Abstract
Introduction: Anti-BCMA bispecific antibodies (BiAbs) have shown encouraging response rates in clinical trials of heavily pre-treated multiple myeloma (MM). BCMA has an important physiologic role in humoral immunity, and inhibiting BCMA causes decreased response to vaccines in mice as well as in MM patients (pts) receiving COVID-19 vaccines. Infection has emerged as an important toxicity, with clinical trials demonstrating >30% rates of grade 3 or higher infections. As these therapies come into widespread use in MM, a deeper understanding of infections and prophylactic measures is urgently needed.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all MM pts treated with anti-BCMA BiAbs at Mount Sinai from 2019-2022. Data were collected on baseline characteristics, treatment, disease response, hypogammaglobulinemia (HGG), infections, and prophylactic measures, including intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg). Chi-squared analysis was used for univariate associations and the Kaplan-Meier method was used for time-to-event calculations. Incidence rates ratios (IRR) were calculated using the exact Poisson method. This study was approved by the Mount Sinai IRB.
Results: 37 pts were treated with anti-BCMA BiAbs; the median age was 66 years (range 41-85) and 62% were female. The median time from diagnosis to treatment was 7.4 years, with a median of 7 prior lines of therapy (range 2-13). 65% had high risk cytogenetics, and pts had a median of 2 infections (range 0-10) in the year prior to BiAb.
Pts were treated for a median of 13 months (range 0.3-33.8), with a median PFS of 18.8 months and median OS of 26.6 months. Of the 70% who had a disease response, 100% developed HGG, with 100% in the severe range (IgG<200 mg/dL), censoring for IVIg use if IgG<200 mg/dL was not reached (5 pts). IVIg was used in 92% of pts who achieved a disease response, and these pts were on IVIg 56% of the time. Six (25%) pts were on IVIg at the start of therapy. All patients received VZV prophylaxis but no bacterial or fungal prophylaxis.
There were a total of 118 infections during 424 months of follow-up (3.3 per pt-year), including 26 grade 3-5 infections (0.7 per pt-year) among 14 pts (38%), among whom the median time to first grade 3-5 infection was 3.8 months. There were 2 grade 5 infections, which occurred at 15.1 months (COVID-19) and 17.6 months (bacterial sepsis). Infections were mostly in the respiratory tract (58%), followed by urinary tract and skin (15% each), and GI (8%), and were split among viral (46%) and bacterial (43%), with 11% fungal. There were 6 unusual opportunistic infections, including bacteremia, empyema, pericarditis, fungal pneumonia and two viral esophagitis. CMV reactivation occurred in 22%, including two cases of esophagitis. Of those treated since 2020, 12 (43%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, with 3 severe cases including 1 death in a vaccinated patient.
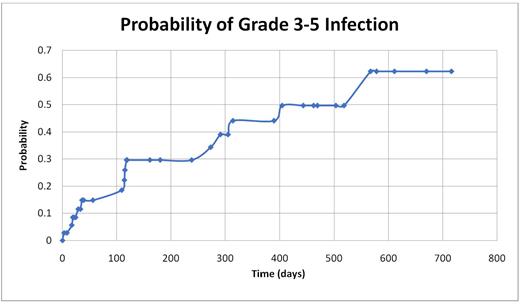
The estimated median time to first grade 3-5 infection among the whole population was 13.5 months (Figure 1). There was no association between neutrophil and lymphocyte counts and severity of infection. For patients who responded to treatment, the grade 3-5 infection rate while on IVIg was 0.25 per pt-year compared with 1.23 per pt-year off IVIg (IRR 0.20, 95% CI [0.06-0.52], p<0.001), with only 21% of grade 3-5 infections occurring on IVIg. This effect was more pronounced for bacterial infections, with 0.10 grade 3-5 infections per pt-year on IVIg vs 0.89 off IVIg (IRR 0.11, 95% CI [0.01-0.49], p<0.001).
Discussion: Patients treated with anti-BCMA BiAbs had high rates of all grade and grade 3-5 infections, including opportunistic infections. Although most grade 3-5 infections occurred in the first 4 months, the risk continues to increase with time, raising the question of optimal duration/schedule of therapy. Severe hypogammaglobulinemia was universal among responders. The rate of grade 3-5 infections was 80% lower on IVIg (and 89% lower for bacterial grade 3-5 infections), with only 5 serious infections occurring on IVIg, suggesting a role for IVIg as primary prophylaxis. IVIg may be additionally useful now given the high prevalence of COVID-19 antibodies in the donor pool. Neutrophil and lymphocyte counts were not significant factors for severe infections, further highlighting the role of impaired humoral immunity in this population. Lastly, CMV should be monitored monthly given the significant reactivation rate.
Disclosures
Lancman:Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Rodriguez:Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Richter:BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy; Secura Bio: Consultancy, Honoraria; Oncopeptides: Consultancy, Honoraria. Cho:Takeda: Other: Receive laboratory research support from the above companies. Salary value is less than $10,000 per company., Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Other: Receive laboratory research support from the above companies. Salary value is less than $10,000 per company., Research Funding. Richard:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; C4 Therapeutics: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Rossi:BMS: Consultancy; sanofi: Consultancy; gsk: Consultancy; adaptive: Consultancy; janssen: Consultancy. Jagannath:Sanofi: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Legend Biotech: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy. Chari:Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Array Biopharma: Research Funding; Glaxo Smith Klein: Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Oncoceutics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal