Hydroxyurea is usually the first line treatment for high-risk polycythemia vera (PV) and essential thrombocythemia (ET), but interferon is an equally effective treatment. However, unlike hydroxyurea, several studies have shown higher rate of molecular response with pegylated interferon-alpha (PegINFa) and tolerable toxicity. We had reported earlier that in some female patients, polyclonal hematopoiesis is restored (Liu E et al, Blood, 2003) after interferon therapy. However, the mechanism of action of interferon on rescue of normal dormant hematopoiesis in PV and ET is not fully understood. Presence of immune response against PV & ET clone is long speculated and we had previously screened human testis cDNA library in plasma from a PV subject who converted to polyclonal hematopoiesis after interferon therapy, where presence of immune response were noted.
We analyzed 48 patients diagnosed with PV and ET per WHO 2012 criteria who were treated with PegINFa at our institution. The majority of patients receiving PegINFa - 28 (58%) were second-line treatments after receiving hydroxyurea. The overall hematological response rate for PegINFa treated patients was 46 (95.8%), but 14 (29%) had to discontinue due to various toxicities. Of the 48 patients, 31 had evaluable JAK2V617F allelic burden at least at 2 time points, and the overall molecular response rate was 45% (14 of 31) with a median time of 24 months. In 4 (12.9%) patients, JAK2V617F allelic burden decreased to <1% after PegINFa treatment, with a median time of 29.5 months; however, no patients achieved complete molecular remission when examined by sensitive quantitative assay (Nussenzveig RH et al, Exp Hematol 2007) and also by digital PCR.
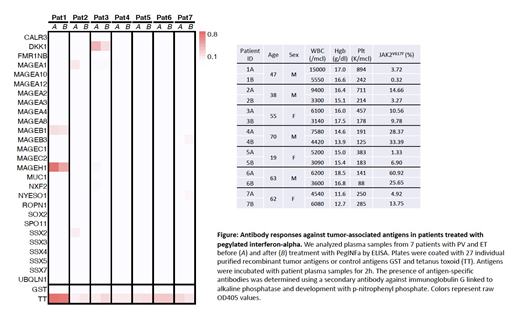
In this pilot study, using plasma samples from 7 PV patients collected before and after treatment with PegINFa, we screened for antibody responses to a panel of 16 commercially available and 11 custom generated recombinant tumor-associated antigens (TAA) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) as previously described (Luetkens T et al., Leukemia Research 2010). In brief, we coated 96-well MaxiSorp (Nunc) plates over night at 4°C with 5mg/ml recombinant protein, blocked plates in 4% non-fat milk PBS (M-PBS) and incubated antigens with patient sera diluted 1:100 in M-PBS for 2h at room temperature. Bound antibodies were detected using a secondary anti-human immunoglobulin G antibody linked to alkaline phosphatase (Southern Biotech) followed by development with p-nitrophenyl phosphate. In patients #1, #2 and #3, who showed a decrease in JAK2V617F allelic burden after PegINFa treatment, we observed antibody responses against antigens MAGEB1, MAGEH1, MAGEA1, and DKK1 before and after PegINFa treatment. In patients #4, #5 and #7, JAK2V617F allelic burden increased after PegINFa treatment, and we did not detect substantial immune responses against any antigens in our panel. In patient #6, no immune response was seen against any antigen on the panel even though there was a decrease in JAK2V617F allele burden.
These preliminary data suggest that PegINFa can induce deep molecular responses in a subset of PV and ET patients, and is associated with presence of immune responses against tumor antigens. We speculate that PegINFa may augment the efficacy of pre-existing TAA-specific immune responses against PV and ET clone. We are in the process of validating these findings in a larger cohort of PV and ET patients treated with PegINFa.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal