Introduction: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HCT) remains the only curative treatment for many hematologic conditions. However, significant mortality risk and risk of severe graft-vs-host disease (GvHD) limit its usefulness. Some patient characteristics such as performance status are used routinely as prognostic markers for poor outcomes after transplant. Steatohepatitis is a metabolic dysfunction manifesting as increased hepatic adiposity and resulting inflammation. A pre-clinical murine study suggests steatohepatitis is associated with GvHD. We assessed whether pre-HCT hepatic steatosis was associated with risk of developing GvHD and post transplant mortality.
Methods: This retrospective study reviewed adult patients who underwent allogeneic stem cell transplants at Duke University over a 10-year period between 2008 and 2017 and had a computed tomography scan (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast within a 1-year period preceding the transplant. Patients with an acute illness as the indication for CT were excluded. We measured the attenuation of the liver vs. spleen as an estimate of hepatic steatosis. We used the widely accepted definition of hepatic steatosis as present when the difference in average attenuation between the spleen and liver was greater than or equal to 10 Hounsfield units and as absent when the difference was less than 10 Hounsfield units. Baseline pre-HCT factors as well as post-HCT outcomes were abstracted from the medical record.
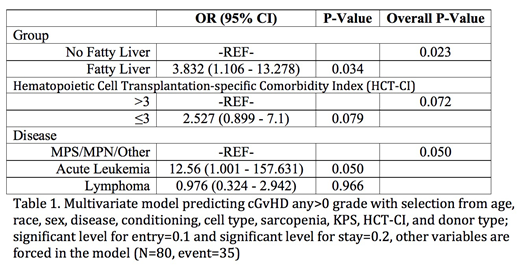
Results: We identified 80 patients with pre-HCT CT scans; of those, 59 (74%) had hepatic steatosis as defined above. Patients with hepatic steatosis tended to be older (median 52 vs. 38 years, p=0.0522); there were no statistically significant differences in gender, race, ethnicity, height, weight, Karnofsky Performance Status, HCT Comorbidity Index, history of diabetes, history of coronary artery disease, history of elevated liver function tests, primary disease, conditioning regimen, or stem cell source. Hepatic steatosis did not predict acute GvHD grade II-IV (OR 1.003, 95% CI 0.259 - 3.888, p=0.997). However, it was significantly associated with chronic GvHD on both univariate as well as multivariate analysis (Table 1, multivariate OR 3.83, 95% CI 1.11 - 13.28, p=0.023). There was no difference in overall survival or non-relapse mortality between the two groups.
Conclusions: This study suggests that hepatic steatosis may predict chronic GvHD but does not predict acute GvHD or overall/non-relapse mortality. This study can be improved by using other imaging techniques such as a noncontrast CT, which is more accurate for assessment of hepatic steatosis. It is also important to note that imaging can only be used to predict the existence of hepatic steatosis; lobular inflammation, which is required to diagnose steatohepatitis, can only be proven on biopsy. Larger studies with liver biopsy or other noninvasive imaging measures of liver stiffness and steatosis will be needed to confirm the above results.
Gasparetto:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodations, or other expenses paid or reimbursed ; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodations, or other expenses paid or reimbursed ; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodations, or other expenses paid or reimbursed . Horwitz:Abbvie Inc: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Rizzieri:Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Millennium: Speakers Bureau; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy; Spectrum: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; TEVA: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy. Bashir:Metacrine, Inc.: Research Funding; ProSciento, Inc.: Research Funding; Pinnacle Clinical Research: Research Funding; CymaBay Therapeutics: Research Funding; Siemens Healthcare: Research Funding; NGM Biopharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Madrigal Pharmaceulticals: Research Funding. Sung:Novartis: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Seres: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal