Abstract
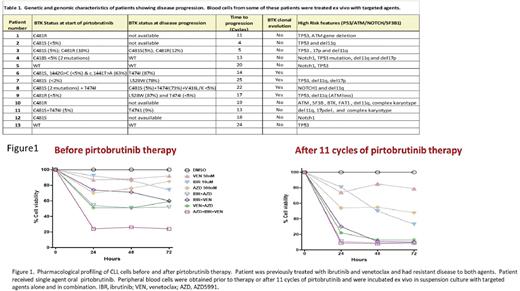
Covalent (c) Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors (BTKi) are effective agents for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). As single agent or in combination they result in long-term disease-free survival. However, some patients are intolerant to cBTKi while in others disease relapses due to pathogenic mutation in the C481 domain where cBTKi bind. More selective and noncovalent (nc) BTKi have proven to be efficacious for this patient population. Among ncBTKi, pirtobrutinib (previously known as Loxo-305) has been successfully used in the clinic (NCT03740529) for patients with CLL after cBTKi therapy. Previously treated patients with CLL entered on this protocol from Oct 2019 till Sept 2021 and received single agent oral pirtobrutinib until disease progression. Data from 27 CLL patients are available while one is lost to follow-up; baseline BTK status was wildtype (WT) in 10 and mutant (Mt) in 16 patients. Among these 26 patients, 13 (50%) progressed while on pirtobrutinib therapy (Table1). BTK profiling results at start of therapy show that among those who progressed, 11 patients had mutant BTK (85%) and 2 patients had WT-BTK (15%) suggesting that mutant BTK may be more likely to have disease recurrence while on pirtobrutinib therapy. Most common mutations were C418S, C418R, C481F, T4741 and PLCGy2 alone or in combination. Some patients with progression developed BTK clonal evolution with new nonC481 Mt-BTK clone or increase in variant allele frequency (VAF) of mt-BTK. BTK profiling at time of DP indicated that in some of these patients the original pathological clone of C481 Mt-BTK resolved. Disease progression (13 patients) typically occurred during the first two years of therapy with median time to progression 22 cycles for patients harboring WT-BTK and 14 cycles for those with Mt-BTK. Most of these patients (12) also showed high risk CLL features of TP53 mutation (9 patients), ATM/11qdel (9 patients), Notch1 mutation (4 patients), complex karyotype (6 patients) or trisomy 12 (3 patients). There are limited therapeutic options post pirtobrutinib progression. Therefore, we conducted pharmacological profiling for these patients by ex-vivo testing CLL cells post progression. We incubated peripheral blood mononuclear cells for three days with cBTKi - ibrutinib; glutathione inhibitor (also known as mtTP53 modulator) - APR-246; Bcl-2 antagonist - venetoclax; and Mcl-1 antagonist - AZD5991; as single agent and in double or triple combinations and apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. Endogenous cell death was negligible even after 3 days in suspension culture indicating highly resistant cell population. Single agent venetoclax at 50 nM was most effective with a median 70% cell death (range 40-90%) after 3 days. Interestingly, cells harboring mt-BTK appeared to be more sensitive to venetoclax (p = 0.01). APR-246 alone showed heterogeneity with 10% to 85% cell death yet it was able to sensitize cells to venetoclax, ibrutinib, and AZD5991 in both WT and mutant BTK patient cohorts. Loss of C481S original clone after pirtobrutinib therapy made cells sensitive to ibrutinib. Four (4) patients, both pretreatment and during therapy or progression samples were available. Intra-patient comparison demonstrated that compared to pretreatment sample, cells were sensitized to targeted agents after 10 - 14 cycles of pirtobrutinib therapy (Figure 1). Additional samples are being tested during this ongoing clinical trial. In conclusion, progression on pirtobrutinib therapy was more common in patients with Mt-BTK. Pharmacological profiling based on BTK status at disease progression showed venetoclax and APR-246 as the most effective single agents. Combination of APR-246 or venetoclax with ibrutinib or AZD5991 showed maximum cell death. Patients were re-sensitized to ibrutinib after loss of C481S clone. Genomic and genetic profile along with pharmacological landscape provide precision medicine for these heavily pretreated patients whose disease is resistant to BTK inhibitors.
Disclosures
Thompson:AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Genentech, Amgen: Honoraria; AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Genentech: Consultancy; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie, Pharmacyclics, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Genentech: Research Funding. Jain:Genentech, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; Cellectis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support; Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Precision Biosciences: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; Servier Pharmaceuticals LLC: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria; MEI Pharma: Honoraria; Ipsen: Honoraria; Dialectic Therapeutics: Research Funding; Novalgen: Research Funding; TransThera Sciences: Research Funding; Newave: Research Funding; Beigene: Honoraria; Cellectis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Medisix: Research Funding; Loxo Oncology: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Aprea Therapeutics: Research Funding; Fate Therapeutics: Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Mingsight: Research Funding; CareDx: Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding. Wierda:Juno: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Oncternal Therapeutics, Inc.: Research Funding; Loxo Oncology, Inc./Lilly: Research Funding; Miragen: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy; GSK/Novartis: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; Xencor: Research Funding; Genzyme: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company: Research Funding; Bristol Meyers Squibb (Juno and Celgene): Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma. Inc.: Research Funding. Gandhi:Clear Creek Bio: Consultancy, Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; LOXO: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Sunesis: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal