BACKGROUND
In DLBCL, and mainly in advanced-stage, the presence of an activated B-cell phenotype or a non-GCB phenotype, and the coexpression of Myc and Bcl2 protein by IHC, are usually considered to be associated with inferior outcomes. Some recent studies however found that non-GCB COO did not have prognostic impact in limited stage DLBCL patients. Further, in real life patient management, the clinical relevance of the assessment of the COO, and of Myc and Bcl2 protein overexpression (DE), is still not fully clarified. The aim of the research was to evaluate in a real-life context the prognostic impact of the COO and of DE status together with R-IPI. With this purpose we have therefore evaluated 142 DLBCL patients in stage I/IV by PET-CT.
METHODS
This is a retrospective multicenter study which recruited 142 DLBC patients with PET-CT-defined stage I/IV treated with R-CHOP or R-CHOP like between 2010 and 2016 in Modena, Rome and Pisa (Italy) and Haifa (Israel). Eligible patients had a morphologic diagnosis of DLBCL.
All clinical data were recorded at diagnosis and during follow up including response assessment and survival outcome. COO was determined on FFPE diagnostic specimens either by IHC applying Hans algorithm, or at RNA level with Lymph2Cx assay by Nanostring technology. Expression of Myc and Bcl2 to define DE status was evaluated by IHC considering Myc and Bcl2 positive ≥40% and ≥50%, respectively. PET-CT imaging was interpreted locally utilizing Deauville criteria. The end points of the study were to determine the impact of COO, Myc/Bcl2 status and R-IPI on PFS and OS. PFS and OS were calculated using the Kaplan-Meyer method with 95 confidence interval (95C%CI), comparison between groups were made with logrank test. The effect of covariates was estimate by means of Cox PH regression, as hazard ratio (HR) with 95%CI. Statistical tests with P<0.10 were considered clinically interesting.
RESULTS
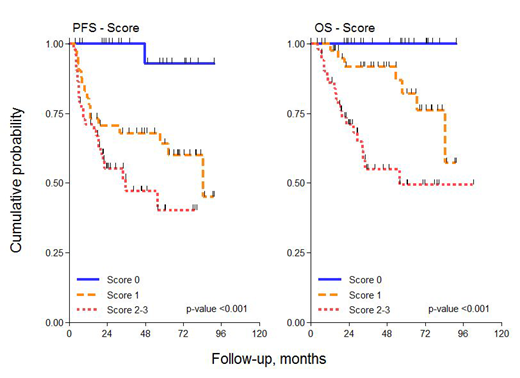
We identified 142 patients with morphological diagnosis of DLBCL and with PET-CT-defined Stage I/IV treated with R-CHOP or CHOP-like regimens between 2011 and 2018. Patients with evidence of histologic transformation from indolent lymphoma, and double-hit high grade lymphoma were excluded. Median age was 63 yrs, 55% were more than 65 yrs old, 64% had stage III/IV, and 38% had R-IPI 3-5. Bcl2 and Myc were positive in 65% and 20%, respectively. Double expression of Bcl2 and Myc was found in 20% of cases. By Lympho2Cx, COO subtypes were ABC, CGB and Unclassified in 37 %, 46 % and 16 %, respectively. We observed a good concordance between COO determined by Lympho2Cx and Hans algorithm (0.718). Analysis of association between COO subtype by Lympho2Cx and baseline characteristics showed significant association of ABC subtype with B symptoms, R-IPI 3-5, BCL2+, but not with Myc+ , end of treatment PET+, and Response. After a median follow up of 49 months, 3 yrs and 5 yrs PFS and OS were 65% and 59%, respectively in PFS and 80% and 73 % in OS. By univariable analysis we observed significant differences between R-IPI 3-5 vs 0-2, stage III-IV vs I-II, and Bcl2 + vs -. GCB and Unclassified subtypes, Myc - and DE - showed better PFS and OS in comparison with ABC subtype, Myc + and DE +, but the differences were not statistically significant. Forty-seven of the 142 patients underwent SNC prophylaxis with MTX IT or IV. While in patients who received consolidation treatment no difference in PFS or OS between GCB and ABC were observed, patients with GCB subtype showed better PFS and OS in comparison with ABC patients (P=0.05). Based on the results of the univariable analysis, we have assembled a Score from 0 to 3 with R-IPI 3-5 (weight 1), Bcl2 + (weight 1) and ABC subtype (weight 1). The differences in 5 yrs PFS and OS between Score 0, 1, 2-3 were statistically significant (Fig 1).
Discussion
Although COO is considered a relevant prognostic factor, several studies have produced conflicting results. Our retrospective study conducted on a relatively small group of cases shows that patients with GCB and Unclassified subtypes and DE have a moderately improvement of survival outcome. However, a score based on ABC subtype, Bcl2 overexpression and a high R-IPI score is able to identify a group of poor prognosis patients. As determination of COO by Lympho2Cx is rapid to perform and potentially applicable to clinical practice as well as the determination of Bcl2 and Myc protein expression by IHC, we believe that the use of the Score is useful in patient management in the real life context.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal