Abstract
INTRODUCTION:
NXT007 is a bispecific antibody (BsAb) that bridges activated factor IX (FIXa) and factor X (FX), thereby mimicking the cofactor function of activated factor VIII, and was discovered by engineering the first-in-class drug of emicizumab. Nonclinical investigations suggested the potential of NXT007 to provide a supra-emicizumab and even non-hemophilic level of coagulation activity to patients with hemophilia A [1,2]. Meanwhile, quantitative characterization and comparison of the in vivo hemostatic activity of NXT007 with factor VIII (FVIII) and emicizumab remained to be addressed. This research aimed to quantitatively estimate the in vivo hemostatic activity of NXT007 in terms of relative potency to FVIII ("equivalent FVIII activity") by leveraging and analyzing previously published nonclinical data with model-based approaches.
METHODS:
Simulation of factor IX (FIX)-BsAb-FX ternary complex formation in human plasma using a binding kinetic model was employed for predicting the in vivo equivalent FVIII activity of NXT007, as previously investigated to associate the ternary complex concentration with in vivo equivalent FVIII activity in a non-human primate model of acquired hemophilia A for emicizumab [3]. Dissociation constants against human FIX and FX, which were determined by a surface plasmon resonance analysis in buffer solution, were used for simulating the equilibrium binding of the BsAbs with these antigens as functions of their plasma concentrations. The conversion factor from ternary complex concentration to in vivo equivalent FVIII activity for NXT007 was assumed to be equivalent to that for emicizumab, given their comparable effects for increasing the turnover rate of FIXa-catalyzed FX activation on top of their similar affinities to FIX/FIXa. To support the validity of this assumption, in vitro equivalent FVIII activities of NXT007 and emicizumab were estimated and compared. Peak height data from in vitro activated factor XI (FXIa)- or tissue factor (TF)-triggered thrombin generation (TG) assays, in which FVIII-deficient human plasma was spiked with vehicle, FVIII (10.0 to 150 IU/dL), NXT007 (0.0300 to 3000 μg/mL), or emicizumab (0.0300 to 3000 μg/mL), were used for developing pharmacodynamic models to describe the concentration-response relationships of the three active drugs. The developed models were then transformed to derive the corresponding in vitro equivalent FVIII activities of NXT007 and emicizumab as functions of their plasma concentrations.
RESULTS:
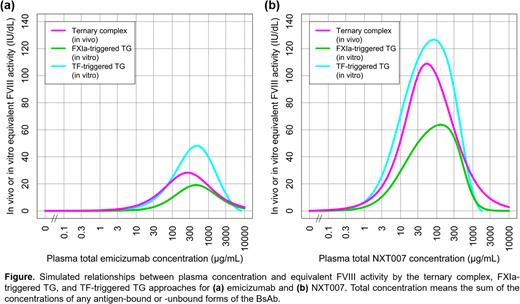
The simulated relationships between plasma concentration and equivalent FVIII activity by the ternary complex, FXIa-triggered TG, and TF-triggered TG approaches for NXT007 and emicizumab were all bell-shaped, peaking at 109, 63.7, and 127 IU/dL with 53.1, 130, and 82.8 μg/mL, respectively, for NXT007 and at 28.2, 19.0, and 48.2 IU/dL with 265, 452, and 476 μg/mL, respectively, for emicizumab (Figure). With higher peak equivalent FVIII activities achieved with lower plasma concentrations for NXT007 than emicizumab, the interrelationship among the simulated relationships between plasma concentration and equivalent FVIII activity by the three approaches appeared consistent between NXT007 and emicizumab, as characterized by the same order of peak equivalent FVIII activity, i.e., TF-triggered TG > ternary complex > FXIa-triggered TG. This consistency may suggest comparable coagulation activities per ternary complex between NXT007 and emicizumab, supporting the validity of assuming an equivalent conversion factor from ternary complex concentration to in vivo equivalent FVIII activity for NXT007 and emicizumab. By the ternary complex approach, the minimum plasma concentrations of NXT007 to achieve in vivo equivalent FVIII activities of 15 (anticipated therapeutic level with emicizumab), 40 (threshold for hemophilia A), and 100 (typical normal) IU/dL were predicted to be 2.50, 7.26, and 30.2 μg/mL, respectively (Figure).
CONCLUSIONS:
Model-based approaches supported application of the ternary complex approach for predicting the in vivo equivalent FVIII activity of NXT007. Findings from this research provided a basis for designing a phase I/II clinical study of NXT007 that is currently ongoing (NXTAGE; JapicCTI-194919).
REFERENCES:
1. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 2020;4 Suppl 1:579.
2. Blood 2020;136 Suppl 1:19.
3. Thromb Haemost 2017;117:1348-57.
Disclosures
Yoneyama:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Current Employment, Patents & Royalties: Inventor of patents related to anti-FIXa/FX bispecific antibodies. Soeda:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Current Employment, Patents & Royalties: Inventor of patents related to anti-FIXa/FX bispecific antibodies. Yamaguchi:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Current Employment, Patents & Royalties: Inventor of patents related to anti-FIXa/FX bispecific antibodies. Miwa:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Current Employment. Ishida:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Current Employment. Saito:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Patents & Royalties: Inventor of patents related to an anti-interleukin-31 receptor A antibody.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal