
Background: The rate of complete response (CR) in multiple myeloma (MM) has dramatically increased because of the development of novel agents. In addition, the development of methods for measuring minimal residual disease (MRD), such as multiparameter flow cytometry and next-generation sequencing, has made it possible to stratify CR patients according to the MRD extent. EuroFlow next-generation flow (EuroFlow-NGF) is considered one of the gold standard methods for evaluating the negative status of MRD in MM. The automated gating strategy of EuroFlow-NGF has been shown to detect MRD as accurately as the manual gating strategy by experts. Oberle et al. (Haematologica, 2017) have found that daratumumab persisted on the surface of myeloma cells treated with it and that the anti-CD38 multi-epitope antibody used in EuroFlow-NGF has partial cross-reactivity with daratumumab, leading to generally lower mean fluorescence intensities of CD38. Therefore, MRD levels may have been underestimated in patients who were treated with anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) using the automated gating strategy, leading to inappropriate management of the patients. Because no studies have examined the correlation of MRD extent between the manual and automated gating strategies in patients with MM who have received anti-CD38 mAbs, we compared MRD detection between the two gating strategies of EuroFlow-NGF in patients with MM.
Methods: The study included bone marrow samples from 51 patients with MM (27 male and 24 female patients), including 13 patients treated with anti-CD38 mAb (12 treated with daratumumab and 1 treated with isatuximab). The median patient age was 70 years (range, 32-92 years) at MRD assessment. The disease statuses at MRD assessment were stringent CR in 26 patients (51%), CR in 7 (14%), very good partial response in 13 (26%), partial response in 1 (2%), and progressive disease in 4 (8%). The sample preparation protocol, Ab panel, and automated gating strategy of EuroFlow-NGF have been reported previously (Flores-Montero et al. Leukemia 2017). Briefly, we performed the EuroFlow-NGF method, which involved ammonium chloride-based bulk lysis, followed by surface staining using antibodies against CD138-BV421, CD27-BV510, CD38 multiepitope (ME)-FITC, CD56-PE, CD45-PerCP Cy5.5, CD19-PECy7, CD117-APC, and CD81-APC C750 in tube 1 and surface/intracellular staining using antibodies against CD138-BV421, CD27-BV510, CD38 ME-FITC, CD56-PE, CD45-PerCP Cy5.5, CD19-PECy7, CD117-APC, CD81-APC C750, cytoplasmic (cy) Igκ-APC, and cyIgλ-APC C750 after permeabilization in tube 2. For data analysis, events from both eight-color tubes (tubes 1 and 2) were merged, and the values of all parameters per tube were mathematically calculated using the merge and calculation functions of Infinicyt software (Cytognos SL, Salamanca, Spain). Automatic identification and enumeration of total plasma cells (tPCs) and abnormal plasma cells (MRD) were performed using the automatic gating function of Infinicyt software as described previously (Flores-Montero et al. Leukemia 2017). We compared the total nucleated cell number, tPC ratio, and MRD ratio between the manual (by experts) and automated gating strategies of EuroFlow-NGF.
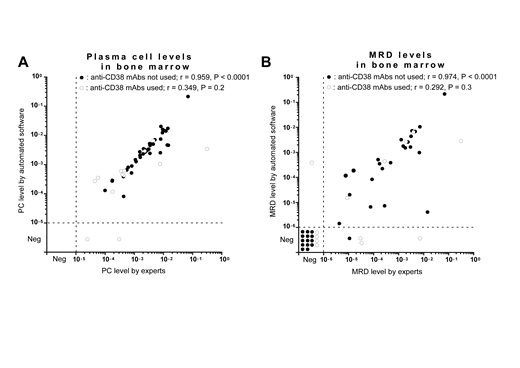
Results: In patients with MM who did not receive any anti-CD38 mAb therapy, we observed high correlations for both the tPC (r = 0.959, P < 0.0001) (Figure A) and MRD (r = 0.974, P < 0.0001) (Figure B) ratios between the manual and automated gating strategies of EuroFlow-NGF. On the other hand, in patients with MM who received anti-CD38 mAb therapy, we did not observe good correlations for both the tPC (r = 0.349, P = 0.2) (Figure A) and MRD (r = 0.292, P = 0.3) (Figure B) ratios between the two strategies owing to a lower fluorescence intensity of CD38 on PCs. In addition, when the MRD threshold was set to 10-5, the discordance of MRD positivity/negativity between the two strategies was significantly higher in patients who received anti-CD38 mAb therapy than in those who did not receive anti-CD38 mAb therapy [4/13 (31%) vs. 1/38 (3%), P = 0.012].
Conclusion: Although the automated gating strategy of EuroFlow-NGF could be a viable alternative to the manual strategy for the assessment of MRD in MM, we may have to utilize the manual strategy to obtain precise MRD results for patients with MM who received anti-CD38 mAbs.
Takamatsu:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ono pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; CSL Behring: Research Funding; SRL: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceutical: Consultancy, Honoraria; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Honoraria; Fujimoto Pharmaceutical: Honoraria; Becton, Dickinson and Company: Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy; Daiichi-Sankyo Company: Honoraria. Yoroidaka:Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria. Yamashita:Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; Daiichi-Sankyo Company: Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin: Honoraria; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd: Honoraria; TEIJIN PHARMA LIMITED: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Murata:Celgene: Honoraria; Ono pharmaceutical: Honoraria. Nakao:Daiichi-Sankyo Company, Limited: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; SynBio Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Ohtsuka Pharmaceutical: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria; Novartis Pharma K.K: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Honoraria; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd: Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin: Honoraria; Alaxion Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Matsue:Novartis Pharma K.K: Honoraria; Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal