Key Points
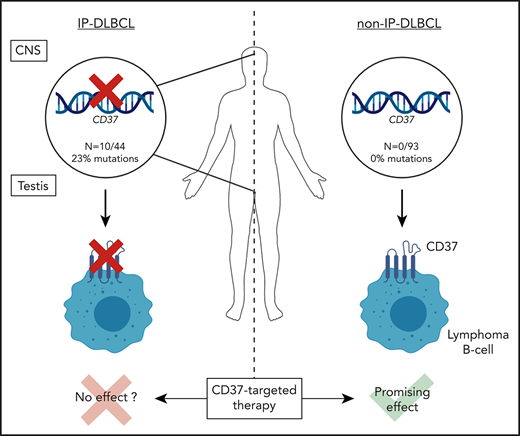
Loss-of-function mutations in CD37 occur predominantly in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma at immune-privileged sites.
CD37-mutated lymphoma B cells show impaired CD37 cell-surface localization, which may have implications for anti-CD37 therapies.
Abstract
Tetraspanin CD37 is predominantly expressed on the cell surface of mature B lymphocytes and is currently being studied as novel therapeutic target for B-cell lymphoma. Recently, we demonstrated that loss of CD37 induces spontaneous B-cell lymphoma in Cd37-knockout mice and correlates with inferior survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Here, CD37 mutation analysis was performed in a cohort of 137 primary DLBCL samples, including 44 primary immune-privileged site-associated DLBCL (IP-DLBCL) samples originating in the testis or central nervous system. CD37 mutations were exclusively identified in IP-DLBCL cases (10/44, 23%) but absent in non-IP-DLBCL cases. The aberrations included 10 missense mutations, 1 deletion, and 3 splice-site CD37 mutations. Modeling and functional analysis of CD37 missense mutations revealed loss of function by impaired CD37 protein expression at the plasma membrane of human lymphoma B cells. This study provides novel insight into the molecular pathogenesis of IP-DLBCL and indicates that anti-CD37 therapies will be more beneficial for DLBCL patients without CD37 mutations.
Introduction
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Several genetic aberrations are known to underlie DLBCL development and progression. Recently, we identified that Cd37-knockout mice spontaneously develop B-cell lymphoma.1 Moreover, CD37 protein expression has been reported to be an independent prognostic factor for patient outcome in R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone)-treated DLBCL patients.2
CD37 (Tspan-26), a member of the tetraspanin superfamily, is highly expressed on mature B lymphocytes3 and is currently studied as novel target for chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy4 and antibody-based therapies for patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.5,6 Tetraspanins control the spatial distribution of membrane proteins through specific interactions with (immune-)receptors and signaling molecules, thereby facilitating intracellular signaling pathways.7,8 Tetraspanins are associated with different malignancies,9 but the role of altered tetraspanin function in DLBCL pathogenesis is unclear.
This study evaluated the mutational status of the human CD37 gene in DLBCL patients, particularly in DLBCL at immune-privileged sites (IP-DLBCL), including primary testis lymphoma (PTL) and primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). With functional analysis, the effect of identified CD37 mutations on CD37 protein expression at the cell membrane was studied.
Study design
Cases
The study was conducted with 137 archived primary DLBCL samples, including 44 IP-DLBCL. The discovery cohort included 31 DLBCL samples and 106 DLBCL samples were analyzed in the validation cohort. Samples were collected from multiple Dutch university hospitals (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood Web site).
Mutation analysis
CD37 mutation analysis of the discovery cohort was performed by amplicon-based sequencing with Ion Torrent and Sanger sequencing. For the validation cohort, single-molecule molecular inversion probe mutation analysis and sequencing with Ion Torrent included the CD37 gene and hotspot loci of CARD11, CD79A, CD79B, and MYD88.
Functional analysis of mutant CD37
The CD37-Gly88Asp-green fluorescent protein (GFP) and CD37-Gly65Glu-GFP mutant constructs were generated by introducing point mutations c.263G>A or c.194G>A in hCD37-wild-type (WT)-GFP1 using site-directed mutagenesis. Human BJAB and OCI-Ly8 lymphoma B cells were transfected with the AMAXA Nucleofector or the Neon transfection system and analyzed for CD37 protein expression and subcellular localization using western blot and confocal fluorescence microscopy.
Additional experimental details are provided in supplemental Materials and methods.
Results and discussion
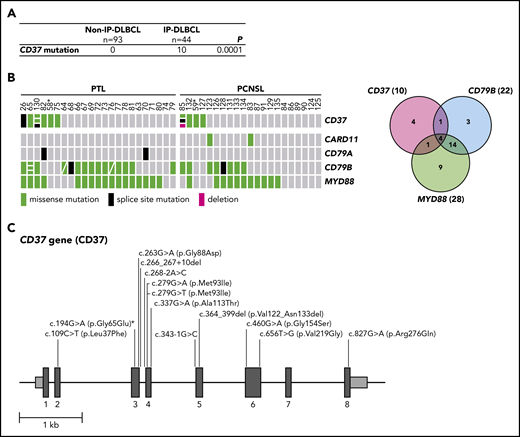
In a discovery cohort of 31 DLBCL cases, including 5 PTL cases, CD37 mutations were analyzed. CD37 mutations were identified in 2 PTL cases, 1 harboring a missense mutation (c.263G>A (p.Gly88Asp)) and the other a splice-site mutation (c.343-1G>C), but none were identified in the non-IP-DLBCL samples (n = 26). To confirm this finding, a validation cohort consisting of 39 IP-DLBCL cases (18 PTL and 21 PCNSL) and 67 non-IP-DLBCL cases was analyzed for CD37 mutations along with CARD11, CD79A, CD79B, and MYD88 hotspot mutations (Figure 1; supplemental Table 2). In this analysis, we also included the 5 PTL cases from the discovery cohort. Besides confirmation of the 2 initially identified CD37 mutations, we uncovered 12 additional mutations (variant allele frequency 5.7% to 49%; Figure 1B-C). Intriguingly, all CD37 mutations were exclusively present in IP-DLBCL cases (n = 10/44, 23%); and none were present in the non-IP-DLBCL cases (n = 0/93; Fisher’s exact test, P = .0001; Figure 1A). Mutation rates of frequently affected genes CARD11 (5%), CD79A (5%), CD79B (50%), and MYD88 (64%) in our cohort (Figure 1B; supplemental Table 2) were in line with other DLBCL studies.10,,-13 Whole-genome and exome sequencing studies of DLBCL report low mutation frequencies of CD37, ranging from no mutations to 8%.11,14,,-17
High frequency of mutated CD37 in IP-DLBCL. (A) Frequency of CD37 mutations in non-IP-DLBCL vs IP-DLBCL. The total number of lymphoma cases for each group is indicated. Numbers in the CD37 mutation row indicate the number of lymphoma cases carrying ≥1 CD37 mutation. P values were obtained using the Fisher’s exact test. (B) OncoPrint (left) and Venn diagram (right) show the frequencies of CD37, CARD11, CD79A, CD79B, and MYD88 mutations in all IP-DLBCL cases studied (23 PTL and 21 PCSNL). Columns show individual tumors. Asterisk indicates samples from the same patient containing the CD37 germline mutation. Genetic details per mutation can be found in supplemental Table 2. Green, missense mutation; black, splice-site mutation; magenta, deletion; gray, no mutation. (C) Schematic representation of mutations detected in the CD37 gene. Dark gray boxes represent the coding sequence of CD37, light gray boxes are the noncoding sequence before exon 1 (begin) and after exon 8 (end), and black lines represent introns. Asterisk indicates the CD37 germline mutation.
High frequency of mutated CD37 in IP-DLBCL. (A) Frequency of CD37 mutations in non-IP-DLBCL vs IP-DLBCL. The total number of lymphoma cases for each group is indicated. Numbers in the CD37 mutation row indicate the number of lymphoma cases carrying ≥1 CD37 mutation. P values were obtained using the Fisher’s exact test. (B) OncoPrint (left) and Venn diagram (right) show the frequencies of CD37, CARD11, CD79A, CD79B, and MYD88 mutations in all IP-DLBCL cases studied (23 PTL and 21 PCSNL). Columns show individual tumors. Asterisk indicates samples from the same patient containing the CD37 germline mutation. Genetic details per mutation can be found in supplemental Table 2. Green, missense mutation; black, splice-site mutation; magenta, deletion; gray, no mutation. (C) Schematic representation of mutations detected in the CD37 gene. Dark gray boxes represent the coding sequence of CD37, light gray boxes are the noncoding sequence before exon 1 (begin) and after exon 8 (end), and black lines represent introns. Asterisk indicates the CD37 germline mutation.
The CD37 mutations identified in the validation cohort were detected in 8 IP-DLBCL cases and included 9 missense mutations (c.109C>T (p.Leu37Phe), c.194G>A (p.Gly65Glu) [twice], c.279G>A (p.Met93Ile), c.279G>T (p.Met93Ile), c.460G>A, (p.Gly154Ser), c.656T>G (p.Val219Gly), c.337G>A (p.Ala113Thr), and c.827G>A (p.Arg276Gln)), 1 in-frame deletion (c.364_399del (p.Val122_Asn133del)), and 2 splice-site mutations (c.266_267+10del, c.268-2A>C) (Figure 1C; pathogenicity scores are listed in supplemental Table 2). Within 1 patient, missense mutation c.194G>A (p.Gly65Glu) was detected in 2 primary lymphoma specimens as well as healthy control tissue, but not described as a single-nucleotide polymorphism, indicating the presence of a CD37 germline mutation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported CD37 germline mutation in humans.
To determine the effect of splice-site mutation c.343-1G>C, complementary DNA of this DLBCL sample was sequenced, which revealed an 11-bp deletion (supplemental Figure 1). This resulted in a frameshift in the CD37 mRNA sequence, leading to a completely altered protein after transmembrane domain 3. Based on previous studies on tetraspanin CD81 in B cells,18 this mutation is predicted to result in a nonfunctional CD37 protein, since the essential extracellular domain 2 is truncated.19 Next, the CD37 missense mutations and in-frame deletion were mapped onto the reported crystal structure of tetraspanin CD8120 (supplemental Figure 2). Deletion c.364_399del (p.Val122_Asn133del) disrupts an important structural element of extracellular domain 2, namely the A helix, and is therefore also predicted to result in a nonfunctional CD37 protein.19
To further assess whether the observed missense mutations resulted in CD37 loss of function, we introduced 2 of the identified CD37 mutations, c.263G>A (p.Gly88Asp) and c.194G>A (p.Gly65Glu), in human lymphoma B cells using a GFP expression vector. WT CD37 protein appeared as 50- to 75-kDa bands on western blot (Figure 2A-B; supplemental Figure 3A) due to heavy glycosylation. Protein isoforms with the highest glycosylation state (±70 kDa) were less pronounced in lymphoma B cells expressing mutant CD37-Gly88Asp-GFP (Figure 2A), and CD37-Gly65Glu-GFP showed a lower-molecular-weight band on western blot indicating a glycosylation defect (Figure 2B). Total CD37-GFP protein levels of both mutants were similar to CD37-WT-GFP (Figure 2A-B).
Mutations in CD37 cause aberrant CD37 glycosylation and localization. Western blot analysis of CD37 protein expression in BJAB lymphoma B cells transfected with CD37-WT-GFP, CD37-Gly88Asp-GFP (A), or CD37-Gly65Glu-GFP (B). Blots were probed with α-GFP to detect CD37-GFP expression (50-75 kDa; upper blot). α-Tubulin was used as a loading control (lower blot). Protein expression level of CD37-mutant-GFP was normalized to CD37-WT-GFP for each experiment (n = 3). ns, not significant (P = .73 [left], P = .96 [right]), paired t test. (C) Confocal microscopy images of BJAB cells expressing CD37-WT-GFP and CD37-Gly88Asp-GFP or CD37-Gly65Glu-GFP (green) costained for MHC-I (red) to identify the plasma membrane. Overview images (top) and single-cell images (bottom left) show representative cells of 3 independent experiments for both CD37-WT-GFP and CD37-mutant-GFP. Scale bar, 10 µm. Ratio between membrane and cytoplasmic GFP expression was quantified from 10 representative cells of 3 independent experiments. *P = .023 (left), P = .011 (right), paired t test. All data represent mean ± standard error of the mean.
Mutations in CD37 cause aberrant CD37 glycosylation and localization. Western blot analysis of CD37 protein expression in BJAB lymphoma B cells transfected with CD37-WT-GFP, CD37-Gly88Asp-GFP (A), or CD37-Gly65Glu-GFP (B). Blots were probed with α-GFP to detect CD37-GFP expression (50-75 kDa; upper blot). α-Tubulin was used as a loading control (lower blot). Protein expression level of CD37-mutant-GFP was normalized to CD37-WT-GFP for each experiment (n = 3). ns, not significant (P = .73 [left], P = .96 [right]), paired t test. (C) Confocal microscopy images of BJAB cells expressing CD37-WT-GFP and CD37-Gly88Asp-GFP or CD37-Gly65Glu-GFP (green) costained for MHC-I (red) to identify the plasma membrane. Overview images (top) and single-cell images (bottom left) show representative cells of 3 independent experiments for both CD37-WT-GFP and CD37-mutant-GFP. Scale bar, 10 µm. Ratio between membrane and cytoplasmic GFP expression was quantified from 10 representative cells of 3 independent experiments. *P = .023 (left), P = .011 (right), paired t test. All data represent mean ± standard error of the mean.
Next, the subcellular localization of the CD37 mutants was determined using confocal microscopy. Lymphoma B cells expressing the CD37-GFP mutants had significantly lower cell membrane expression and more retention of intracellular CD37 protein than cells expressing CD37-WT-GFP (Figure 2C; supplemental Figure 3B). Moreover, CD37-Gly88Asp had a dominant-negative effect on the membrane expression of CD37-WT protein (supplemental Figure 4). These data indicate that these missense mutations result in defective glycosylation and trafficking of CD37 in human lymphoma B cells, which corresponds to the reported role of glycosylation as a sorting signal for protein transport to the plasma membrane.21 Moreover, modification of cell-surface proteins by defective glycosylation frequently contributes to cancer development by enhancing invasive growth and tumor cell migration.22
We previously showed that loss of CD37 results in increased interleukin-6 signaling and STAT3 activation,1 which are both known to be involved in the pathogenesis of hematological malignancies.23 MYD88 mutations also stimulate cell survival by promoting JAK/STAT3 signaling and interleukin-6 secretion, suggesting a similar phenotype.24 As proposed for MYD88 and CD79B mutations in IP-DLBCL,12 mutations in CD37 could therefore provide a survival advantage in the otherwise stimulus-poor environment of immune-privileged sites.
Seven out of 9 evaluable cases with a CD37 mutation did not express CD37 protein (supplemental Figure 5 and supplemental Table 1). Since immunohistochemistry does not distinguish between cell-surface and cytosolic expression, the importance of CD37 in DLBCL biology1,2 is likely underestimated. Moreover, the recent identification of loss of CD19 expression as a mechanism underlying disease relapse upon CD19 CAR-T cell therapy25 emphasizes the need to investigate CD37 surface expression in hematologic malignancies prior to the use of novel CD37 CAR-T cell therapies.
In conclusion, inactivating CD37 mutations occur predominantly in IP-DLBCL and lead to aberrant CD37 cell-surface expression. This study provides novel molecular insight into DLBCL at immune-privileged sites and indicates that CD37-based therapies are more likely to be beneficial for DLBCL patients that harbor no CD37 mutations.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Piet Gros (Department of Chemistry, Utrecht University) for his valuable help with the modeling studies and Shannon van Lent-van Vliet and Sanne Sweegers (Department of Pathology, Radboudumc) for their valuable help with the single-molecule molecular inversion probe analysis. The authors apologize to all authors whose work could not be cited due to space limitations.
S.E. is supported by a Radboudumc grant. C.M.d.W. is supported by a Rubicon Fellowship from The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (019.162LW.004). J.V., A.C., and R.G. are supported by research funding from Stichting Fonds Oncologie Holland. A.B.v.S. is recipient of a Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research grant (NWO-ALW VIDI grant 864.11.006), a Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research Gravitation Programme 2013 grant (ICI-024.002.009), and a Dutch Cancer Society grant (KUN2014-6845) and was awarded an European Research Council Consolidator grant (Secret Surface, 724281).
Authorship
Contribution: S.E., C.M.d.W., M.v.d.B., S.v.D., B.S., and A.B.v.S. designed the study; S.E., C.M.d.W., M.v.d.B., S.v.D., and A.B.v.S. wrote the manuscript; M.v.d.B., C.J.H., W.S., M.G.M.R., D.d.J., J.S.P.V., A.H.G.C., and B.S. collected DLBCL tissue and corresponding pathological information; S.E., C.M.d.W., M.v.d.B., E.J., A.v.d.S., S.v.D., P.J.T.A.G., A.E., R.A.L.d.G., and M.B. performed mutation analysis; S.E., F.A., L.J., and S.v.D. performed functional in vitro experiments; V.N. performed CD37 modeling studies; and J.H.v.K., S.v.D., B.S., and A.B.v.S. supervised the work.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Annemiek B. van Spriel, Department of Tumor Immunology, Radboud Institute for Molecular Life Sciences, Radboud University Medical Center, Geert Grooteplein-Zuid 26-28, 6525 GA Nijmegen, The Netherlands; e-mail: annemiek.vanspriel@radboudumc.nl.
REFERENCES
Author notes
S.E., C.M.d.W., and M.v.d.B. contributed equally to this study.
S.v.D. and B.S. contributed equally to this study.

![Mutations in CD37 cause aberrant CD37 glycosylation and localization. Western blot analysis of CD37 protein expression in BJAB lymphoma B cells transfected with CD37-WT-GFP, CD37-Gly88Asp-GFP (A), or CD37-Gly65Glu-GFP (B). Blots were probed with α-GFP to detect CD37-GFP expression (50-75 kDa; upper blot). α-Tubulin was used as a loading control (lower blot). Protein expression level of CD37-mutant-GFP was normalized to CD37-WT-GFP for each experiment (n = 3). ns, not significant (P = .73 [left], P = .96 [right]), paired t test. (C) Confocal microscopy images of BJAB cells expressing CD37-WT-GFP and CD37-Gly88Asp-GFP or CD37-Gly65Glu-GFP (green) costained for MHC-I (red) to identify the plasma membrane. Overview images (top) and single-cell images (bottom left) show representative cells of 3 independent experiments for both CD37-WT-GFP and CD37-mutant-GFP. Scale bar, 10 µm. Ratio between membrane and cytoplasmic GFP expression was quantified from 10 representative cells of 3 independent experiments. *P = .023 (left), P = .011 (right), paired t test. All data represent mean ± standard error of the mean.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/134/12/10.1182_blood.2019001185/3/m_bloodbld2019001185f2.png?Expires=1765894404&Signature=qXTbBllKuEyZ6Z-8Gpd7FO~maCg4aIIwtLra~RxqNvGkJHOMQGujKrgT871WCI6WzsnQWWJhQv82jYueZwabVZdW7aZhykuHLpGFLV9X0GzRkI~LVeRjP28Pk71bxiBk~VRSnhjCu5RAUc9Z2NiPRdOfsDIRqywUu-wIFPIkD5L1wpo1SZa75N5mdEa4BVbFVamTD4dmOpnCiXQsWCBNBfcLqsxptcQX95lKs5v99Cww3-RWtgqjD3CDOLKibuCjDNMzFuUdvFjTZXZG9MnecwDVn9iEKJmjkghTarEMq5cvczwkYsMpwVsJq5~7029O1SOTHZ6dgS7YETW4CP0amg__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal