(Text above this line is not copy/pasted in the abstract body)
INTRODUCTION
Allogeneic HCT using RIC regimens is the standard treatment for patients with relapsed/refractory cHL, however there is significant heterogeneity amongst the different regimens and a lack of data supporting a preferred RIC regimen. Using the CIBMTR database we evaluate the outcomes of the 3 most commonly used RIC regimens for cHL.
METHODS
In the CIBMTR registry, 492 adult patients underwent a first alloHCT using either a matched related or unrelated donor for cHL between 2008-2016, utilizing a RIC regimen with either fludarabine/ i.v. busulfan (6.4mg/kg) (Flu/Bu, n=102), fludarabine/melphalan 140mg/m^2 (Flu/Mel140, n=318) or fludarabine/cyclophosphamide (Flu/Cy, n=72). Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis was calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) plus methotrexate, mycophenolate mofitil (MMF) or other agents, however post transplantation cyclophosphamide (post-CY) was excluded. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Secondary endpoints included acute (a) and chronic (c) GVHD, non-relapse mortality (NRM), relapse/progression and progression-free survival (PFS). Probabilities of OS and PFS were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier estimator. Multivariable regression analysis was performed for GVHD, relapse/progression, NRM, PFS, and OS. Covariates with a p<0.01 were considered significant.
RESULTS
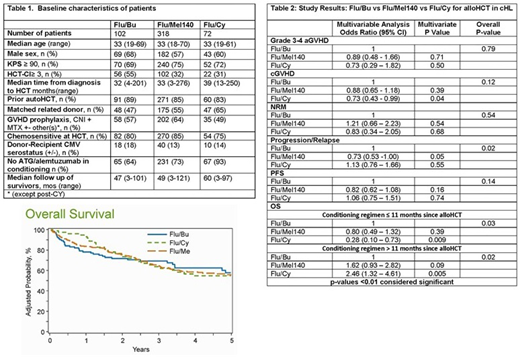
Baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. The median patient age of the complete study cohort was only 33 years, with more than 80% receiving a prior autologous HCT. On multivariate analysis (Table 2), the 3 conditioning regimen cohorts were not statistically different in either risk of cGVHD nor risk of grade 3-4 aGVHD. No significant differences were seen in the NRM risk between the three regimens (p=0.54). Similarly, the risk of relapse (p=0.02) and PFS was comparable between regimens (p=0.14). Flu/Cy conditioning was associated with decreased risk of mortality in first 11months after alloHCT (OR 0.28, 95% CI 0.10-0.73, p=0.009, but beyond 11 months post alloHCT it was associated with a significantly higher risk of mortality, (OR 2.46, 95% CI 0.1.32-4.61, p=0.005; Figure 1) [11months post alloHCT cutoff chosen on the basis of the maximum likelihood value in the Cox model]. Four year adjusted PFS and OS were similar across the three regimens at 29% for Flu/Bu, 37% for Flu/Mel140 and 25% for Flu/Cy (p=0.07) for PFS and 62% for Flu/Bu, 59% for Flu/Mel140 and 55% for Flu/Cy (p=0.64) for OS, respectively. Relapse was the most common cause of death across all the regimens, followed by organ failure and GVHD.
CONCLUSIONS
The most commonly used RIC regimen in alloHCT for cHL is Flu/Mel140, which was compared to Flu/Bu and Flu/Cy, the next most frequently used regimens. The choice of conditioning regimen, in these young cHL patients (median age 33 years) did not confer any benefit in terms of the risk of relapse, decrease in NRM or improvement in PFS. There was no OS benefit between, Flu/Bu and Flu/Mel 140, but Flu/Cy was associated with a significantly higher risk of mortality in patients beyond 11 months from allo-HCT. Novel approaches are still needed to decrease post-HCT relapse risk and improve overall results.
Ghosh:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Research Funding; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; T G Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Forty Seven Inc: Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Astra Zeneca: Speakers Bureau. Kharfan-Dabaja:Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Sureda:Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support; Gilead: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hamadani:Merck: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Otsuka: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Medimmune: Consultancy, Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Sanofi Genzyme: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal