Abstract
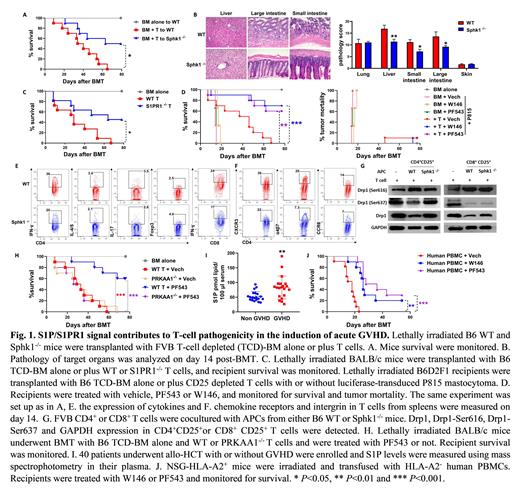
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) is a curative option for the treatment of hematological malignancies, which is primarily mediated by donor immune cells. Acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) mainly induced by transplanted donor T cells is a major and life-threating complication leading to severe "cytokines storm" and multiple organ damage, which contributes to high morbidity and mortality and thus limits the success of allo-HCT. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a bioactive lysophospholipid, is synthesized from sphingosine by sphingosine kinase 1 (Sphk1) or Sphk2 and degraded by S1P lyase. S1P signal plays an important role in regulating biological functions and homeostasis of T lymphocytes, and thus has been considered as a therapeutic candidate against autoimmune disease. In current study, we demonstrated that Sphk1 but not Sphk2 is required for antigen-presenting cells (APC) to activate allogeneic T cells. Using murine allo-HCT models, we found that secretory S1P produced by Sphk1 in the recipients was required for the development of full-blown GVHD (Fig. 1 A-B). Consistently, S1PR1, a primary receptor for S1P, plays a critical role in the pathogenicity of donor T cells to induce GVHD (Fig. 1C). Using pharmacologic inhibitors, we demonstrated that specific inhibition of Sphk1 (PF543) or S1PR1 (W146) substantially attenuated GVHD while preserving graft-vs.-leukemia (GVL) effect (Fig. 1D). Mechanistically, S1P/S1PR1 signal facilitated T-cell activation and differentiation towards Th1/Th17 but away from Tregs (Fig. 1E) and also promoted T-cell migratory potential into GVHD target organs (Fig. 1F). S1P/S1PR1 signaling increased mitochondrial fission of pathogenic CD4 + T cells through PRKAA1 dependent Drp1 and phosphorylated S6 (pS6) activation (Fig. 1 G-H). Whereas CD8 + T cells were much less sensitive to S1P-S1PR1-PRKAA1-pS6/Drp1 axis, which likely contributed to the GVL maintenance when S1P/S1PR1 signaling is absent or inhibited (Fig. 1 D, G). Furthermore, clinical data demonstrated that patients with acute GVHD exhibited a comparable level of sphingosine but a significantly higher level of S1P, as compared to the patients without GVHD, suggesting a positive role of S1P in GVHD development in clinic (Fig. 1I). Finally, we validated the efficacy of inhibiting Sphk1/S1PR1 in GVHD prevention induced by human T cells in a xenograft model (Fig. 1J). Taken together, our results provide a rationale and novel mechanism of targeting Sphk1/S1PR1 in the prevention of GVHD and leukemia relapse after allo-HCT. This novel strategy may be translated in the clinic to benefit patients with hematologic malignancies.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal