Abstract
INTRODUCTION: The human B-Cell maturation antigen (BCMA) is a surface marker that is highly expressed on plasma cells and has been recognized as a novel target in multiple myeloma (MM). TNB-383B is a fully human bispecific monoclonal IgG4 antibody. TNB-383B consists of 2 heavy and 1 light chain(s) paired through knob-in-hole technology. The first heavy chain and a kappa light chain form the paratope to recognize and bind human CD3. The second heavy chain is comprised of two identical VH domains in sequence and targets human BCMA with high affinity and avidity. Herein, we describe the ability of TNB-383B to mediate killing of patient-derived tumor cell lysis by endogenous T-cells was assessed ex vivo.
METHODS: Bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMCs) were isolated by density gradient centrifugation from 7 relapsed MM patients enrolled in an IRB-approved biospecimen collection protocol. Freshly isolated BMMC subsets were characterized by flow cytometry, specifically plasma cell (PC) / cytotoxic T cell (CTL) distribution, PC BCMA expression and PC viability were determined. BMMCs were then incubated for 24h (± 2h) with TNB-383B, or negative control, at concentrations ranging from 0.001-1μg. Following incubation, PC lysis, viability, BCMA expression, as well as CTL distribution and degranulation were assessed by flow cytometry. Tukey's sequential trend test was performed for each measured variable, utilizing ANOVA models and contrast statements, to detect linear dose response trends to TNB-383B or negative control treatments. Additionally, a parametric model (EMax) was used for each measured variable to estimate dose response curves, interpolating between tested doses. Two-way factorial ANOVA was utilized to compare the main effects of E:T ratio (or PC phenotype) and dose level and the interaction effect between E:T ratio and dose level on measured variables.
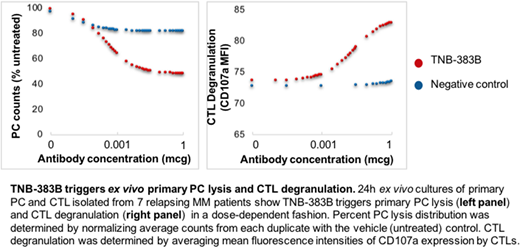
RESULTS: Dose-dependent PC lysis was triggered by TNB-383B at concentrations as low as 0.001μg (p=0.0102) while no significant loss of PC was observed with negative control (Figure). This effect was coupled with significant CTL degranulation as expressed by increased CD107a mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) specific to TNB-383B treatment (p=0.0153 at 1μg). Although apoptotic rates (7-AAD+, Annexin V+) of the remaining PC tend to increase among TNB-383B treated compared with isotype control-treated cells, this trend was not significant. As opposed to CTL degranulation, CTL proliferation was not significantly triggered by TNB-383B but was significantly increased when BMMCs were exposed to negative control antibody (p=0.0057 at 0.001 μg). BMMC containing effector to target (E:T) ratio >10 contained lower viable (7-AAD-) PC and higher apoptotic PC counts compared with BMMC specimen with E:T ratio <10 (p<0.001). Using CD45 expression as a surrogate marker of PC maturation and BCMA expression, CD45+ PC displayed higher BCMA expression than CD45- PC (p=0.0189) and were more sensitive TNB-383B-induced killing (p<0.001). Noticeably, overall BCMA expression pre/post TNB-383B exposure remained unaltered.
CONCLUSION: Taken together, our findings demonstrate TNB-383B triggers primary PC lysis and CTL degranulation in a dose-dependent fashion ex vivo. The ex vivo bispecific monoclonal antibody assay employed in this study allowed us to identify underlying biological drivers of PC killing efficacy by TNB-383B and may provide a valuable preclinical platform to screen bispecific antibodies and clinical platform to identify mechanism of primary or acquired resistance to the drug. Enrollment of patients with relapsed/refractory MM into a phase I clinical trial with TNB-383B is expected in early 2019.
Foureau:Teneobio Inc.: Research Funding. Pham:Teneobio Inc.: Employment. Force Aldred:Teneobio Inc.: Employment. Buelow:Teneobio Inc.: Employment. Voorhees:Oncopeptides: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: served on an IRC; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: served on an IRC; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: served on an IRC; Amgen Inc.: Speakers Bureau; TeneoBio: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Usmani:Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Genmab, Merck, MundiPharma, Janssen, Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Janssen, Merck, Pharmacyclics,Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Takeda: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal