Background:
The prognosis of patients with chronic-phase myeloid leukaemia (CML) has drastically improved with the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). During the period of this study, availability of treatment options in the UK were limited and determined by the date reimbursement was granted and when restrictions on the use of individual licensed TKIs were removed. Currently, imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib are reimbursed for 1st line treatment (1L) with bosutinib and ponatinib reimbursed for 2nd line or subsequent lines of treatment.
Aims:
The primary aim was to determine the sequence of 2nd generation (2G) TKIs (nilotinib, dasatinib, bosutinib) in patients with chronic-phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) CML who had received their 3rd and subsequent lines of TKIs in a real world UK setting.
Methods:
A multi-centre, retrospective, chart review was undertaken in the UK from November 2018 to July 2019. To be included, patients had to be aged ≥18 with chronic phase Ph+ CML who had started a third line of TKI treatment between June 2013 and February 2018. Patients were excluded if they had >3-month gap in treatment before progression or relapse, or were treated with a 2G TKI within an interventional clinical study during third line treatment.
At each line, molecular responses, cytogenetic responses, duration of therapy and reasons for stopping were recorded until the date of last hospital follow-up or death. Overall survival was determined from date of initiation of 3rd or 4th line TKI therapy until death by any cause.
Results:
An interim analysis was undertaken for 65 patients from 11 sites. Median age at diagnosis was 53.0 years. 50.8% were male and 49.2% were female. Of these 65 patients, 48 patients were still being treated at the end of observation (29 patients in 3rd, 18 in 4th and 1 in 5th line). Patient demographics are typical of CML populations.
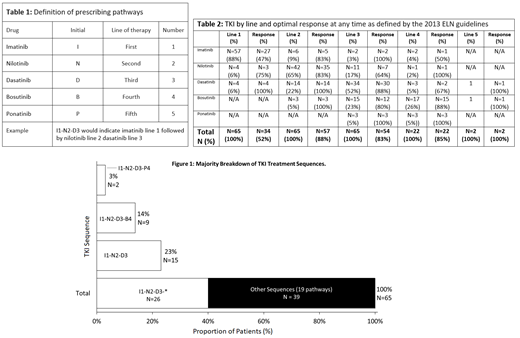
Throughout the study, imatinib was 1L treatment of choice for the majority of patients (57/65; 88%) and this held true (21/22; 95%) even when nilotinib and dasatinib were reimbursed for use 1L. Nilotinib was most commonly prescribed in 2L (42/65; 56%), reflecting the greater availability of this drug during the study period. Dasatinib and bosutinib constituted 22% and 4% respectively of 2L treatments. The most frequent sequencing pathway observed was I1-N2-D3 (Table 1, Fig. 1). 19 other pathways at low frequencies were observed across 39 patients.
97% of patients (63/65) achieved an optimal response at any time as defined by the 2013 ELN guidelines (Table 2) during the observation period. Of the 31 (48%) patients who were resistant to 1L, 24 (37%) achieved a response in 2L and of the 7 (10.7%) patients who were resistant to 1L and 2L, 5 (7.7%) achieved a response in 3L. At the end of the observation period, only 2 (3%) patients never achieved a response. In 3L: 29 (45%) patients are still ongoing, 4 died, 3 were lost to follow up and 3 underwent transplantation. In 4L: 18 (69%) are still ongoing, 3 died, and 3 underwent transplantation. Median overall survival for L3 was 21 months and 12 months in L4.
In all lines of treatment, the main cause of switching away from imatinib was lack of efficacy (61%), and for all 2G TKIs the main cause was intolerance (66%).
During the period when only imatinib was available in 1L, median duration of 1L treatment was longer at 26 months for patients failing to respond vs 9 months when nilotinib and dasatinib were also available.
Conclusions:
In this UK real-world study, for patients requiring 3 or more lines of treatment, sequencing of TKIs may have been determined by drug reimbursement. As availability of TKIs increased, time to switch therapy decreased for all patients, suggesting that clinicians were following guidelines and switching treatments more readily. However, initial 1L prescribing behaviour has not changed in this observation period despite better access to 2G TKI, and there appears to be a trend of physicians preferring to repeat 2G TKIs treatment sequences that yield a favourable outcome.
Byrne:Ariad/Incyte: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Ewing:Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship ; Bristol Myers-Squibb: Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship . Mead:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel/accommodation expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bristol Myers-Squibb: Consultancy; CTI: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding. Oakervee:Novartis: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Bristol Myers-Squibb: Honoraria. Campbell:Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Educational support; Takeda: Consultancy, Other: Educational support; Bristol Myers-Squibb: Other: Educational support; Roche: Other: Educational support; Celgene: Other: Educational support. Amott:Celgene: Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship . Goringe:Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Speaker. Heartin:Celgene: Other: Speaker's fees; Janssen: Other: Speaker's fees; Takeda: Other: Speaker's fees; Alexion: Other: Speaker's fees; Novartis: Other: Speaker's fees. Dimitriadou:Celgene: Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship . Arami:Takeda: Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship ; Gilead: Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship ; Roche: Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship ; Celgene: Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship . Neelakantan:Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Frewin:Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship ; AbbVie: Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship . Pillai:Celgene: Honoraria. De Lavallade:BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Incyte biosciences: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Cross:Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy. Thompson:Incyte: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal