Background: Hydroxyurea (HU) therapy in adults with sickle cell anemia (SCA) increases total hemoglobin (Hb) and percent fetal hemoglobin (HbF) levels, reduces total white cell (WBC) and neutrophil (ANC) count, and increases the mean corpuscular volume (MCV). Case management and community health workers are both evidence-based health management strategies. Patient navigators (PN) are community health workers trained specifically in case management for patients with SCA. We therefore hypothesized that HU-eligible patients exposed to patient navigators (PN) would have improved laboratory characteristics reflecting improved uptake and adherence to HU.
Methods: We enrolled 224 adult patients eligible for HU into the Start Healing in Patients with Hydroxyurea (SHIP-HU) Randomized Controlled Trial. All patients received care from trained physicians who implemented use of a standardized HU prescribing protocol using NIH guidelines. Pateints were randomized to either PN intervention (which included case management and education through home, telephone, and/or other visits from PNs) plus standard care by their treating physician (Experimental, E), or standard care by their physician alone (Control, C). Study physicians were blinded to study arm. At baseline, 6 months and 12 months we assessed: Complete Blood Count including WBC, ANC, total hemoglobin (Hb), platelet count (plt), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), and; HbF via HPLC and electrophoresis. Main analyses consisted of comparisons of the hematological variables between arms. Mixed model analysis of variance was used to analyze follow-up visits, controlling for site and baseline value of outcome variable. Any missing baseline values for subjects were imputed.
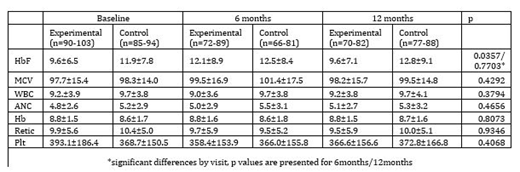
Results: 206 of 224 patients had at least one lab value at follow-up. Patients had mean age 30.1, 45.6% were male, 82.5% had been prescribed HU at baseline. HbF was higher at the 6 month visit for group E vs. group C when controlled for baseline values. Neither WBC, ANC, Hb, Hb F, Plt, nor MCV were different between groups E and C at any other time point (Table).
Conclusions: In our sample, there were no differences in hematological variables among patients who were exposed to PNs vs those who weren't. Several factors may have impacted these outcomes. HU was prescribed to 82.5% of enrolled patients at baseline, with higher % HbF than anticipated in study design. The intention to study change in % HbF as a singular marker for HU uptake and adherence did not assume high utilization of HU at baseline. We are currently analyzing data to enable comparisons between patients who were on HU at baseline and those who were not, which we believe will be able to speak to the true impact of the PN intervention. Future analyses will examine these and other factors influencing outcomes.
Smith:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Villella:Pfizer: Other: Site PI for the Rivipansel Clinical Trial; Emmaus: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Liles:Novartis: Other: PI on clinical trial Sickle cell ; Shire: Other: PI on clinical trial Sickle cell ; Imara: Other: PI on Clinical trial- Sickle cell.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal