TO THE EDITOR:
Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome (aHUS) is a life-threatening disease that in most cases progresses to end-stage kidney disease.1 Rare pathogenic mutations in complement components or regulatory proteins play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of aHUS in 50% to 60% of patients.2-4 These rare variants cause defective regulation of the complement alternative pathway in the endothelial cell surface, which triggers episodes of thrombotic microangiopathy in the renal microvasculature and other vital organs.5-11 Finding complement pathogenic mutations in genetic analyses, or not finding them, improves diagnosis and facilitates a personalized treatment with eculizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that avoids the pathological consequences of cell surface complement dysregulation.1 Genetic analyses are widely used to help clinically diagnose aHUS, and they can help identify numerous asymptomatic relatives who carry different loads of aHUS genetic risk factors. A recurring question from both clinicians and patients is, How much risk of developing aHUS do these individuals have? There has been awareness of incomplete penetrance of aHUS in mutation carriers for a long time.12,13 However, our current estimates of disease penetrance in mutation carriers are based on very small cohorts and may be biased by uncertainties about the pathogenicity of the genetic variants found.12,14,15 To provide reliable estimates of the aHUS penetrance in mutation carriers, we searched the Spanish aHUS registry for patients with family data, in whom a comprehensive genetic analysis resulted in the identification of true pathogenic complement variants.
The Spanish aHUS registry includes 640 entries with a clinical diagnosis of aHUS based on established criteria1 (supplemental Materials and Methods, available on the Blood Web site). Genetic analysis of complement in the DNA from these patients was performed as previously described7 (supplemental Materials and Methods). Ninety-six patients fulfilled the criteria of having family data and carrying complement pathogenic variants that have been demonstrated to cause reduced protein levels or altered function. Seven additional patients carrying mutations most likely pathogenic were also included in these studies. Supplemental Tables 1 and 2 provide a detailed description of the mutations found in each of the 103 aHUS patients selected for this study. All available relatives (n = 372) were analyzed for the mutations that had been identified in the respective index patient and genotyped for the aHUS risk haplotypes CFH-H3 and MCPggaac. Overall, the relatives had a balanced sex distribution, with only 21.3% corresponding to descendants of the probands (supplemental Table 3). The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Spanish Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (ref: SAF2015-66287-R), and all patients included in this study provided written consent.
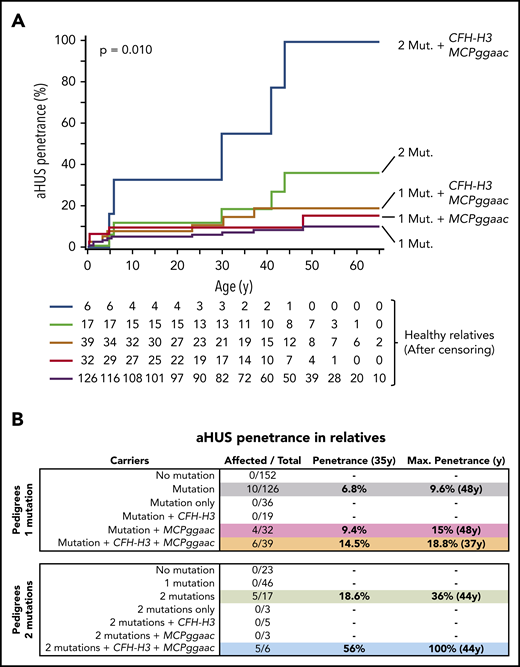
Eighty of the selected aHUS pedigrees carry a single complement pathogenic variant. These pedigrees include 286 relatives of whom 134 were carriers of the pathogenic variant. Notably, 10 of these 134 mutation carriers developed the disease, whereas there were none among the non-carrier relatives (n = 152) (P < .0004) (Table 1). As expected, these data confirm that the main driver of aHUS in these pedigrees is the pathogenic mutation. Affected relatives carry pathogenic mutations in C3 (2), CFH (3), CFB (3), or MCP (2) genes. A detailed age-adjusted analysis of the relatives who carry mutations showed a relatively low aHUS penetrance of 6.8% by age 35 years, which raises the aHUS penetrance to a maximum of 9.6% at age 48 years (Figure 1B).
Pathogenic variants and risk haplotypes in aHUS pedigrees with a single pathogenic variant (n = 80)
| . | Index cases (n = 80) . | Non-carrier relatives (n = 152) . | Carrier relatives (n = 134) . | Total affected carriers (%) (n = 90) . | P . | OR (95%CI) . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affected (n = 0) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 142) . | Affected (%) (n = 10) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 116) . | |||||
| CFH-H3 allele frequency | 76/160 (47.50) | 0 | 80/284 (28.17) | 6/20 (30) | 63/232 (27.16) | 82/180 (45.56) | .00011 | 2.24 (1.48-3.39) |
| MCPggaac allele frequency | 70/160 (44.38) | 0 | 93/284 (32.75) | 11/20 (55) | 76/232 (32.76) | 82/180 (45.56) | .010 | 1.71 (1.14-2.57) |
| CFH-H3 only | 22/80 (27.50) | 0 | 30/142 (21.13) | 0 | 19/116 (16.38) | 22/90 (24.72) | .162 | 0 |
| MCPggaac only | 13/80 (16.25) | 0 | 47/142 (33.10) | 4/10 (40) | 28/116 (24.14) | 17/90 (17.97) | .399 | 0 |
| CFH-H3 + MCPggaac | 37/80 (46.25) | 0 | 36/142 (25.35) | 6/10 (60) | 33/116 (28.45) | 43/90 (48.31) | .0056 | 2.3 (1.29-4.10) |
| None | 8/80 (10) | 0 | 29/142 (20.42) | 0 | 36/116 (31.03) | 8/90 (8.98) | .00012 | 0.21 (0.1-0.50) |
| . | Index cases (n = 80) . | Non-carrier relatives (n = 152) . | Carrier relatives (n = 134) . | Total affected carriers (%) (n = 90) . | P . | OR (95%CI) . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affected (n = 0) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 142) . | Affected (%) (n = 10) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 116) . | |||||
| CFH-H3 allele frequency | 76/160 (47.50) | 0 | 80/284 (28.17) | 6/20 (30) | 63/232 (27.16) | 82/180 (45.56) | .00011 | 2.24 (1.48-3.39) |
| MCPggaac allele frequency | 70/160 (44.38) | 0 | 93/284 (32.75) | 11/20 (55) | 76/232 (32.76) | 82/180 (45.56) | .010 | 1.71 (1.14-2.57) |
| CFH-H3 only | 22/80 (27.50) | 0 | 30/142 (21.13) | 0 | 19/116 (16.38) | 22/90 (24.72) | .162 | 0 |
| MCPggaac only | 13/80 (16.25) | 0 | 47/142 (33.10) | 4/10 (40) | 28/116 (24.14) | 17/90 (17.97) | .399 | 0 |
| CFH-H3 + MCPggaac | 37/80 (46.25) | 0 | 36/142 (25.35) | 6/10 (60) | 33/116 (28.45) | 43/90 (48.31) | .0056 | 2.3 (1.29-4.10) |
| None | 8/80 (10) | 0 | 29/142 (20.42) | 0 | 36/116 (31.03) | 8/90 (8.98) | .00012 | 0.21 (0.1-0.50) |
CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio.
Disease penetrance in relatives of aHUS patients. (A) Kaplan-Meier estimations of the aHUS penetrance for different loads of genetic risk factors. (B) aHUS penetrance at age 35 years and maximum aHUS penetrance in relatives of probands carrying 1 or 2 pathogenic variants and contribution of the CFH-H3 and MCPggaac risk haplotypes.
Disease penetrance in relatives of aHUS patients. (A) Kaplan-Meier estimations of the aHUS penetrance for different loads of genetic risk factors. (B) aHUS penetrance at age 35 years and maximum aHUS penetrance in relatives of probands carrying 1 or 2 pathogenic variants and contribution of the CFH-H3 and MCPggaac risk haplotypes.
There are several single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human CFH and MCP gene regions, but the very strong linkage disequilibrium between them reduces the genetic variability within these regions to a few single nucleotide polymorphisms haplotype blocks that span these genes. The CFH-H3 haplotype, which encodes for slightly reduced plasma levels of factor H, is strongly associated with a risk for aHUS.16,17 Similarly, the MCPggaac haplotype, which shows reduced MCP transcriptional activity, is also an important risk factor for aHUS.6,13,18 Identification of the CFH-H3 and MCPggaac haplotypes has diagnostic value and explains the incomplete penetrance of aHUS among carriers of complement pathogenic variants, but it is currently unknown how much these polymorphisms contribute to aHUS penetrance.
As expected, the allele frequencies of the CFH-H3 and MCPggaac risk haplotypes are increased in the affected mutation carriers in the single-mutation aHUS pedigrees (Table 1). To determine the contribution of CFH-H3 and MCPggaac to the aHUS penetrance, we divided the single-mutation carriers into 4 groups, carriers of only CFH-H3, carriers of only MCPggaac, carriers of both, and non-carriers (Table 1). Notably, the frequency of carriers of both risk haplotypes is significantly increased in the affected group compared with the non-affected group (48.3 vs 28.5; odds ratio, 2.32; 95% confidence interval, 1.29-4.10; P = .0056), and correspondingly, the frequency of individuals who lacked both risk haplotypes is significantly increased in non-affected mutation carriers compared with affected individuals (31 vs 8.98; odds ratio, 0.21; 95% confidence interval, 0.1-0.5; P = .00012) (Table 1). Consistent with these data, we found that carrying the MCPggaac haplotype or both the MCPggaac and the CFH-H3 haplotypes, in addition to the complement pathogenic mutation, raises the aHUS penetrance by age 35 years to 9.4% and 14.5%, and the maximum aHUS penetrance to 15% (age 48 years) and 18.8% (age 37 years), respectively (Figure 1). Interestingly, the 4 affected relatives without the CFH-H3 haplotype carry C3 (2) and FB (2) gain-of-function mutations.
Twenty-three additional families from our registry, in which the proband presents 2 variants that were demonstrated to be pathogenic, provided similar data: only relatives carrying the 2 mutations developed aHUS (Table 2). The overall risk of developing aHUS in double-mutation carriers was ∼threefold that of single-mutation carriers (Figure 1), suggesting that increasing the load of genetic risk factors reduces the dependence of environmental triggers and elevates aHUS penetrance. Consistently, the age-adjusted analysis in double-mutation carrier relatives showed an aHUS penetrance of 18.6% by age 35 years and a maximum aHUS penetrance of 36% at age 44 years (Figure 1).
Pathogenic variants and risk haplotypes in aHUS pedigrees with 2 pathogenic variants (n = 23)
| . | Index cases (%) (n = 23) . | Non-carrier relatives (n = 23) . | Carrier relatives with 1 mutation (n = 46) . | Carrier relatives with 2 mutations (n = 17) . | Total affected carriers (%) (n = 28) . | P . | OR (95%CI) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affected (n = 0) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 23) . | Affected (n = 0) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 46) . | Affected (%) (n = 5) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 12) . | |||||
| CFH-H3 allele frequency | 13/46 (28.26) | 0 | 9/46 (19.57) | 0 | 20/92 (21.74) | 5/10 (50) | 8/24 (33.33) | 18/56 (32.14) | 1 | — |
| MCPggaac allele frequency | 24/46 (52.17) | 0 | 6/46 (13.04) | 0 | 35/92 (38.04) | 6/10 (60) | 4/24 (16.67) | 30/56 (53.57) | .0028 | 5.76 (1.74-19) |
| CFH-H3 only | 3/23 (13.04) | 0 | 5/23 (21,74) | 0 | 8/46 (17.39) | 0 | 5/12 (41.67) | 3/28 (10.71) | .038 | 0.16 (0.03-0.9) |
| MCPggaac only | 7/23 (30.43) | 0 | 1/23 (4.35) | 0 | 15/46 (32.61) | 0 | 3/12 (25) | 7/28 (25) | 1 | — |
| CFH-H3 + MCPggaac | 9/23 (39.13) | 0 | 3/23 (13.04) | 0 | 11/46 (23.91) | 5/5 (100) | 1/12 (8.33) | 14/28 (50) | .029 | 11 (1.24-97) |
| None | 4/23 (17,39) | 0 | 14/23 (60,87) | 0 | 12/46 (26.09) | 0 | 3/12 (25) | 4/28 (14.29) | .65 | — |
| . | Index cases (%) (n = 23) . | Non-carrier relatives (n = 23) . | Carrier relatives with 1 mutation (n = 46) . | Carrier relatives with 2 mutations (n = 17) . | Total affected carriers (%) (n = 28) . | P . | OR (95%CI) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affected (n = 0) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 23) . | Affected (n = 0) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 46) . | Affected (%) (n = 5) . | Non-affected (%) (n = 12) . | |||||
| CFH-H3 allele frequency | 13/46 (28.26) | 0 | 9/46 (19.57) | 0 | 20/92 (21.74) | 5/10 (50) | 8/24 (33.33) | 18/56 (32.14) | 1 | — |
| MCPggaac allele frequency | 24/46 (52.17) | 0 | 6/46 (13.04) | 0 | 35/92 (38.04) | 6/10 (60) | 4/24 (16.67) | 30/56 (53.57) | .0028 | 5.76 (1.74-19) |
| CFH-H3 only | 3/23 (13.04) | 0 | 5/23 (21,74) | 0 | 8/46 (17.39) | 0 | 5/12 (41.67) | 3/28 (10.71) | .038 | 0.16 (0.03-0.9) |
| MCPggaac only | 7/23 (30.43) | 0 | 1/23 (4.35) | 0 | 15/46 (32.61) | 0 | 3/12 (25) | 7/28 (25) | 1 | — |
| CFH-H3 + MCPggaac | 9/23 (39.13) | 0 | 3/23 (13.04) | 0 | 11/46 (23.91) | 5/5 (100) | 1/12 (8.33) | 14/28 (50) | .029 | 11 (1.24-97) |
| None | 4/23 (17,39) | 0 | 14/23 (60,87) | 0 | 12/46 (26.09) | 0 | 3/12 (25) | 4/28 (14.29) | .65 | — |
Our data also show an additional contribution of the MCPggaac and CFH-H3 risk haplotypes to aHUS development when concurring with 2 pathogenic mutations, increasing the aHUS penetrance to 56% by age 35 years and to a complete penetrance (100%) at age 44 years (Figure 1). Notably, no single-mutation carriers (n = 46) developed aHUS in these 23 double-mutation pedigrees, when 2 to 3 affected relatives were expected. This may be because the pathogenicity associated with these mutations is lower than that of mutations found in the single-mutation pedigrees. Alternatively, the lack of affected individuals in this group could be related to the fact that they have a reduced load of aHUS risk haplotypes, resembling that of non-affected carriers in single-mutation pedigrees (Tables 1 and 2).
In conclusion, the analysis of 372 relatives of aHUS patients carrying 1 or 2 complement pathogenic variants provided us with reliable estimates of the disease penetrance in individuals carrying different loads of true pathogenic genetic risk factors. As expected, none of the non-carrier relatives developed aHUS. An important finding of our study has been to determine the contribution of the CFH-H3 and MCPggaac risk haplotypes to the aHUS penetrance in mutation carriers. Accordingly, the presence of both risk haplotypes in single-mutation and double-mutation carriers increases the aHUS penetrance twofold to threefold, whereas the absence of both risk polymorphisms reduces their risk of developing aHUS significantly. aHUS is a complex disease, with additive genetic risk factors delineating the predisposition to aHUS and environmental risk factors that trigger disease development. We have shown how different genetic risk factors contribute to aHUS penetrance and would like to suggest that these penetrance values have an inverse correlation with the intensity of environmental triggers required for disease development. Data presented in this report have the limitations associated with low numbers that characterize ultra-rare diseases but should help clinicians improve tailored management of aHUS patients and facilitate genetic counseling to their family members.
Please send requests for data to Santiago Rodríguez de Córdoba at srdecordoba@cib.csic.es.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all patients and their relatives who participated in this study.
This work was supported by the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad/FEDER grants SAF2015-66287-R, RTI2018-095955-B-100, and RYC-2013-13395 and Autonomous Region of Madrid grant S2017/BMD-3673. This work was developed under the supervision of the Spanish Registry of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and C3-Glomerulopathy.
Authorship
Contribution: S.R.d.C. and E.A. designed the research; E.A., A.H., E.G.d.J., and S.R.d.C. collected and analyzed the data; and S.R.d.C. wrote the letter.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Santiago Rodríguez de Córdoba, Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas, Ramiro de Maeztu 9, 28040 Madrid, Spain; e-mail: srdecordoba@cib.csic.es.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal