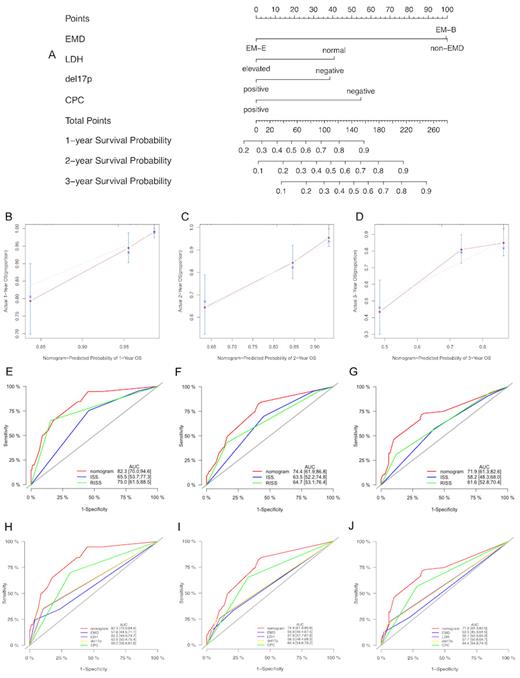
Extramedullary disease (EMD) is an unusual event in patients with MM. This study aimed to assess the prognostic impact of EMD and develop an EMD-based risk model to estimate the survival of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM). A total of 518 patients were enrolled in this study, of which 121 presented with EMD at the initial diagnosis. Patients were divided into non-EMD, extramedullary-bone-related (EM-B), and extramedullary-extraosseous (EM-E) groups. Clinical characteristics were compared using the chi-squared test or Fisher's exact test. Survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method, and a nomogram was constructed based on the Cox proportional hazards model. Compared to patients without EMDs, patients with EM-E were younger ( P=0.028), and those with EM-B had less renal damage ( P<0.001). The EM-E group had the worst progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). In addition, patients with multiple sites of EMD invasion or high Ki67 expression had poor OS. Lenalidomide-based treatment showed the worst outcome, and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) remarkably improved the survival of patients with EMD. A prognostic model (MM prognostic index, MM-PI) comprising lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), circulating plasma cells (CPC), del(17p), and type of extramedullary involvement was developed, and a 4-factor nomogram. In conclusion, we established a risk model incorporating extramedullary disease that provides accurate and individualized survival estimates for patients with NDMM.
Disclosures
Chen:Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.: Honoraria, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal