Cancer immunotherapy using chimeric antigen receptor-armed T cells (CAR-T cells) have shown excellent outcomes in hematological malignancies. However, cytokine release syndrome (CRS), characterized by excessive activation of CAR-T cells and macrophages remains to be overcome. Steroid administration usually resolves signs and symptoms of CRS but abrogates CAR-T cell expansion and persistence. Tocilizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody against interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R), attenuates CRS without significant loss of CAR-T cell activities, while perfect rescue of CRS symptoms cannot be achieved by IL-6/IL-6R blockade. There is actual need for novel strategies to prevent or cure CRS. TO-207, an N-benzoyl-L-phenylalanine derivative compound, significantly inhibits inflammatory cytokine production in a human monocyte/macrophage-specific manner. Here we tested TO-207 for its ability to inhibit cytokine production without impaired CAR-T cell function in a CRS-simulating co-culture system consisting of CAR-T cells, target leukemic cells and monocytes.
To observe a precise pattern of cytokine release from CAR-T cells and monocytes, we first established a co-culture system that mimics CRS using K562/CD19 cells, 19-28z CAR-T cells, and peripheral blood CD14+ cells. IFN-γ was produced exclusively from CAR-T cells, and TNF-α, MIP-1α, M-CSF, and IL-6 were produced from both CAR-T cells and monocytes, but monocytes were the major source of these cytokine production. MCP-1, IL-1β, IL-8, and IL-10 were released exclusively from monocytes.
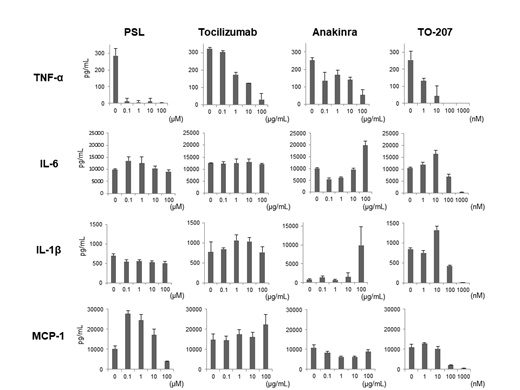
To observe the effect of drugs on cytokine production, prednisolone (PSL), TO-207, tocilizumab, and anakinra (an IL-1R antagonist) were added to the co-culture. PSL exhibited suppressive effects on TNF-α and MCP-1 production. Tocilizumab did not suppress these cytokines. Anakinra up-regulated IL-6 and IL-1β production, probably due to activation of negative feedback loops. Interestingly, TO-207 widely suppressed all of these monocyte-derived cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, MCP-1, IL-8, and GM-CSF.
Next, we observed whether the cytokine inhibition by TO-207 attenuates killing effect of CAR-T cells. PSL attenuated killing effect of CD4+ CAR-T cells and CD8+ CAR-T cells toward K562/CD19 cells. In contrast, TO-207 did not exhibit any change in cytotoxicity of CD4+ CAR-T cells and CD8+ CAR-T cells. To determine whether the effect of PSL and TO-207 on cytotoxicity changes in the presence of CD14+ monocytes, CD14+ cells were added to the co-culture. In the absence of CAR-T cells, PSL induced a modest attenuation of cytotoxicity, whereas to the CAR-T cells, PSL exhibited a significant attenuation of cytotoxicity. TO-207 exhibited a minimal effect on cytotoxicity in the absence or presence of CAR-T cells. These results suggested that CAR-T cells play a major role in the cytotoxicity toward leukemia cells, and drugs that do not affect CAR-T cell functions, such as TO-207, maintain their cytotoxic effects on leukemia cells.
In conclusion, our present co-culture model with K562/CD19 cells, 19-28z CAR-T cells, and CD14+ monocytes accurately recapitulate killing effect and cytokine release profiles. IFN-γ was produced exclusively by CAR-T cells, but majority of other cytokines such as TNF-α, MIP-1α, M-CSF, IL-6, MCP-1, IL-1β, IL-8, and IL-10 were from CD14+ monocytes/macrophages. Because killing effect was largely dependent on CAR-T cells while cytokine production was dependent on monocytes/macrophages, selective inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines from monocytes by TO-207 would be ideal for treatment of CAR-T-related CRS. These results encourage us to consider a clinical application for CRS.
Futami:Torii Pharmaceutical: Research Funding. Suzuki:Torii Pharmaceutical: Employment. Kato:Torii Pharmmaceutical: Research Funding. Tahara:Torii Pharmaceutical: Employment. Imai:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Mimura:Torii Pharmaceutical: Employment. Watanabe:Torii Pharmaceutical: Employment. Tojo:AMED: Research Funding; Torii Pharmaceutical: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal