Background
In February 2019, the National Medicinal Products Administration (NMPA) approved the first China-manufactured rituximab (RTX) biosimilar, HLX01, for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in accordance to the development of biosimilar guidelines with stepwise approach demonstrating bioequivalence. HLX01 was also developed as a novel drug for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) since the indication has not been approved in China. Studying pharmacokinetics (PK) in healthy volunteers as the most sensitive population is not ethically acceptable due to the safety concerns associated with rituximab. The NMPA approval was based on a comprehensive data package of extensive analytical characterization, non-clinical studies, clinical trials and the population PK (PopPK) model. Here, we report the Phase 3 confirmatory study aimed to establish equivalence in safety and efficacy of HLX01 and RTX in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and the PopPK model derived from the PK data of HLX01 and RTX in RA compared the PK data in DLBCL and the Caucasian RTX data in RA.
Methods
In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel active-controlled, Phase 3 study (NCT02787239), treatment-naïve adults aged 18-80 years with histologically confirmed CD20+ DLBCL were treated with cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin-vincristine-prednisone (CHOP) and randomly assigned at 1:1 ratio to co-administer with HLX01 (H-CHOP) or RTX (R-CHOP) every 21 days cycle treatment. The primary efficacy endpoint was the best overall response rate (ORR) for HLX01 and RTX over 6-cycle therapy. The therapeutic equivalence was concluded if 95% confidence interval (CI) of the difference in best ORRs between the two treatments fell within the pre-specified range of ±12%. Additional endpoints included long-term efficacy outcomes, safety and immunogenicity profiles and sparse PK samplings for peak and trough levels comparison. The PopPK model was developed from the randomized, double-blind PK study (NCT03355872) of HLX01 and RTX in 196 patients with moderately to severely active RA (serum sample=4289) using non-linear mixed-effect modeling (NONMEM®) and the first-order estimation with interaction (FOCEI) method. The PK and PK-pharmacodynamic relationship being characterized with various covariates were tested on forward addition (p<0·01) / backward elimination (p<0·001). After the final model being examined with Bayesian bootstrapping, visual predictive check (VPC) and 1000 simulations from the observed covariates, external validations were tested using the Phase 3 PK data in 110 patients with DLBCL and comparing the Chinese data with other races by simulations from several published PK data in Caucasian RA patients.
Results
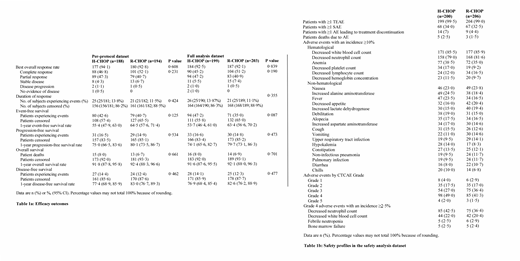
The best ORRs [95% CI] within 6 cycles therapy were 94·1% [89·77%, 97·04%] in H-CHOP and 92·8% [88·19%, 96·00%] in R-CHOP with the ORR difference (1·4% [−3·59%, 6·32%], p=0·608) fell in the pre-specified equivalent margin. Long-term efficacy and safety profiles, including the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (p=1·000) and serious adverse events (p=0·752), were similar in two treatment groups (Table 1). The best model fit for the PopPK was a two-compartment model with first-order elimination. The estimated clearance (CL), central volume (Vc), peripheral-compartment volume and clearance-of-distribution from the central-to-peripheral-compartment were 27·32%, 16·56%, 21·61%, and 40·79%, respectively. The correlation between CL and Vc was 0.02239. The observed concentrations and simulations for the corresponding model predicted all subjects in the dataset with no significant difference in area under the curve from zero to infinity between two clinical studies of HLX01 and RTX. The PK results were also similar to the existing model in Caucasian.
Conclusion
HLX01 demonstrated equivalent safety and efficacy to the reference RTX with no clinically meaningful differences in CD20+ DLBCL. The PopPK model successfully proved the PK similarity between HLX01 and RTX in patients with RA or DLBCL with no racial differences. Based on the totality of evidence with the results from this Phase 3 study and PopPK modeling, China NMPA approved HLX01 as the first China RTX biosimilar with the potential to provide alternative treatment option for patients. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first reporting the establishment of biosimilarity with RTX in DLBCL patient population.
Zhao:Certara Strategic Consulting China: Employment. Hong:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Ma:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Cheng:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Ting:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Li:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Jiang:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Liu:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Liu:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Zhang:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Chai:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Yao:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment. Luk:Shanghai Henlius Biotech, Inc.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal