Abstract
Background: We have previously reported initial high response rates of the BRAF inhibitor, vemurafenib, in patients (pts) with relapsed or refractory (R/R) hairy cell leukemia (HCL) treated in the United States (Tiacci and Park et al. N Engl J Med 2015). However, follow-up duration of the study was short (median, 11.7 months) and outcome of the pts who relapsed after vemurafenib remains largely unknown. Herein, we report the updated results of 36 pts from the completed clinical trial in the U.S. (NCT01711632) with a longer follow-up duration with analysis on the rates and timing of relapse as well as outcomes after retreatment with vemurafenib.
Methods: In the U.S. phase II clinical trial, adult pts with R/R HCL received vemurafenib 960mg bid monotherapy for 3-6 months. Vemurafenib dose reductions were allowed for drug-related adverse events (AEs). During subsequent follow-up, pts with relapsed disease were allowed to be retreated with vemurafenib at doses ranging from 240mg bid to 960mg bid at the discretion of treating physician based on prior tolerability information. The primary objective was to evaluate overall response rates (ORR) of vemurafenib in R/R HCL, as assessed by the rate of complete remission (CR) and partial remission (PR). CR was defined as normalization of any organomegaly and cytopenia with a morphologic absence of hairy cells in the blood and bone marrow (BM). PR was defined as a normalization of cytopenia with ≥50% reduction in organomegaly and BM hairy cells. Patients with normalization of cytopenia without confirmatory BM were classified as complete hematologic remission (CHR). Secondary objectives included assessment of duration of response and efficacy of vemurafenib at retreatment.
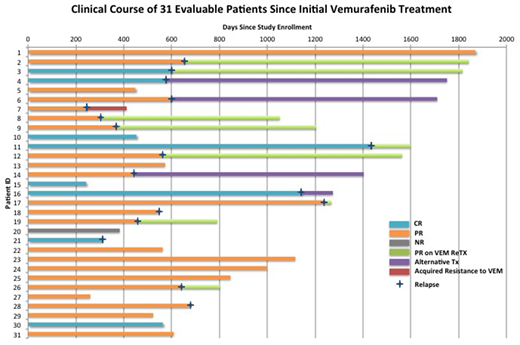
Results: A total of 36 pts were enrolled to the study; 32 pts completed at least 4 weeks of treatment and are evaluable for response, and 4 pts discontinued therapy before 4 weeks due to toxicity (n=2), infection (n=1) and patient request (n=1). The ORR was 86% (31/36 pts), including 33% CR (12/36) and 53% PR (19/36). With a median follow-up of 24 months (range, 1-64 months), 18 pts (50%) experienced relapse (Figure). The median time to relapse was 19.5 months (range, 8.0-45.7 months). Among the 18 pts with relapse, 13 pts (72%) received retreatment with vemurafenib, 4 pts (22%) received alternative treatments, and 1 pt (6%) received supportive care. Eleven of the 13 pts (85%) retreated with vemurafenib at relapse achieved PR/CHR and 1 pt developed acquired resistance to vemurafenib with KRAS mutation. Vemurafenib retreatment was well-tolerated but the majority (62%) of pts received a reduce dose of 240mg bid (n=5) or 480mg bid (n=3) with a median duration of therapy of 7 months (range, 1.5-39 months). The most common drug-related AEs during vemurafenib retreatment were similar to the initial treatment and included arthralgia (38%) and rash (23%), all of which were grade 1 or 2, except one case of grade 3 rash. During the entire follow-up period of all pts, cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) developed in 5 pts (14%) and cutaneous basal cell carcinoma (BCC) developed in 1 pt (3%), 4 of whom had a prior history of SCC (n=1), BCC (n=1), BCC/melanoma in situ (n=1) and actinic keratosis (n=1). All these cases were managed by simple excision.
Conclusion: With a longer follow-up duration of up to 64 months, we confirm the high response rates with vemurafenib monotherapy in pts with R/R HCL and a favorable safety profile. While relapses were common, all cases of relapse retained BRAF V600E mutation and acquired resistance to vemurafenib was rare, observed in only 1 pt with KRAS mutation. Re-treatment with vemurafenib at relapse was highly effective with 85% ORR confirming the retained high sensitivity of HCL to repeated BRAF inhibition. Based on the high anti-tumor efficacy and tolerability of BRAF inhibition with vemurafenib, we are now investigating the combination of vemurafenib and an anti-CD20 antibody, obinutuzumab, as a frontline therapy in a phase II trial in pts with previously untreated HCL (NCT03410875).
Park:AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; Shire: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy. Altman:Bayer: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Boeringer Ingelheim: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Epizyme: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Incyte: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Cyclacel: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Syros: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Ariad: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Genetech: Other: Payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Agios: Other: Payment to the institution to conduct the trial ; Astellas Pharma: Other; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; FujiFilm: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Celator: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; Pfizer: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; GSK: Other: payment to the institution to conduct clinical trial work; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Immune Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Rai:Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche/Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cellectis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Tallman:Daiichi-Sankyo: Other: Advisory board; AROG: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Cellerant: Research Funding; BioSight: Other: Advisory board; Orsenix: Other: Advisory board; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal