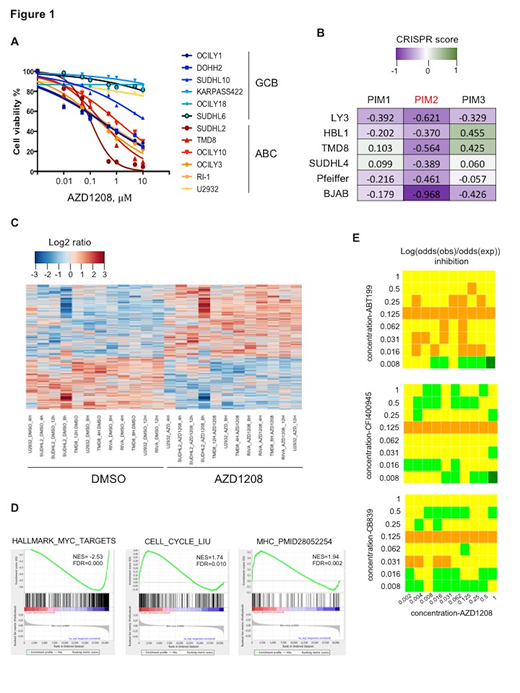
The PIM kinases are highly expressed in activated B-cell (ABC) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Oncogenic cooperation between PIMs and MYC has been demonstrated. Transgenic mice co-expressing Em-PIM and Em-MYC showed accelerated lymphomagenesis. Conversely, knockdown of PIMs dramatically decreased cMYC levels and lowered tumor incidence. Based on these preclinical data, a treatment strategy aiming at disrupting the oncogenic cooperation between PIMs and MYC may improve the outcome of DLBCL. Therefore, we treated a panel of DLBCL cell lines with increasing dose of the clinically relevant pan-PIM inhibitor (PIMi) AZD1208 (from 0.1 to 10μM) for 48 hours (Hrs), which resulted in a dose-dependent growth inhibition with a stronger efficacy in ABC DLBCL cell lines. (Figure 1A)The analysis of a CRISPR loss-of-function screening in three ABC (LY3, TMD8, HBL1) and three GCB (SUDHL-4, Pfeiffer, BJAB) DLBCL cell lines (Reddy et al, 2017) showed that PIM2 silencing led to significantly decreased viability irrespective of cell-of-origin (Figure 1B), suggesting that this oncogene is essential for cell proliferation in DLBCLs. To identify the genes through which PIMs drive the lymphoma phenotype we performed gene expression profiling using 4 ABC DLBCL cell lines (RIVA, TMD8, SUDHL-2, U2932) treated with either DMSO or AZD1208 at 1μM for 4, 8 and 12 Hrs. We observed induction of 3,439 genes whereas 2,473 genes were downregulated. (Figure 1C) Gene pathway analysis showed that AZD1208 led to downregulation of genes regulated by MYC, including its known downstream p53 and NFKB target genes. On the other hand, AZD1208 treatment broadly induced MHC class II and antigen presentation genes as well as PI3K/AKT, cell cycle and glutaminase genes. (Figure 1D) Using a high-throughput screening approach, we found that the inhibitors of cell cycle (such as the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax/ABT199 and the PLK4 inhibitor CFI-400945) and of glutaminase (CB839) enhanced the antiproliferative effect of AZD1208, whereas combinations with the PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors had negligible synergistic effect. (Figure 1E) In conclusion, our study revealed previously unknown mechanisms of action of PIM inhibitors and provides a framework for future combination strategies.
Younes:Xynomics: Consultancy; Biopath: Consultancy; Genentech: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Syndax: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; HCM: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Epizyme: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Curis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding. Bertoni:Nordic Nanovector ASA: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Bayer AG: Research Funding; Cellestia: Research Funding; CTI Life Sciences: Research Funding; EMD Serono: Research Funding; Helsinn: Consultancy, Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Research Funding; Menarini Ricerche: Consultancy, Research Funding; NEOMED Therapeutics 1: Research Funding; Oncology Therapeutic Development: Research Funding; PIQUR Therapeutics AG: Other: travel grant, Research Funding; HTG: Other: Expert Statements ; Amgen: Other: travel grants; Astra Zeneca: Other: travel grants; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: travel grants.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal