Abstract
Introduction: Previous studies indicated that PIGN gene is crucial in regulating mitotic integrity to maintain chromosomal stability and prevent MDS leukemic transformation and progression. Alternative Polyadenylation (APA) regulation and 3' RNA cleavage are 2 known vital processes in cellular DNA damage response to maintain genomic stability. NUDT21 gene encodes protein that is one subunit of the cleavage factor Im complex required for 3' RNA cleavage and APA processing. Although PIGN gene has six potential polyadenylation sites, the exact role of NUDT21 product on PIGN expression regulation has not been illustrated before. In this study, we assessed NUDT21 product regulation of PIGN expression via APA in MDS and AML patient samples, cell lines, and in mouse.
Methods: At first, we used bioinformatics methods to analyze NUDT21 gene expression profile in AML, MDS, and normal control specimens and to plot the relationship between NUDT21 gene expression status and patient survival length from 5 datasets. We also used correlation regression analysis method to predict the gene expression correlations between NUDT21 gene and PIGN gene. Then, we used Caspas9 technology and vector overexpression technology to knockout or overexpress PIGN in HEK293 cells; RNA interference to knockdown the NUDT21 gene in HEK293, HL60, K562, THP-1,SKM-1 and MUTZ-1 cells. MTT and CCK8 methods were used to evaluate cell proliferation. Meanwhile, cell cycle, apoptosis, Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and GPI-anchored proteins (CD55, CD59, and CD235) expression profiles were evaluated by flowcytometry; Immunofluorescence experiment, RT-PCR were used to evaluate the impact of NUDT21 gene knockdown on PIGN expression. in vivo mice siRNA interference tests were conducted to verify the impact of NUDT21 knockdown on PIGN gene expression. RNA-Seq & Dapars analyses were conducted on mRNAs from THP-1,SKM-1 and MUTZ-1 cell lines with various PIGN gene expression status to observe the effects of NUDT21 knockdown on PIGN 3'UTR processing.
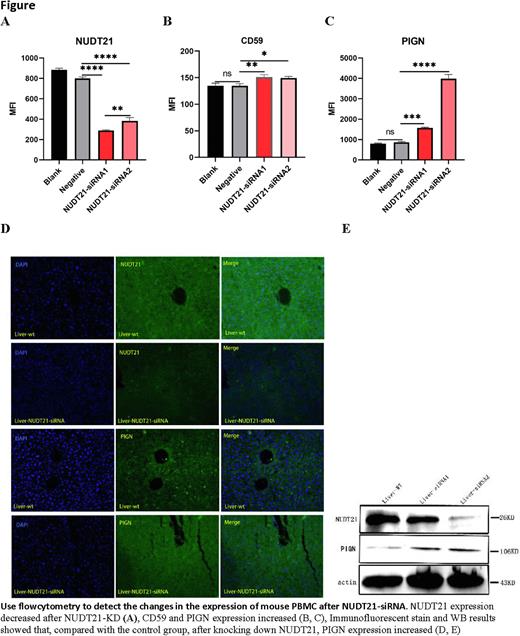
Results:NUDT21 expression increases in mononuclear cells from AML and high-risk MDS. NUDT21 expression level is negatively correlated with the overall survival. NUDT21 knockdown decreases cell proliferation but increases cell differentiation via prolonging G1 phase, decreasing S phase, and increasing apoptosis. NUDT21 knockdown increases cell membrane GPI-anchoring proteins (CD55, CD59, and CD235) expressions; increases ROS and Caspas3 expressions but decreases CyclinD1 expression. NUDT21 knockout can increase the PIGN expression, but PIGN expression status has no impact on NUDT21 expression. RT-PCR and WB results showed that NUDT21 knockdown can increase TP53 expression but decrease p21 expression. in vivo mice siRNA interference tests confirmed that NUDT21 knockdown increases PIGN gene expression (Figure). The RNA-Seq/Dapars analyses results showed that 3'UTR of PIGN transcript was significantly shortened and PIGN expression increased after NUDT21 knockdown.
Conclusion:NUDT21 modulates PIGN gene expression through APA mechanism. PIGN polyadenylation modulation may regulate cell cycle and cell proliferation through NUDT21-PIGN-P21- Cyclin D1 pathway and may regulate cell apoptosis through NUDT21-PIGN-TP53-ROS-caspas3 pathway.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal