Introduction: Acute B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) is the most common form of childhood leukemia and the leading cause of death in children with cancer. While therapy is often curative, about 10-15% of children will relapse with recurrent disease and abysmal outcomes. Actionable mechanisms that mediate relapse remain largely unknown. The gene encoding the High Mobility Group A1(HMGA1) chromatin regulator is overexpressed in diverse malignancies where high levels portend poor outcomes. In murine models, we discovered thatHmga1 overexpression is sufficient for clonal expansion and progression to aggressive acute lymphoid leukemia (Cancer Res 2008,68:10121, 2018,78:1890; Nature Comm 2017,8:15008). Further, HMGA1 is overexpressed in pediatric B-ALL (pB-ALL) blasts with highest levels in children who relapse early compared to those who achieve chronic remissions. Together, these findings suggest that HMGA1 is required for leukemogenesis and may foster relapse in B-ALL. We therefore sought to: 1) test the hypothesis that HMGA1 is a key epigenetic regulator required for leukemogenesis and relapse in pB-ALL, and, 2) elucidate targetable mechanisms mediated by HMGA1 in leukemogenesis.
Methods: We silenced HMGA1 via lentiviral delivery of short hairpin RNAs targeting 2 different sequences in cell lines derived from relapsed pB-ALL (REH, 697). REH cells harbor the TEL-AML1 fusion; 697 cells express BCL2, BCL3, and cMYC. Next, we assessed leukemogenic phenotypes in vitro (proliferation, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and clonogenicity) and leukemogenesis invivo. To dissect molecular mechanisms underlying HMGA1, we performed RNA-Seq and applied in silico pathway analysis.
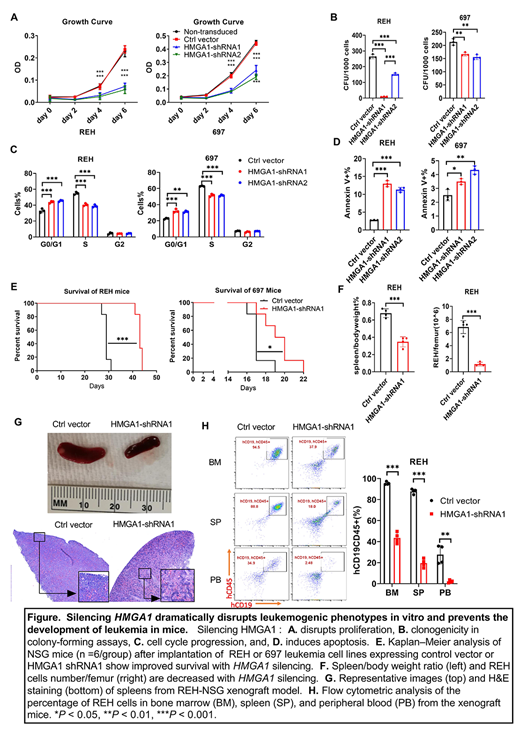
Results: There is abundant HMGA1 mRNA and protein in both pB-ALL cell lines and HMGA1 was effectively silenced by short hairpin RNA. Further, silencing HMGA1 dramatically halts proliferation in both cell lines, leading to a decrease in cells in S phase with a concurrent increase in G0/S1. Apoptosis also increased by 5-10% after HMGA1 silencing based on flow cytometry for Annexin V. In colony forming assays, silencing HMGA1 impaired clonogenicity in both pB-ALL cell lines. To assess HMGA1 function in leukemogenesis in vivo, we implanted control pB-ALL cells (transduced with control lentivirus) or those with HMGA1 silencing via tail vein injection into immunosuppressed mice (NOD/SCID/IL2 receptor γ). All mice receiving control REH cells succumbed to leukemia with a median survival of only 29 days. At the time of death, mice had marked splenomegaly along with leukemic cells circulating in the peripheral blood and infiltrating both the spleen and bone marrow. In contrast, mice injected with REH cells with HMGA1 silencing survived for >40 days (P<0.001) and had a significant decrease in tumor burden in the peripheral blood, spleen, and bone marrow. Similar results were obtained with 697 cells, although this model was more fulminant with control mice surviving for a median of only 17 days. To determine whether the leukemic blasts found in mice injected with ALL cells after HMGA1 silencing represented a clone that expanded because it escaped HMGA1 silencing, we assessed HMGA1 levels and found that cells capable of establishing leukemia had high HMGA1 expression, with levels similar to those observed in control cells without HMGA1 silencing. RNA-Seq analyses from REH and 697 cell lines with and without HMGA1 silencing revealed that HMGA1 up-regulates transcriptional networks involved in RAS/MAPK/ERK signaling while repressing the IDH1 metabolic gene, the latter of which functions in DNA and histone methylation. Studies are currently underway to identify effective agents to target HMGA1 pathways.
Conclusions: Silencing HMGA1 dramatically disrupts leukemogenic phenotypes in vitro and prevents the development of leukemia in mice. Mechanistically, RNA-Seq analyses revealed that HMGA amplifies transcriptional networks involved cell cycle progression and epigenetic modifications. Our findings highlight the critical role for HMGA1 as a molecular switch required for leukemic transformation in pB-ALL and a rational therapeutic target that may be particularly relevant for relapsed B-ALL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal