+) and 10 male and 9 female IL-18BP−/− (−/−) mice between 3 and 12 weeks of age is reported. (Ci) White and (Cii) red blood cell counts as well as (Ciii) platelet counts are shown for naive WT littermate and IL-18BP−/− mice (n = 11). Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The number of (Di) total and CD45+ cells, (Dii) total T cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and B cells, and (Diii) conventional DCs (cDCs), plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), monocytes/macrophages (mono/macro), and neutrophils (neutro) in the spleen are shown for naive WT littermates and IL-18BP−/− female mice (n = 5, data are from 1 experiment representative of 2). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and IL-18BP−/− mice. ns, nonsignificant.
Laboratory tests and cytokine measurements
Blood cell counts were assessed on peripheral blood collected in EDTA-coated vials using a Sysmex blood cell counter (Sysmex, Yverdon, Switzerland). The plasma levels of ferritin and IFN-γ were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) purchased from ALPCO (Salem, MA) and eBioscience (Vienna, Austria), respectively. An ELISA was developed from the previously described human assay6 to determine the circulating levels of free IL-18 in mice. The mouse ELISA protocol was identical to that of the human ELISA, except that the standard curve was realized using recombinant mouse IL-18 (MBL, Nagoya, Japan), and the detection antibody was a biotinylated monoclonal rat anti-mouse IL-18 antibody (MBL). Plasma CXCL9 levels were determined by Bio-Plex according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity in plasma was measured by the Wroblewski and LaDue method using the monoreagent provided by Biolabo (Maizy, France).
Validation of mouse free IL-18 ELISA
The mouse free IL-18 ELISA was validated by spiking increasing amounts of recombinant mouse IL-18 into IL-18BP−/− and WT mouse serum (supplemental Figure 1A-B). The specificity of the ELISA for mature free IL-18 was assessed as described in the supplemental Methods.
Standard histology, immunohistochemistry, and bone marrow smears
Spleen and liver samples were fixed in 4% neutral buffered formalin, paraffin embedded, and sectioned (4 µm). Hematoxylin and eosin stains were performed for standard histology. Spleen lymphoid follicles were stained using a rat anti-human CD3 (clone MCA1477, 1/200; Bio-Rad Laboratories) antibody. Tissue sections were deparaffinized, and antigens were retrieved by pressure cooking. Slides were blocked with hydrogen peroxide for endogenous peroxidase activity and incubated with the anti-CD3 antibody for 1 hour at room temperature. Subsequently, slides were incubated with a goat anti-rat horseradish peroxidase–conjugated secondary antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, Texas; dilution 1:250) and developed with diaminobenzidine (Dako, Baar, Switzerland). Mayer’s hemalum (BioGnost, Zagreb, Croatia) was used for nuclear counterstaining. Slides were scanned on a Mirax Midi slide scanner (Carl Zeiss Microscopy, Feldbach, Switzerland). ZEN blue software (Carl Zeiss Microscopy) was used for image acquisition of spleen and liver sections and lymphoid follicle area measurement.
Bone marrow was flushed from the femurs and tibias and resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline. Dry smears were stained with May-Grünwald Giemsa.
Flow cytometric analysis of mononuclear cells
Spleen single-cell suspensions were treated with red blood cell lysis buffer (155 mM ammonium chloride, 1 mM potassium bicarbonate, and 77.5 µM EDTA [Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO]). Cells were then immunostained with monoclonal antibodies specific for extracellular markers, using either a “lymphocyte” mix, including: CD45-PE (clone 104), CD3ε-FITC (clone 17A2), B220-A700 (clone RA3-6B2) (eBioscience), CD4-PerCP (clone RM4-1) (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ), and NK1.1-BV421 (clone PK136) (BioLegend); or a “myelocyte” mix, including: CD45-PE (clone 104), CD11b-APC-Cy7 (clone M1/70), CD11c-APC (clone HL3) (BD Biosciences), and Ly6G-PerCP-Cy5.5 (clone 1A8) (BioLegend). Staining was performed in the presence of rat anti-mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Fc block, BD Biosciences). Cell viability was assessed with Zombie Yellow (BioLegend). Data were acquired on a Gallios 4 cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA) and analyzed using Kaluza flow cytometry analysis software (Beckman Coulter). The gating strategies are illustrated in supplemental Figure 2.
Reverse transcription quantitative PCR
Pieces of spleen and liver were frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after sacrifice and stored at −80°C until use. Total RNA was extracted from these samples using TRIzol (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) and further purified on RNeasy columns (Qiagen, Hombrechtikon, Switzerland). Complementary DNA was obtained from 500 ng total RNA using SuperScript II Reverse Transcriptase (Life Technologies). Ribosomal protein L32, Il18, Il18bp, Ifnγ, Cxcl9, CIIta, and Socs1 complementary DNA levels were estimated by quantitative PCR (40 cycles, annealing temperature of 60°C) using the iQ SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad Laboratories). The sequences of the primers used are listed in supplemental Table 1. Relative levels of Il18, Il18bp, Ifnγ, Cxcl9, CIIta, and Socs1 were normalized to L32 expression using a comparative method (2–ΔCt). Non–reverse-transcribed RNA samples and water were included as negative controls.
Statistical analyses
Results are represented as individual values except for body weight and variations from baseline body weight, which are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Because of the small size of samples and non-Gaussian distribution of values, only nonparametric tests (Mann-Whitney U test and Wilcoxon signed-rank test, as appropriate) were used. P < .05 was considered significant. All plots and statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 7 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA).
Results
IL-18BP−/− mice do not display a spontaneous proinflammatory phenotype
Because the proinflammatory cytokine IL-18 is believed to be naturally inhibited by IL-18BP at steady state, we examined whether IL-18BP−/− mice display a spontaneous inflammatory phenotype. Naive IL-18BP−/− and IL-18BP+/− mice appeared healthy, and their breeding capacities were normal (data not shown). Compared with WT littermates, IL-18BP−/− mice showed similar weight gain from birth to at least 12 weeks of age (Figure 1B). No gross morphological or histological abnormalities, especially signs of inflammation, were observed in IL-18BP−/− mice. Peripheral blood cell analysis did not show any significant difference between WT littermates and IL-18BP−/− mice (Figure 1C). The numbers of spleen T and B cells, dendritic cells (DCs), monocytes/macrophages, and neutrophils were similar in IL-18BP−/− mice and WT littermates (Figure 1D).
IL-18BP−/− mice display a severe form of MAS on repeated CpG injections
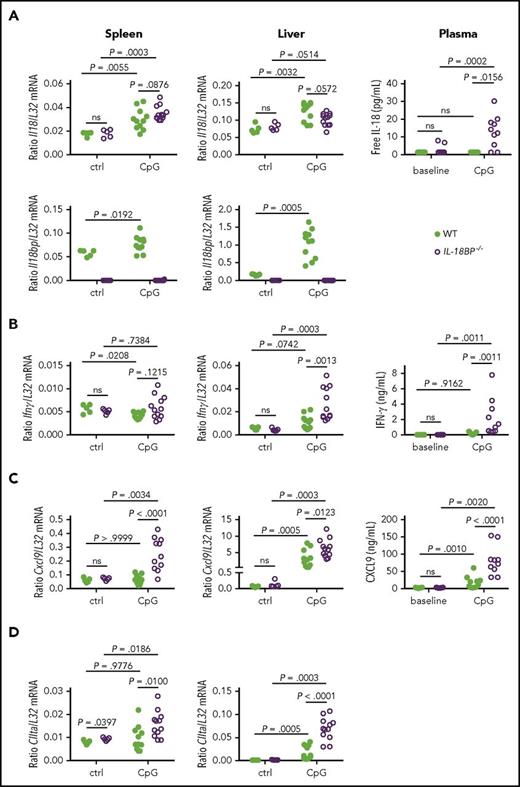
Because elevated serum levels of IL-18 have been reported in the TLR9-induced mouse model of MAS,16 we examined whether IL-18BP deficiency could lead to a more severe form of MAS on repeated CpG injections. We observed a marked weight loss and poor general condition in CpG-treated IL-18BP−/− mice, which compelled us to terminate the study on day 7. As shown in Figure 2A, the body weight loss was already significantly higher in IL-18BP−/− than WT littermates 2 days after the first CpG injection, and their condition worsened thereafter and up to day 7. Repeated TLR9 stimulation induced peripheral pancytopenia that was significantly more marked in IL-18BP−/− mice, except for white blood cells (P = .0778, Figure 2B). Elevated ferritin levels were also detected on day 7, which were significantly higher in IL-18BP−/− mice (Figure 2C). We observed hemophagocytes in the bone marrow smears of CpG-challenged IL-18BP−/− mice, but not in WT mice (Figure 2D). IL-18BP−/− mice developed splenomegaly (Figure 3A) and hepatomegaly (supplemental Figure 3A) that were significantly more pronounced than in WT mice. Repeated CpG injections induced a disruption of the normal spleen architecture with nucleated cell infiltration into the red pulp, which was more pronounced in IL-18BP−/− mice (data not shown). The total lymphoid follicle area, revealed with CD3 staining, was significantly decreased on CpG injection and was significantly lower in IL-18BP−/− as compared with WT mice (Figure 3B). In the absence of IL-18BP, repeated CpG challenge also resulted in a higher increase in CD45+ cell counts in the spleen, which was associated with a higher number of B cells and monocytes/macrophages (Figure 3C). A mild cellular infiltrate was present in the liver after CpG administration, but without any obvious difference between the 2 genotypes (supplemental Figure 3B). Yet, repeated CpG injections induced a significant increase of measured plasma ALT activity in IL-18BP−/− mice only (supplemental Figure 3C). To summarize, repeated CpG challenge induced more severe MAS manifestations in IL-18BP−/− than in WT mice.
IL-18BP−/−mice display a severe form of MAS after repeated CpG injections. Female WT and IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were killed on day 7. (A) Variations from baseline body weight are represented as mean ± SD for WT (n = 11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 12) littermates. Circulating (Bi) white blood cell, (Bii) red blood cell, and (Biii) platelet counts and (C) plasma ferritin levels of WT and IL-18BP−/− mice obtained before (baseline) and after CpG injections are represented as individual values for each mouse. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. (D) Hemophagocytes (arrowhead) were observed on May-Grünwald Giemsa–stained bone marrow smears only in CpG-challenged IL-18BP−/− mice (original magnification ×1000). The Mann-Whitney test was used to compare WT and IL-18BP−/− mice at 1 time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare baseline and day 7 values within each genotype when data were paired. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .005.
IL-18BP−/−mice display a severe form of MAS after repeated CpG injections. Female WT and IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were killed on day 7. (A) Variations from baseline body weight are represented as mean ± SD for WT (n = 11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 12) littermates. Circulating (Bi) white blood cell, (Bii) red blood cell, and (Biii) platelet counts and (C) plasma ferritin levels of WT and IL-18BP−/− mice obtained before (baseline) and after CpG injections are represented as individual values for each mouse. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. (D) Hemophagocytes (arrowhead) were observed on May-Grünwald Giemsa–stained bone marrow smears only in CpG-challenged IL-18BP−/− mice (original magnification ×1000). The Mann-Whitney test was used to compare WT and IL-18BP−/− mice at 1 time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare baseline and day 7 values within each genotype when data were paired. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .005.
Splenic changes related to TLR9-induced MAS are more pronounced in IL-18BP−/−mice. Female WT and IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were killed on day 7. (Ai) Spleen weights, normalized to body weight, of naive (control [ctrl]) and CpG-challenged WT (n = 8-11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 9-12) littermates (data pooled from 2 independent experiments) and (Aii) a representative photograph of the spleens of CpG-injected WT (left) and IL-18BP−/− (right) mice are shown. (Bi) CD3 staining of spleen sections of 1 WT (left) and 1 IL-18BP−/− (right) mouse before (upper panels, ctrl) and after (lower panels) CpG injections (original magnification ×20), representative of 2 independent experiments. The ratio between lymphoid follicles and spleen section area of naive (ctrl) and CpG-challenged WT (n = 6-10) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 8-12) littermates is reported in panel Bii. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The number of (Ci) total and CD45+ cells (n = 6-7), (Cii) total T cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and B cells (n = 10-11), and (Ciii) conventional DCs (cDCs), plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), monocytes/macrophages (mono/macro), and neutrophils (neutro) (n = 10-11) in the spleen are shown for naive WT littermate and IL-18BP−/− female mice (results were pooled from 2 independent experiments). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and 18BP−/− mice at 1 time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice.
Splenic changes related to TLR9-induced MAS are more pronounced in IL-18BP−/−mice. Female WT and IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were killed on day 7. (Ai) Spleen weights, normalized to body weight, of naive (control [ctrl]) and CpG-challenged WT (n = 8-11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 9-12) littermates (data pooled from 2 independent experiments) and (Aii) a representative photograph of the spleens of CpG-injected WT (left) and IL-18BP−/− (right) mice are shown. (Bi) CD3 staining of spleen sections of 1 WT (left) and 1 IL-18BP−/− (right) mouse before (upper panels, ctrl) and after (lower panels) CpG injections (original magnification ×20), representative of 2 independent experiments. The ratio between lymphoid follicles and spleen section area of naive (ctrl) and CpG-challenged WT (n = 6-10) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 8-12) littermates is reported in panel Bii. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The number of (Ci) total and CD45+ cells (n = 6-7), (Cii) total T cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and B cells (n = 10-11), and (Ciii) conventional DCs (cDCs), plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), monocytes/macrophages (mono/macro), and neutrophils (neutro) (n = 10-11) in the spleen are shown for naive WT littermate and IL-18BP−/− female mice (results were pooled from 2 independent experiments). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and 18BP−/− mice at 1 time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice.
IL-18 and IL-18BP are upregulated on repeated CpG injections
Because IL-18BP deficiency is associated with a more severe MAS phenotype, we assessed the expression of IL-18 and IL-18BP after CpG injections. Il18 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in the spleen and liver was increased in CpG-challenged mice as compared with controls, but there was no significant difference between WT and IL-18BP−/− mice (Figure 4A). Il18bp mRNA expression in WT mice was markedly enhanced by repeated CpG injections, especially in the liver. The serum levels of free IL-18 were specifically increased in IL-18BP−/− mice after CpG injections, but remained undetectable in naive IL-18BP−/− mice, as well as in WT mice with or without CpG injections (Figure 4A, right panel).
IL-18 and IL-18BP are upregulated and IL-18BP−/−mice show a more pronounced IFN-γ signature than WT littermates after repeated CpG injections. (A) Il18, Il18bp, (B) Ifnγ, (C) Cxcl9, and (D) CIIta mRNA levels in the spleen (left panels) and liver (middle panels) are shown for naive (ctrl) or CpG-challenged (CpG) WT (n = 5-11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 5-12) female mice. Data are from 1 experiment at baseline and 2 pooled independent experiments after TLR9 stimulation. Plasma levels (right) of (A) free IL-18, (B) IFN-γ, and (C) CXCL9 are represented at baseline and on day 7 after CpG injections in WT (n = 11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 10) mice. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and IL-18BP−/− mice at 1 time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare baseline and day 7 values within each genotype when data were paired.
IL-18 and IL-18BP are upregulated and IL-18BP−/−mice show a more pronounced IFN-γ signature than WT littermates after repeated CpG injections. (A) Il18, Il18bp, (B) Ifnγ, (C) Cxcl9, and (D) CIIta mRNA levels in the spleen (left panels) and liver (middle panels) are shown for naive (ctrl) or CpG-challenged (CpG) WT (n = 5-11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 5-12) female mice. Data are from 1 experiment at baseline and 2 pooled independent experiments after TLR9 stimulation. Plasma levels (right) of (A) free IL-18, (B) IFN-γ, and (C) CXCL9 are represented at baseline and on day 7 after CpG injections in WT (n = 11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 10) mice. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and IL-18BP−/− mice at 1 time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare baseline and day 7 values within each genotype when data were paired.
Repeated TLR9 stimulation in IL-18BP−/− mice leads to increased IFN-γ production and signature
IFN-γ is thought to play a critical role in human MAS, as well as mouse models of MAS. We thus examined IFN-γ production and signature in IL-18BP−/− and WT mice. Baseline spleen and liver levels of Ifnγ mRNA and IFN-γ concentrations in plasma (Figure 4B) were not different between WT and IL-18BP−/− mice. On repeated CpG administration, the levels of Ifnγ mRNA were significantly higher in the livers of IL-18BP−/− mice compared with WT littermates (Figure 4B, middle panel). Consistently, plasma levels of IFN-γ were significantly increased in CpG-challenged IL-18BP−/− mice as compared with WT mice (Figure 4B, right panel). In contrast, CpG stimulation was devoid of any stimulatory effect on Ifnγ gene expression in the spleens of either IL-18BP−/− or WT mice (Figure 4B, left panel). We also explored the expression of 2 IFN-γ response genes: CXCL9, a T-cell chemoattractant, and the class II major histocompatibility complex transactivator (CIITA). CIIta and Cxcl9 gene expression was significantly increased in the liver after CpG injections in both IL-18BP−/− and WT mice (Figure 4C-D, middle panels). Moreover, CIIta and Cxcl9 mRNA levels were higher in the livers and spleens of IL-18BP−/− mice as compared with WT mice (Figure 4C-D, left and middle panels). CXCL9 plasma levels were also significantly higher in CpG-stimulated IL-18BP−/− mice than in their WT littermates (Figure 4C, right panel).
A single CpG injection was associated with an enhanced IFN-γ signature in IL-18BP−/− mice
Because the effects of repeated TLR9 stimulation on cytokine levels are difficult to interpret due to potential feedback and cross-regulatory mechanisms, we assessed the regulation of IL-18 and IFN-γ expression by TLR9 activation 4 and 24 hours after a single CpG injection. Il18 mRNA levels increased in the spleen as soon as 4 hours after CpG injection (Figure 5A, left upper panel) without any difference between IL-18BP−/− and WT mice. Il18bp gene expression was rapidly stimulated in the spleens and livers of WT mice after CpG administration (Figure 5A, left and middle lower panels). Circulating free IL-18 levels were significantly increased after 4 and 24 hours of stimulation in IL-18BP−/− mice only (Figure 5A, right panel). Spleen and liver Ifnγ mRNA levels were significantly higher in IL-18BP−/− than WT mice 24 hours after CpG injection (Figure 5B, left and middle panels). Serum levels of IFN-γ were also significantly higher in IL-18BP−/− mice, not only 24 hours, but also 4 hours after CpG injection (Figure 5B, right panel). Cxcl9 and CIIta mRNA levels were significantly upregulated in the spleen and liver 4 hours and 24 hours after CpG injection (Figure 5C-D, left and middle panels). In addition, Cxcl9 and CIIta mRNA levels, as well as CXCL9 serum levels (Figure 5C), were significantly higher in IL-18BP−/− than in WT littermates 24 hours after CpG injection. To summarize, a single CpG injection was sufficient to induce the production and release of IL-18, associated with an IFN-γ signature, which was notably higher in IL-18BP−/− mice.
Cytokine expression is modified by a single CpG injection in WT and IL-18BP−/−mice. WT and IL-18BP−/− male mice were sacrificed either 4 (H4, n = 7 per genotype) or 24 hours (H24, n = 7 or 8 per genotype) after a single CpG injection. These mice were compared with naive WT (n = 8) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 7) male mice (H0). (A) Il18 and Il18bp, (B) Ifnγ, (C) Cxcl9, and (D) CIIta mRNA levels were assessed in the spleen (left) and liver (middle), and serum levels of (A) free IL-18, (B) IFN-γ, and (C) CXCL9 were measured (right). For each time point, data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and IL-18BP−/− mice at each time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice.
Cytokine expression is modified by a single CpG injection in WT and IL-18BP−/−mice. WT and IL-18BP−/− male mice were sacrificed either 4 (H4, n = 7 per genotype) or 24 hours (H24, n = 7 or 8 per genotype) after a single CpG injection. These mice were compared with naive WT (n = 8) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 7) male mice (H0). (A) Il18 and Il18bp, (B) Ifnγ, (C) Cxcl9, and (D) CIIta mRNA levels were assessed in the spleen (left) and liver (middle), and serum levels of (A) free IL-18, (B) IFN-γ, and (C) CXCL9 were measured (right). For each time point, data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and IL-18BP−/− mice at each time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice.
IL-18 blockade reverses the severity of MAS and the increased IFN-γ signature in IL-18BP−/− mice
Our findings in IL-18BP−/− mice suggest that excessive IL-18 signaling contributes to the severity of MAS manifestations observed on repeated TLR9 stimulation. To confirm this hypothesis, we tested the effects of IL-18 inhibition in IL-18BP−/− mice. The injection of a blocking monoclonal anti–IL-18R antibody before each CpG injection markedly attenuated the severity of MAS manifestations, as compared with control isotype antibody–treated mice. On CpG challenge, IL-18BP−/− mice treated with anti–IL-18R antibody displayed corrected weight loss (Figure 6A), higher white blood cell, red blood cell, and platelet counts (Figure 6B), and lower ferritin levels (Figure 6C) and ALT activity (Figure 6D) in comparison with IL-18BP−/− mice treated with an isotype control. IL-18R pathway blockade also resulted in a reduction of CpG-induced splenomegaly (Figure 7A). FACS analysis of the spleen revealed a global decrease in the total number of spleen cells in anti–IL-18R antibody–treated compared with isotype-treated mice, involving most of the lymphoid and myeloid cell subpopulations (Figure 7B). Circulating levels of IFN-γ (supplemental Figure 4A, left panel) and CXCL9 (supplemental Figure 4B, left panel) were markedly decreased in IL-18BP−/− mice treated with the anti–IL-18R antibody as compared with isotype control–treated mice. Anti–IL-18R antibody treatment of CpG-challenged IL-18BP−/− mice also significantly reduced Ifnγ, Cxcl9, CIIta, and Socs1 mRNA expression in the liver and Cxcl9 and Socs1 mRNA expression in the spleen in comparison with isotype control treatment (supplemental Figure 4C-F, left panels).
IL-18 blockade with a monoclonal anti–IL-18R antibody attenuates the severity of MAS in IL-18BP−/−mice. Male IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were either treated with an isotype control (n = 11) or a monoclonal anti–IL-18R (n = 12) antibody. All mice were killed on day 7. (A) Variations from baseline body weight are represented as mean ± SD in isotype and anti–IL-18R–treated mice. Circulating (Bi) white blood cell, (Bii) red blood cell, and (Biii) platelet counts and plasma levels of (C) ferritin and (D) ALT were measured before (baseline) and on day 7 after CpG injections (CpG) in isotype and anti–IL-18R antibody–treated IL-18BP−/− mice. All data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare isotype control and anti–IL-18R antibody–treated mice at 1 time point. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare baseline and day 7 values within each treatment group when data were paired. **P < .01; ***P < .005.
IL-18 blockade with a monoclonal anti–IL-18R antibody attenuates the severity of MAS in IL-18BP−/−mice. Male IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were either treated with an isotype control (n = 11) or a monoclonal anti–IL-18R (n = 12) antibody. All mice were killed on day 7. (A) Variations from baseline body weight are represented as mean ± SD in isotype and anti–IL-18R–treated mice. Circulating (Bi) white blood cell, (Bii) red blood cell, and (Biii) platelet counts and plasma levels of (C) ferritin and (D) ALT were measured before (baseline) and on day 7 after CpG injections (CpG) in isotype and anti–IL-18R antibody–treated IL-18BP−/− mice. All data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare isotype control and anti–IL-18R antibody–treated mice at 1 time point. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare baseline and day 7 values within each treatment group when data were paired. **P < .01; ***P < .005.
IL-18 blockade with a monoclonal anti–IL-18R antibody protects from splenic changes induced by repeated TLR9 stimulation in IL-18BP−/−mice. Male IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were either treated with an isotype control (n = 11) or a monoclonal anti–IL-18R (n = 12) antibody. All mice were killed on day 7. (A) Spleen weights, normalized to body weight, from isotype and anti–IL-18R–treated IL-18BP−/− mice are shown. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The number of (Bi) total and CD45+ cells, (Bii) total T cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and B cells, and (Biii) conventional DCs (cDCs), plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), monocytes/macrophages (mono/macro), and neutrophils (neutro) in the spleen are reported for isotype (n = 6) and anti–IL-18R antibody–treated (n = 6) IL-18BP−/− mice. Data are from 1 experiment and are representative of 2 experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare isotype control and anti–IL-18R antibody–treated mice at 1 time point.
IL-18 blockade with a monoclonal anti–IL-18R antibody protects from splenic changes induced by repeated TLR9 stimulation in IL-18BP−/−mice. Male IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were either treated with an isotype control (n = 11) or a monoclonal anti–IL-18R (n = 12) antibody. All mice were killed on day 7. (A) Spleen weights, normalized to body weight, from isotype and anti–IL-18R–treated IL-18BP−/− mice are shown. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The number of (Bi) total and CD45+ cells, (Bii) total T cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and B cells, and (Biii) conventional DCs (cDCs), plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), monocytes/macrophages (mono/macro), and neutrophils (neutro) in the spleen are reported for isotype (n = 6) and anti–IL-18R antibody–treated (n = 6) IL-18BP−/− mice. Data are from 1 experiment and are representative of 2 experiments. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare isotype control and anti–IL-18R antibody–treated mice at 1 time point.
As opposed to the results in IL-18BP−/− mice, the administration of anti–IL-18R did not attenuate the severity of CpG-induced MAS in WT mice (supplemental Figure 5).
IFN-γ blockade attenuates the severity of MAS similarly to IL-18 blockade in IL-18BP−/− mice
Because IL-18 blockade, which reverses most features of MAS, also decreases the IFN-γ signature in IL-18BP−/− mice, we wondered whether blocking IFN-γ would also improve the disease. Behrens et al demonstrated that IFN-γ blockade using a monoclonal anti–IFN-γ antibody (clone XGM1.2) attenuated splenomegaly and cytopenia in CpG-challenged WT mice.15 Using the same monoclonal anti–IFN-γ antibody, we observed significantly reduced weight loss (supplemental Figure 6A), splenomegaly and total spleen cell counts (supplemental Figure 6B), anemia (supplemental Figure 6Cii), plasma ferritin levels (supplemental Figure 6D), and ALT activity (supplemental Figure 6E) in anti–IFN-γ–treated as compared with isotype control–treated IL-18BP−/− mice. The levels of plasmatic IFN-γ and splenic Ifnγ mRNA were significantly increased in anti–IFN-γ–treated mice (supplemental Figure 4A,C, right panels), but IFN-γ–inducible genes Cxcl9 (supplemental Figure 4D, right panel) and CIIta (supplemental Figure 4E, right panel) were downregulated in the liver of anti–IFN-γ–treated as compared with isotype-treated IL-18BP−/− mice. CXCL9 plasma levels (supplemental Figure 4B, right panel) and spleen CIIta mRNA expression (supplemental Figure 4E, right panel) were also significantly reduced in anti–IFN-γ–treated IL-18BP−/− mice. Socs1 mRNA levels were decreased in the liver of anti–IFN-γ–treated mice as compared with isotype controls (supplemental Figure 4F, right panel). To summarize, IFN-γ blockade using anti–IFN-γ antibodies resulted in attenuation of MAS severity in IL-18BP−/− mice, similarly to IL-18 blockade.
Discussion
Our results show that IL-18BP–deficient mice have no spontaneous inflammatory phenotype, but that, on repeated TLR9 stimulation, they develop more severe inflammatory responses than WT mice, comprising characteristic manifestations of MAS, such as cytopenia, splenomegaly, hyperferritinemia, hepatitis, and hemophagocytosis. Remarkably, these pathological features are associated with the presence of free IL-18 in the circulation of IL-18BP−/− but not WT mice. Furthermore, the administration of blocking anti–IL-18R antibodies markedly attenuated the severity of CpG-induced inflammatory responses in IL-18BP−/− mice. These findings indicate that excessive IL-18 signaling is associated with severe manifestations of MAS and that endogenous IL-18BP plays a critical role in regulating IL-18–induced systemic responses. IFN-γ blockade with anti–IFN-γ antibodies also significantly improved CpG-induced MAS in IL-18BP−/− mice.
Several experimental models of MAS, including primary and secondary, have been developed. The role of IFN-γ has been demonstrated in models of primary HLH.17,18 A large body of evidence also indicates that IFN-γ is critical in the development of secondary HLH. Most pathological manifestations induced by repetitive CpG injections were attenuated in IFN-γ–deficient mice, although hyperferritinemia was unchanged compared with WT mice.15 More recently, other investigators reported that anti–IFN-γ antibodies attenuated all clinical and biological manifestations induced by repeated CpG challenge, including hyperferritinemia. Of note, markers of IFN-γ response, such as CXCL9 and CXCL10, correlated with IFN-γ levels, hyperferritinemia, thrombocytopenia, and lymphopenia.19 Spleen and liver Cxcl9 and Cxcl10 mRNA levels also correlated with serum ferritin levels in another model of secondary HLH induced by the administration of LPS in IL-6 transgenic mice.20 Circulating levels of CXCL9 and CXCL10 correlated with several disease-associated laboratory abnormalities in patients with secondary HLH,19 and IFN-γ and the IFN-γ–induced chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 were also significantly higher in active MAS and secondary HLH than in patients with sJIA.20 We observed that excessive IL-18 signaling was associated with increased IFN-γ production and an enhanced IFN-γ molecular signature, as reflected by Cxcl9 and CIIta mRNA levels. Attenuation of MAS severity by IFN-γ blockade in IL-18BP−/− mice further supports the pathogenic role of IFN-γ in this model. Taken together, our recent findings are consistent with a role for IL-18 and IFN-γ in MAS, where IL-18 acts upstream of IFN-γ.
We also observed that Ifnγ was overexpressed in the spleens and livers of CpG-challenged, anti–IFN-γ antibody–treated IL-18BP−/− mice as compared with isotype-treated mice. We hypothesize that this finding reflects the attenuation of a negative feedback mechanism. Indeed, the mRNA levels of Socs1, a natural inhibitor of the JAK/STAT pathway,21 were decreased in the spleen and liver on IFN-γ blockade. Socs1 mRNA levels were also reduced with anti–IL-18R antibody administration. However, despite this inhibitory effect of IL-18 blockade on Socs1 expression, Ifnγ mRNA levels were not increased, most likely because IL-18 acts upstream of IFN-γ production. The marked increase of IFN-γ plasma levels in anti–IFN-γ–treated mice could be due to enhanced Ifnγ expression in the spleen and liver and/or could be related to the formation of IFN-γ/anti–IFN-γ antibody complexes.19
HLH is divided into different subsets according to its pathogenesis. Primary or familial forms are mostly related to genetic deficiency of molecules involved in cell cytotoxicity.9 Secondary forms of HLH (also termed MAS) occur in patients with inflammatory diseases, such as sJIA and AOSD, in patients after viral infections, or in patients with cancer. Models of viral infection in Perforin-deficient mice recapitulate the findings of human primary HLH. On the other hand, the occurrence of exaggerated inflammatory responses stimulated by repetitive CpG injections is more likely a model of MAS. Of note, CpG-treated WT mice displayed only minimal CD8+ T- and NK-cell activation, but a 20-fold decrease in splenic NK cell numbers.15 It has recently been reported that IL-18BP−/− naive mice have a reduced number of splenic NK cells compared with WT naive mice.22 The examination of the cytotoxic function of CD8+ T and NK cells in naive and CpG-challenged IL-18BP−/− mice would be of interest to further characterize MAS pathogenesis in this model.
Structurally, IL-18BP has 1 immunoglobulin domain and binds to mature IL-18, but not to pro–IL-18, with high affinity and thus prevents its interaction with cell surface receptors.4 In the case of an imbalance between IL-18 production and the buffering capacities of IL-18BP, the presence of free IL-18 can be detected, such as in patients with active AOSD.6 In addition, we have also observed that free IL-18 levels were elevated in an infant with a gain-of-function mutation of NLRC4 associated with severe autoinflammatory manifestations, including MAS and enteritis refractory to anti–TNF-α and anti–IL-1β therapy. This finding led to the compassionate use of recombinant IL-18BP with a rapidly favorable and sustained clinical response and complete disappearance of serum free IL-18.23
Free IL-18 remained undetectable in the circulation of WT mice, suggesting that the increased production of IL-18BP in response to CpG is sufficient to bind IL-18 and control its biological activity. Consistent with this hypothesis, treatment with anti–IL-18R antibody was devoid of any protective effect in WT mice injected with CpG.
The cytokines of the IL-1 family include different agonists, such as IL-1, IL-18, IL-33, and IL-36, the biological activity of which are tightly controlled by different inhibitors. For example, IL-1Ra–deficient mice exhibit spontaneous inflammatory manifestations, which vary according to the background in which they are bred (reviewed in Gabay et al24 ). In contrast, we did not observe any spontaneous inflammatory phenotype in IL-18BP−/− mice, suggesting that IL-18BP is dispensable in the absence of inflammasome activation and release of mature IL-18. Accordingly, serum-free IL-18 is undetectable in naive IL-18BP−/− mice.
In conclusion, we showed that an imbalance between IL-18 and its natural inhibitor IL-18BP leads to severe MAS in response to TLR9 stimulation, thus recapitulating some of the clinical findings of severe autoinflammatory syndromes, such as AOSD and MAS.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Kaveh Samii (Division of Hematology, University Hospitals of Geneva) for useful discussion on blood and bone marrow smears, Eduardo Schiffrin and Greg del Val (AB2 Bio S.A., Lausanne, Switzerland) for useful discussions on the free IL-18 assay, Dominique Talabot-Ayer for expert technical assistance, Florence Coppo for maintaining the mouse lines, and Sylvie Roulet for help with the Sysmex analyses.
This work was supported by Swiss National Science Foundation grant 310030-172674/1, Federal Commission for Technology and Innovation grant 18772.1PFLS-LS, the Rheumasearch Foundation, the Uniscientia Foundation, and the Institute of Arthritis Research.
Authorship
Contribution: C.G.-G., J.P., P.M., E.R., S.T., and G.P. performed the experiments; C.G.-G., J.P., P.M., and G.P. analyzed the data; and C.G.-G., J.P., G.P., and C.G. designed the experiments, interpreted the data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.G.-G.’s salary was supported by an unrestricted grant from AB2 Bio S.A. (Lausanne, Switzerland). C.G. has received consultant fees and a research grant from AB2 Bio S.A. and owns shares in AB2 Bio S.A. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Cem Gabay, Division of Rheumatology, University Hospitals of Geneva, 26 Ave de Beau Séjour, 1206 Geneva, Switzerland; e-mail: cem.gabay@hcuge.ch.
References
Author notes
C.G.-G. and J.P. contributed equally to this work.



![Figure 3. Splenic changes related to TLR9-induced MAS are more pronounced in IL-18BP−/− mice. Female WT and IL-18BP−/− mice received CpG injections on days 0, 2, and 4 and were killed on day 7. (Ai) Spleen weights, normalized to body weight, of naive (control [ctrl]) and CpG-challenged WT (n = 8-11) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 9-12) littermates (data pooled from 2 independent experiments) and (Aii) a representative photograph of the spleens of CpG-injected WT (left) and IL-18BP−/− (right) mice are shown. (Bi) CD3 staining of spleen sections of 1 WT (left) and 1 IL-18BP−/− (right) mouse before (upper panels, ctrl) and after (lower panels) CpG injections (original magnification ×20), representative of 2 independent experiments. The ratio between lymphoid follicles and spleen section area of naive (ctrl) and CpG-challenged WT (n = 6-10) and IL-18BP−/− (n = 8-12) littermates is reported in panel Bii. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. The number of (Ci) total and CD45+ cells (n = 6-7), (Cii) total T cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and B cells (n = 10-11), and (Ciii) conventional DCs (cDCs), plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), monocytes/macrophages (mono/macro), and neutrophils (neutro) (n = 10-11) in the spleen are shown for naive WT littermate and IL-18BP−/− female mice (results were pooled from 2 independent experiments). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare WT and 18BP−/− mice at 1 time point and to compare naive and CpG-challenged mice.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/131/13/10.1182_blood-2017-06-789552/4/m_blood789552f3.jpeg?Expires=1767709212&Signature=UMwf8Qc4IBSy8WeEpZ6Z6VTngsiAIvZxEq-1gI4uX~QEyJmDI44RyDacmZ-6ueUPq5-AT11iiddPp9CtJdY0ZQ1pwLK37SbNS-AJMefBxaEAfghfHDPHDIpkEAA2XDBtm6TtlOjZcq2qvAcvIHSuANbu~CA5bhEFxlfORoWzJyJ1xcuw~XILf31sYKcpqL6HolTybfnd6kfH-hDRJdDN7s-iTaQC9QiUp8pNe0PWfw3Ma9ExwYrnwPlSqhMwqYDpaJZedNo9M7iZ4vTQFTGZrMiNu-XtMvxF3HmjOtiVOg3348OnTIoa3a75l6XECKR0pFbGEmBdx2KAy7zqZWOQRg__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal