Abstract
The MYC proto-oncogene is a gene product that coordinates the transcriptional regulation of a multitude of genes that are essential to cellular programs required for normal as well as neoplastic cellular growth and proliferation, including cell cycle, self-renewal, survival, cell growth, metabolism, protein and ribosomal biogenesis, and differentiation. Here, we propose that MYC regulates these programs in a manner that is coordinated with a global influence on the host immune response. MYC had been presumed to contribute to tumorigenesis through tumor cell–intrinsic influences. More recently, MYC expression in tumor cells has been shown to regulate the tumor microenvironment through effects on both innate and adaptive immune effector cells and immune regulatory cytokines. Then, MYC was shown to regulate the expression of the immune checkpoint gene products CD47 and programmed death-ligand 1. Similarly, other oncogenes, which are known to modulate MYC, have been shown to regulate immune checkpoints. Hence, MYC may generally prevent highly proliferative cells from eliciting an immune response. MYC-driven neoplastic cells have coopted this mechanism to bypass immune detection. Thus, MYC inactivation can restore the immune response against a tumor. MYC-induced tumors may be particularly sensitive to immuno-oncology therapeutic interventions.
The MYC oncogene in normal cells and cancer
MYC is a family of 3 related gene products (c-MYC, n-MYC, and l-MYC; in this review, however, MYC will refer to c-MYC unless otherwise specified).1 The MYC family members are transcription factors that can coordinate the transcriptional expression of thousands of genes.2-5 The MYC proto-oncogenes normally coordinate cell cycle, cell growth, self-renewal, survival, metabolism, protein synthesis, and differentiation.2-12
MYC regulates the expression of gene products through direct activation or inhibition of gene transcription,5 transcriptional amplification,3,4,13 the induction of microRNA and chromatin regulators,14,15 and/or the global regulation of RNA and protein biogenesis.16 The knockout of MYC is embryonic lethal,17,18 and knockout in mature cells impedes their survival, growth, and differentiation.19 Thus, MYC is a crucial gene product that is essential both during embryonic development and in adult mature cellular growth.
The overexpression of MYC is common in many types of human cancer.6-10,20-22 MYC can be directly genetically activated through chromosomal translocation, genomic amplification, retroviral integration, and mutation,23,24 as well as activated through increased gene expression and/or protein stability by the activation of other oncogenes, including RAS, SRC, NOTCH,25,26 or the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes such as APC.27 Hence, MYC appears to be a gene product that often is induced in neoplastic growth.
Conditional transgenic mouse models have been used to study how MYC initiates and maintains tumorigenesis for several tumor types, including hematopoietic tumors. The suppression of MYC expression in conditional mouse models has been shown to result in rapid and sustained loss of a neoplastic phenotype, which has been described as “oncogene addiction.”6-10,28-37 Initially, MYC was presumed to contribute to tumorigenesis through tumor cell–intrinsic mechanisms, independent of the host or the immune system. We discuss here evidence from multiple reports that illustrate that MYC can contribute to tumorigenesis through an influence on host immune cells.
Inhibition of the MYC oncogene restores immune response to tumors
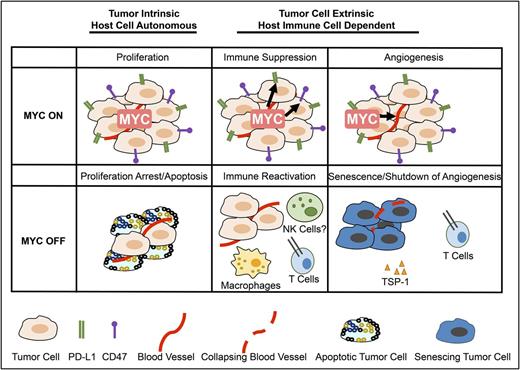
Cancers often exhibit “oncogene addiction” upon targeting or removal of the driver oncoprotein, associated with rapid and sustained tumor regression.9 Oncogene addiction is composed of 2 “phases” following removal of the driver oncoprotein.38,39 The first phase of oncogene addiction occurs through tumor cell–intrinsic mechanisms of proliferative arrest and apoptosis. However, the second phase of oncogene addiction is host dependent and requires an intact host immune system to result in the complete elimination of tumor cells and involves remodeling of the tumor microenvironment associated with cellular senescence of tumor cells and the shutdown of angiogenesis (Figure 1).
MYC inactivation elicits tumor regression through both tumor-intrinsic and host-dependent mechanisms. Left to right: through tumor-intrinsic mechanisms, inactivation of MYC induces proliferative arrest and apoptosis (left panel). The death of tumor cells through apoptosis may contribute to the immune response by recruiting innate immune cells. Inactivation of MYC suppresses immune checkpoints and recruits an adaptive immune-dependent response (center panel), activating macrophages and CD4+ T cells. The final phase of tumor elimination likely involves the recruitment of an immune response through T cells as well as the production of other cytokines. Immune activation has been associated with the remodeling of the tumor microenvironment, including the induction of cellular senescence and the shutdown of angiogenesis. This occurs in part through TSP-1 (right panel).
MYC inactivation elicits tumor regression through both tumor-intrinsic and host-dependent mechanisms. Left to right: through tumor-intrinsic mechanisms, inactivation of MYC induces proliferative arrest and apoptosis (left panel). The death of tumor cells through apoptosis may contribute to the immune response by recruiting innate immune cells. Inactivation of MYC suppresses immune checkpoints and recruits an adaptive immune-dependent response (center panel), activating macrophages and CD4+ T cells. The final phase of tumor elimination likely involves the recruitment of an immune response through T cells as well as the production of other cytokines. Immune activation has been associated with the remodeling of the tumor microenvironment, including the induction of cellular senescence and the shutdown of angiogenesis. This occurs in part through TSP-1 (right panel).
In genetically engineered conditional mouse models of lymphoma/leukemia, inactivation of MYC as well as many other oncogenes induces sustained tumor regression in wild-type animals.6,7,30,33 However, inactivation of an oncogene in a host that is lacking an intact host immune system results in reduced rate of tumor cell elimination, incomplete regression of tumors, and eventual tumor recurrence.40-42 Notably, the absence of CD4+ but not the absence of CD8+ T cells was sufficient to prevent MYC inactivation from causing sustained tumor regression.43 Furthermore, CD4+ T cells were found to require the expression of thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1). Finally, CD4+ T cells were shown to be required for MYC inactivation to elicit cellular senescence in tumor cells and the shutdown of host angiogenesis.
Collectively, these findings suggest that MYC causes and maintains cancer not just through influencing tumor cell proliferation, growth, and survival but also through an influence on the host tumor microenvironment and immune effectors. Here, we discuss how MYC and other oncogenes may regulate the host immune response in a tumor. We suggest why oncogenes may physiologically regulate the immune response.
MYC regulates expression of PD-L1
The mechanism by which MYC regulates the immune response was not clear. Recently, multiple groups described that MYC family members regulate the gene expression of immune checkpoints, including CD47 and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1).44-47 PD-L1 (CD274, also known as B7-H1 and more commonly as PD-L1) suppresses the immune response, causes T cells to disengage, and functions as a “don’t find me” signal,48,49 whereas CD47 functions as a “don’t eat me” signal that suppresses macrophages and T cells.50
Casey and colleagues described that MYC induces transcription of both CD47 and PD-L1 in multiple tumors types, including lymphoma/leukemia and liver cancer.44 First, the suppression of MYC expression was found to result in the reduced messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expression of CD47 and PD-L1 in both mouse and human tumor-derived cell lines and primary tumors, both in vitro and in vivo for transgenic mouse models using the Tet system, and through short hairpin RNA suppression of MYC or use of the Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal motif inhibitor (BETi) JQ1 in human tumor-derived cell lines. Next, MYC was shown by chromatin immunoprecipitation to bind to the promoters of both CD47 and PD-L1 in multiple mouse and human tumors. Third, analysis of publically available datasets suggested that MYC levels correlated with both CD47 and PD-L1 expression in multiple human tumors. Fourth, prevention of downregulation of CD47 or PD-L1 expression upon MYC inactivation through enforced expression of either gene product prevented sustained tumor regression, blocked recruitment of immune effectors, and impeded cellular senescence and the shutdown of angiogenesis. Conversely, knockdown of CD47 or PD-L1 prevented tumors from growing in wild-type but not immune-compromised hosts. Hence, MYC induction of both CD47 and PD-L1 is required to maintain tumorigenesis at least in some cancers.44 However, it is likely that MYC regulates the immune response through many different mechanisms. There are also likely many other mechanisms by which CD47 and PD-L1 expression are regulated.
Similarly, Kim and colleagues characterized the relationship between MYC and PD-L1 in lung cancer.45 They found that expression of PD-L1 correlated with MYC levels in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) lines.45 The knockdown of MYC with a small interfering RNA reduced PD-L1 mRNA and protein expression. MYC and PD-L1 expression was correlated in human lung cancer specimens. Patients with tumors that were double positive for MYC and PD-L1 had a worse clinical outcome. These results suggest that MYC regulates PD-L1 expression in human lung cancer. Lung cancer is clinically responsive to PD-L1 therapy.51 The authors noted that MYC expression might predict clinical response to immune therapy.
Melaiu and colleagues found that MYC and n-MYC may regulate PD-L1 expression in neuroblastoma.47 MYC was shown to regulate PD-L1 mRNA expression in human neuroblastoma cell lines both in vitro and in vivo. MYC suppression by short hairpin RNA reduced PD-L1 levels, and treatment of neuroblastoma cells with JQ1 also reduced PD-L1.47 Combined expression of PD-L1 and HLA-I in the tumor was predictive of clinical outcome in neuroblastoma patients. Finally, PD-L1 transcripts positively correlated with MYC expression in a large dataset of human primary neuroblastoma, although PD-L1 did not positively correlate with n-MYC and tumors with amplified n-MYC were generally PD-L1 low.47 The authors concluded that MYC regulates PD-L1 expression. However, they noted that the low PD-L1 expression in some of the data made the correlation between these molecules quite complex; it is likely that other mechanisms are involved. The authors noted variable expression of PD-L1 expression in stage 3 and stage 4 neuroblastoma patients. Also, the authors noted a possible inhibitory effect of other genes coamplified with n-MYC.47 Hence, other pathways and levels of regulation are almost certainly at play in this disease. Notably, it is known that tumor-infiltrating T cells are positively predictive of clinical outcome in neuroblastoma.52 One possibility is that this may be regulated by MYC expression.
Atsaves and colleagues found that in ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), MYC, and STAT3 transcriptionally regulate PD-L1.46 In ALCL tumor-derived cell lines, overexpressing MYC increased PD-L1 expression. Treatment with the BETi JQ1 or a MYC-targeting small interfering RNA decreased PD-L1 expression. Similarly, STAT3 knockdown decreased MYC as well as PD-L1. Combined shutdown of STAT3 and MYC further decreased PD-L1. Hence, STAT3 might regulate PD-L1 directly as well as through decrease of MYC. This study suggests that, in ALCL, PD-L1 expression is regulated through both STAT3 and MYC.
Maeda and colleagues found that the transmembrane mucin MUC1 regulates PD-L1 in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) by recruiting MYC and NF-κB family member p65 to the PD-L1 promoter.53 Genetically or pharmacologically targeting the MUC1-C subunit led to downregulation of PD-L1, elevated tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells, and tumor destruction. The authors also found that MUC1 expression in TNBCs inversely correlated with T cell markers, such as CD8, CD69, and GZMB, and lower levels of these markers associated with decreased survival.53 Thus, MYC regulates PD-L1 via MUC-1 signaling in TNBC. MYC and MUC-1 are possible therapeutic targets to treat this cancer.
These studies collectively suggest that MYC can regulate PD-L1 expression (Figure 1). However, in only 1 study was MYC’s regulation of PD-L1 suggested to be causally related to the regulation of immune effector cells, including CD4+ T cells and macrophages, and the maintenance of tumor growth.44 Thus, it remains to be more generally examined if MYC is causally involved in the regulation of immune response through immune checkpoints. Other model systems have been described in which CD4+ T cells were similarly found to be oncogene regulated.54 Whether in this model system changes in immune checkpoint expression are involved and whether these effects are regulated by MYC are not known. Furthermore, it will be important to determine whether MYC’s regulation of PD-L1 is associated with changes in the immune response in human tumors. Finally, MYC is very likely to regulate the expression of other immune regulatory molecules. Indeed, as discussed below, other mechanisms have been recently described.
MYC may globally regulate the immune response
Recently, 2 reports suggest that MYC may more globally regulate the immune response. Kortlever and colleagues found that MYC and RAS cooperate to induce lung carcinoma through effects on the tumor microenvironment.55 The authors conditionally activated KRAS through Cre-lox and MYC through MycER. MYC activation results in the influx of macrophages alongside a loss of CD3+ T cells, B220+ B cells, and NKp46+ natural killer (NK) cells and was correlated with the induction of angiogenesis within 24 hours.55 The depletion of NKp46+ NK cells had significant effects on tumor growth. Anti-PD-L1 therapy restored T cells to the microenvironment but did not lead to tumor regression.55 CCL9 (macrophage inflammatory protein-1γ) and interleukin-23 were found to be associated with the influx of F4/80+ PD-L1+ macrophages and loss of CD3+ T cells.55 Thus, MYC appears to more generally regulate the immune response against tumors.
Topper and colleagues similarly found that in human NSCLC cell lines, treatment with DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (DNMTis) had effects on the tumor microenvironment that appear to be mediated by MYC.56 Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulated an interferon-α/β transcriptional program and a decrease in MYC levels. This was in turn associated with an increase in expression of antigen presentation machinery as well as the elevation of the T cell chemoattractant CCL5.56 When the Cre-Lox activated KRASG12D mouse model of lung cancer was treated with the DNMTi, there was an increase in CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. This also increased activated CD8+ T cells in an inflamed tumor as well as recruited CD8+ T cells to a “cold” tumor. The authors conclude that combination of epigenetic therapy to anti-PD-1 antibody therapy improved the overall clinical response.56 Notably, similar results were seen in ovarian cancer, where a combination of DNMTi, histone deacetylase inhibitors, and anti-PD-L1 therapy cooperates to activate immune cells to increase survival.57 Hence, the combination of epigenetic therapy, which appears to work through MYC, with immune therapy, may be a generally more effective approach to treating some cancers.
Notably, there are a multitude of studies from >20 years ago that suggested that MYC (c-MYC and n-MYC) may regulate the immune response through major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I.58-63 In a panel of mouse MYC-driven lymphomas, tumor growth was dependent on MHC I expression that appeared to regulate innate immune surveillance.62,63 In a panel of 11 human melanoma cell lines, MYC levels were inversely correlated with class I HLA.64 In 94 melanoma samples, MYC inversely correlated with class I HLA.65 In human melanoma, MYC was found to downregulate HLA-B.66 MYC can also regulate MHC I NK ligands.62 Treatment of multiple myeloma cell lines with a BETi inhibited MYC and upregulated the expression of the NKG2D receptor ligand MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A.67 MYC also represses the HLA-B promoter.68 Last, MYC was shown to regulate the innate immune response through a mechanism that appears to require p19ARF.69 Hence, MYC is likely to regulate a multitude of immune pathways that regulate the immune response.39,42,70
MYC and other oncogenes regulates PD-L1
Many oncogenes regulate MYC mRNA expression and protein stability. In some cases, the inhibition of these other oncogene gene products has been shown to inhibit PD-L1 expression. BETi can inhibit MYC function and also lead to reduced expression of PD-L1.44,71-75 BETi can result in decreased MYC expression but also can block the ability of MYC to mediate gene amplification.76,77 Therefore, BETi could have influence on MYC function through multiple mechanisms. Moreover, BETi may not always work through inhibition of MYC76-78 ; in 1 study, the BETi JQ1 decreases Brd4 occupancy at the PD-L1/Cd274 locus, leading to a swift decrease in Cd274/PD-L1 mRNA production in a mouse model of MYC-induced lymphoma.71 These authors found that the BETi RG6146 reduces PD-L1 levels.79 Thus, there could be MYC-independent mechanisms through which BETis affect PD-L1. JQ1 also reduces immune checkpoints and influences T cell recruitment in models of ovarian cancer.75 The BET inhibitor PFI-1 reduced PD-L1 levels in lung cancer.72 The BETi OTX015 reduces PD-L1 expression in stromal cells.73 The BETi iBET151 reduces PD-L1 and also inhibits the NF-κB family through inhibitor of κB as well as MYC.74 Hence, BETis generally inhibit PD-L1 expression; as newer BETis are evaluated in the clinic,80,81 it remains to be seen if they generate an immune response.
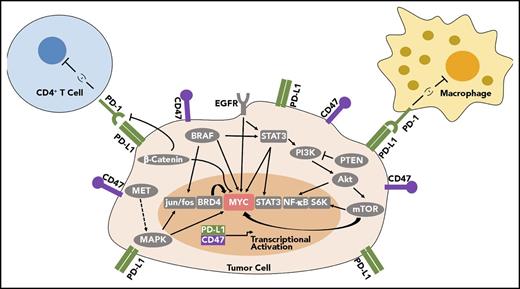
Multiple oncogenes have been shown to regulate the expression of immune checkpoints, including EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, β-catenin, and STAT3, as can tumor suppressive gene products, such as PTEN82-89 (Table 1; Figure 2). NF-κB signaling, which can drive many inflammatory-based cancers, also may regulate PD-L1.74 The AKT/mTOR pathway has also been found to regulate PD-L1 in lung cancer.90 In acute myeloid leukemia, the microRNA, miR-34a, is inversely correlated with PD-L1 expression, and AKT expression elevated PD-L1.91 Blocking CDK5 also lowers PD-L1, inducing an antitumor immune response.92 In erlotinib-resistant NSCLC with amplified MET, targeted inhibition of MET decreased gene and protein expression of PD-L1, and inhibition of downstream MAPK also decreased PD-L1.93 Oncogenic RAS signaling via MEK regulates PD-L1 expression.94 RAS signaling regulates PD-L1 via AU-rich elements in the 3′ untranslated region of PD-L1 transcripts. The AU-rich elements–binding protein tristetraprolin negatively regulates PD-L1 expression. Restoring TPP activity lowered PD-L1 expression and enhanced the antitumor immune response.94 Activation of the RAS pathway is associated with PD-L1 upregulation in human tumors.94 Corresponding therapies targeting oncogenes can stimulate an immune response, including BRAF,95-97 β-catenin,98,99 HER2,100 sonic hedgehog,101 and SNAI1.102 Hence, oncogenic pathways regulate immune checkpoints such as PD-L1 (Figure 2), and targeting these pathways may therapeutically contribute to tumor regression by restoring an immune response to cancer.
Cancer genes known to influence PD-L1 expression
| Gene . | Function . | Relation to MYC . | Refs. (relation to MYC) . | Refs. (induce PD-L1 expression) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYC | Oncogene | N/A | N/A | 44,45 |
| BRD4 | Oncogene | Epigenetic regulator | 110 | 71 |
| RAS | Oncogene | Upstream | 111,112 | 94 |
| NF-kB | Proproliferative | Upstream, downstream | 113 | 74 |
| AKT | Oncogene | Upstream | 114,115 | 90,91 |
| CDK5 | Oncogene | Upstream | 116 | 92 |
| MET | Oncogene | Upstream | 117,118 | 93 |
| MAPK | Oncogene | Upstream | 119,120 | 93 |
| EGFR | Oncogene | Upstream | 121 | 83 |
| ALK | Oncogene | Upstream | 122 | 85 |
| STAT3 | Oncogene | Upstream, downstream | 123 | 46,124 |
| PTEN | Tumor suppressor | Upstream | 125-128 | 82,86 |
| P53 | Tumor suppressor | Upstream, downstream | 129-131 | 132,133 |
| Gene . | Function . | Relation to MYC . | Refs. (relation to MYC) . | Refs. (induce PD-L1 expression) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYC | Oncogene | N/A | N/A | 44,45 |
| BRD4 | Oncogene | Epigenetic regulator | 110 | 71 |
| RAS | Oncogene | Upstream | 111,112 | 94 |
| NF-kB | Proproliferative | Upstream, downstream | 113 | 74 |
| AKT | Oncogene | Upstream | 114,115 | 90,91 |
| CDK5 | Oncogene | Upstream | 116 | 92 |
| MET | Oncogene | Upstream | 117,118 | 93 |
| MAPK | Oncogene | Upstream | 119,120 | 93 |
| EGFR | Oncogene | Upstream | 121 | 83 |
| ALK | Oncogene | Upstream | 122 | 85 |
| STAT3 | Oncogene | Upstream, downstream | 123 | 46,124 |
| PTEN | Tumor suppressor | Upstream | 125-128 | 82,86 |
| P53 | Tumor suppressor | Upstream, downstream | 129-131 | 132,133 |
Expression of many oncogenes, and loss of select tumor suppressors, can influence PD-L1 expression. These are tabulated along with their possible influence on MYC signaling.
N/A, not applicable; Refs., references.
MYC can regulate PD-L1 and CD47 immune checkpoint expression. MYC regulates PD-L1 and CD47 mRNA and protein expression in tumor cells. Many other oncogene signaling pathways have been shown to regulate PD-L1, which may also occur through MYC. BRD4, BRAF, EGFR, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and β-catenin also have been shown to influence PD-L1 expression, and all these gene products are known to regulate MYC mRNA, protein expression, and/or protein stability.
MYC can regulate PD-L1 and CD47 immune checkpoint expression. MYC regulates PD-L1 and CD47 mRNA and protein expression in tumor cells. Many other oncogene signaling pathways have been shown to regulate PD-L1, which may also occur through MYC. BRD4, BRAF, EGFR, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and β-catenin also have been shown to influence PD-L1 expression, and all these gene products are known to regulate MYC mRNA, protein expression, and/or protein stability.
One possible unifying mechanism is that these oncogenic pathways are known to regulate MYC expression and/or protein stability, which could be how they regulate the expression of PD-L1 and other immune checkpoints (Figure 2; Table 1). MAPK, KRAS, BRAF, EGFR, BRAF, β-catenin, AKT/mTOR, and PTEN have all been shown to regulate MYC mRNA or protein expression and/or protein stability.103-105 Thus, MYC may be responsible for much of the effect of these oncogenic signaling pathways on the immune response.
Conclusions
MYC appears to play an important role in globally regulating the immune response to cancers. MYC overexpression results in tumors evading immune response, an essential “hallmark of cancer.”106 Therapeutic manipulation of MYC or genes in the MYC pathway may have efficacy not only directly on tumor cells, “tumor cell–intrinsic mechanisms,” but also by recruiting the immune response, “host-immune–dependent mechanisms” (Figure 2). Thus, upon MYC inactivation, tumor cells undergo proliferative arrest and apoptosis independent of the host immune response (Figure 1 left panel), but complete elimination of the tumor may arise because there is activation of the immune system (Figure 1 center panel); this in turn may lead to the direct elimination of tumor cells but also the induction of senescence of remaining cancer cells and the shutdown of angiogenesis (Figure 1 right panel).
The activation of the host-immune–dependent response to MYC inactivation likely occurs through many mechanisms (Figure 1). MYC inactivation results in the downregulation of CD47 and PD-L1, and this is turn is required to recruit CD4+ T cells and macrophages and to remodel the tumor microenvironment associated with cellular senescence of the tumor cells and the shutdown of host angiogenesis (Figure 1). Additional mechanisms are very likely involved.
MYC is likely to regulate other immune checkpoints. Death of tumor cells through apoptosis as well as through immunogenic cell death may in itself contribute to the immune response of innate immune cells. Other innate and adaptive immune effectors, such as NK cells (Srividya Swaminathan and D.W.F., unpublished data) and B cells (S.C.C. and D.W.F., unpublished data), are likely important. Many cytokines in addition to interferon and TSP-1 may be essential. The final phase of tumor elimination likely involves the recruitment of an antigen-dependent immune response through collaboration between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and B cells as well as the production of other cytokines. Future studies will be required to determine exactly what immune effectors are involved, define if this is a general mechanism across different kinds of cancer, and evaluate if the effects associated with other oncogenic pathways are mediated through the MYC oncogene.
Another consideration is that it is not clear whether it is only “oncogenic” levels of MYC and other gene products that result in the induction of immune checkpoints like PD-L1. Is this a pathologic mechanism or is it an exaggeration of a physiologic mechanism? We think it is more likely that MYC and other oncogenes regulate immune checkpoints through a physiologic mechanism. This is likely required to prevent rapid normal proliferation from inadvertently eliciting an autoimmune response during normal growth and proliferation, for example, during an immune response, wound healing, or development.
MYC mRNA and protein expression levels may predict which patients will respond to immune checkpoint inhibition. The measurement of PD-L1 protein expression is not a good predictor of the clinical response to anti-PD-L1 therapy. In contrast, the measurement of mismatch repair deficiency appears to be a good predictor of therapeutic response.107,108 Attempts to identify patients that will respond favorably to checkpoint inhibition have been challenging. Defects in mismatch repair are most likely to confer sensitivity to immune checkpoints by increasing the number of neoantigens.107 Thus, it might be expected that more direct measurement of neoantigen load, or presence of high levels of type 1 T helper chemokines, low “stemness,” and low levels of suppressive populations may also be predictors of clinical response.107
Therapeutically targeting the MYC pathway may be a new way to restore the immune response against cancers. To date, MYC remains the elusive Achilles heel of cancer targets.109 Observations that MYC is an important regulator of the immune response should encourage interest in developing therapies that target this oncogene that is central to cancer biology. Existing therapies that can target the MYC pathway should be evaluated for their ability to restore an immune response.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Cancer Research Institute Clinic and Laboratory Integration Program grant, National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute (NCI) grants U01CA188383 and R01CA208735, and internal Stanford funding from SPARK, by an NIH National Research Service Award for Individual Postdoctoral Fellows from the NCI (1F32CA177139) (S.C.C.), and the NIH Stanford University Cellular and Molecular Immunobiology Training Grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (5 T32AI07290) (S.C.C.).
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Authorship
Contribution: S.C.C. and D.W.F. wrote the review; and V.B. assisted in writing the review and prepared the figures.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Dean W. Felsher, Stanford University School of Medicine, CCSR 1105B, 269 Campus Dr, Stanford, CA 94305-5151; e-mail: dfelsher@stanford.edu.