High-dose oral vitamin A pre-HSCT was feasible with minimal toxicity in a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial in children.
Vitamin A given in a presumed homeostatic environment before HSCT may lower GVHD.
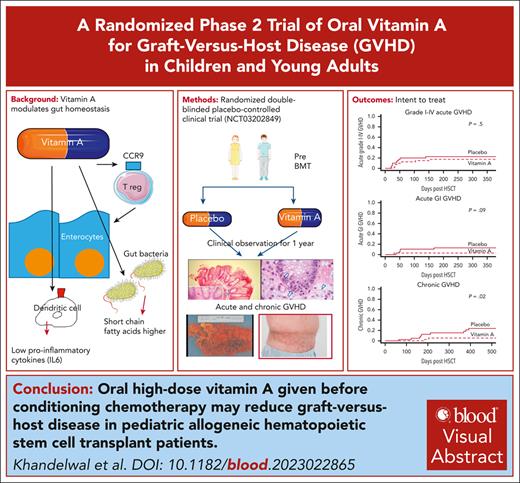
Visual Abstract
Vitamin A plays a key role in the maintenance of gastrointestinal homeostasis and promotes a tolerogenic phenotype in tissue resident macrophages. We conducted a prospective randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial in which 80 recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) were randomized 1:1 to receive pretransplant high-dose vitamin A or placebo. A single oral dose of vitamin A of 4000 IU/kg, maximum 250 000 IU was given before conditioning. The primary end point was incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) at day +100. In an intent-to-treat analysis, incidence of acute GVHD was 12.5% in the vitamin A arm and 20% in the placebo arm (P = .5). Incidence of acute gastrointestinal (GI) GVHD was 2.5% in the vitamin A arm (P = .09) and 12.5% in the placebo arm at day +180. Incidence of chronic GVHD was 5% in the vitamin A arm and 15% in the placebo arm (P = .02) at 1 year. In an “as treated” analysis, cumulative incidence of acute GI GVHD at day +180 was 0% and 12.5% in recipients of vitamin A and placebo, respectively (P = .02), and cumulative incidence of chronic GVHD was 2.7% and 15% in recipients of vitamin A and placebo, respectively (P = .01). The only possibly attributable toxicity was asymptomatic grade 3 hyperbilirubinemia in 1 recipient of vitamin A at day +30, which self-resolved. Absolute CCR9+ CD8+ effector memory T cells, reflecting gut T-cell trafficking, were lower in the vitamin A arm at day +30 after HSCT (P = .01). Levels of serum amyloid A-1, a vitamin A transport protein with proinflammatory effects, were lower in the vitamin A arm. The vitamin A arm had lower interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, and suppressor of tumorigenicity 2 levels and likely a more favorable gut microbiome and short chain fatty acids. Pre-HSCT oral vitamin A is inexpensive, has low toxicity, and reduces GVHD. This trial was registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov as NCT03202849.
Introduction
Acute gastrointestinal (GI) graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) causes significant nonrelapse mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).1 Disruption of intestinal homeostasis is a key precursor of GI GVHD.2 Vitamin A maintains immune homeostasis in the gut, coordinating innate and adaptive immunity3-8 (supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood website). Vitamin A induces a tolerogenic phenotype of gut-resident dendritic cells and these cells then produce lower levels of proinflammatory cytokines, for example interleukin-6 (IL-6).5,9 Recipient gut-resident dendritic cells typically persist after HSCT and can present antigens to incoming donor cells, initiating acute GVHD.2 We have shown previously that low plasma vitamin A levels are associated with higher incidence of acute GI GVHD.10 We hypothesized that induction of a tolerogenic dendritic cell phenotype before administration of allogeneic stem cells would reduce GVHD. Vitamin A has been shown to be proinflammatory in the context of gut inflammation, augmenting IL-17 and interferon-γ,11 in contrast to a more anti-inflammatory role when given in a homeostatic environment.9,12 We therefore administered vitamin A as a single large dose before HSCT, before development of a proinflammatory milieu.11
We present results of a phase 2 randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial of a single oral high dose of vitamin A given before HSCT to reduce GVHD.
Methods
An institutional review board–approved prospective phase 2 randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial was performed at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center between 2018 and 2022. Patients were randomized 1:1 in blocks of 10, to receive high-dose oral vitamin A or placebo before HSCT (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03202849). Randomization was performed using an online randomization tool (http://randomization.com). Randomization was not stratified by additional clinical variables. Vitamin A or placebo was typically given either in clinic ∼7 days before start of conditioning or at inpatient admission before start of conditioning chemotherapy. The study investigators gave consent for patients to be enrolled. Study investigators, treating physicians, bedside nurses, patients, and their families were blinded to the intervention; the investigational pharmacist performed the randomization and was the only person unblinded to the allocation of intervention for patients during study enrollment.
Vitamin A and D act synergistically,13 so we ensured vitamin D sufficiency before giving vitamin A. Patients randomized to either arm received vitamin D supplementation with cholecalciferol as per our previously published study.14 The dose of oral vitamin A was 4000 IU/kg, with a maximum dose of 250 000 IU, determined by a prior prospective safety study (described in supplemental Materials). Our dose-finding study initially allowed for a single repeat dosing of vitamin A at half the initial dose if vitamin A levels dropped to below levels at enrollment. The formulation of oral vitamin A was retinyl palmitate and commercially purchased canola oil served as placebo.
Patients were eligible if their pre-HSCT serum vitamin A levels were below the 75th centile of normal range for age, were scheduled to undergo an allogeneic HSCT, and could tolerate enteral medications. Children aged ≥1 year, and all underlying diagnoses were eligible. Exclusion criteria included pathological fractures, history of nephrocalcinosis or nephrolithiasis, current granulomatous disease, elevated alanine aminotransferase of >10× upper limit of normal for age, pregnancy, and ongoing raised intracranial pressure.
Primary study end point was the incidence of acute GVHD by day +100 after HSCT; secondary end points included incidence of grade 2 to 4 acute GVHD, steroid refractory acute GVHD and acute gastrointestinal (GI) GVHD by day +180, and 1-year incidence of chronic GVHD. Additional exploratory end points included transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy; nonrelapse mortality at 1 year; bloodstream infections and incidence of Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, adenovirus, and BK viremias; and overall survival.
Hypothesis–driven correlative studies were performed for patients who had plasma, peripheral blood mononuclear cell, and/or stool samples available in our institutional biorepository.
Statistical analyses
Study sample size was projected based on institutional acute GVHD rates of 35% between 2013 and 2015 with a goal to reduce to 15%. We planned to enroll 50 patients in each arm to achieve a 1-sided power of 80%. Enrollment on study was slow because of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, prompting a single-blinded interim analysis of our data, which was not prespecified in our protocol. Statistically significant differences between arms were seen in a blinded interim analysis of 80 enrolled patients, so out of concern for patient safety, the medical monitor closed and unblinded the study.
The primary study end point was incidence of acute GVHD by day +100, determined by competing risk analyses, using the Gray test in which acute GVHD was the primary risk and second HSCT, relapse of primary malignancy, or death were competing risks. Secondary end points were, acute GI GVHD by day +180, acute grade 2 to 4 GVHD by day +180, steroid refractory acute GVHD by day +180, and chronic GVHD by 1 year, and were similarly analyzed using a competing risk analysis, using the Gray test. Exploratory end points were also analyzed by competing risk analyses. A P value < .05 determined statistical significance. Two analyses were performed: an intent-to-treat analysis, and an as-treated analysis. Overall survival was analyzed using the log-rank test. Cumulative incidences of acute GVHD (all grades), acute GI GVHD, steroid refractory acute GVHD, grade 2 to 4 GVHD by day +180, and chronic GVHD at 1 year were analyzed. Secondary end points were additionally controlled for multiple testing using the Bonferroni method. To maintain a 0.05 level of significance across all secondary end points, only those with a P value < .0125 were considered statistically significant after adjustment. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare statistically significant differences between medians for correlative studies.
GI biomarkers
Plasma regenerating islet 3α, suppressor of tumorigenicity 2 (ST-2),15 and lipopolysaccharide binding protein16 levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; R&D Systems Inc, Minneapolis, MN; Abcam) per manufacturer’s instructions.17 Plasma cytokines were measured on a Luminex 200 instrument (Luminex Corporation, Austin, TX) according to the manufacturer's instructions based on as-treated cohorts.18 Plasma IL-22,19 IL-23,20 IL6R,21 and glycoprotein-13021 levels were measured by ELISA (R&D Systems Inc, Minneapolis, MN). Short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and additional metabolites were measured in feces by nuclear magnetic resonance.22 Fecal metagenomic shotgun sequencing 23 was performed at days +14 and +30 after HSCT (supplemental Methods). Vitamin A and D levels were measured in a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified laboratory. Retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4),24 serum amyloid A1 and 2 (SAA),25 neutrophil extracellular traps,26 interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1),27 and epidermal growth factor and its ligand neuregulin-128 were measured by ELISA (supplemental Materials). Immunohistochemistry for SAA1 on intestinal biopsies is described in supplemental Methods.
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry of CCR9+ T cells, T regulatory cells, T helper 1 (Th1) cells, Th2 cells, and Th17 cells is described in supplemental Materials.
Results
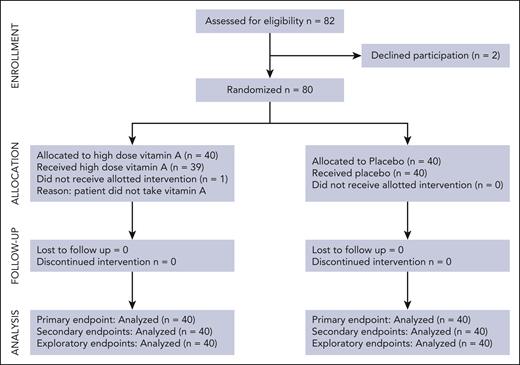
In total, 80 patients were enrolled, and 40 were randomized to receive a high dose of vitamin A whereas 40 received placebo (Figure 1). Patient demographics show similar transplant characteristics between study arms (Table 1). Vitamin D sufficiency was ensured in all patients with a single, high dose of vitamin D given before HSCT in those with vitamin D levels of <50 ng/mL. Seven patients who were randomized to the vitamin A arm met criteria for an additional half dose of oral vitamin A because their vitamin A levels dropped below their enrollment levels, ∼2 to 3 weeks from first dose (supplemental Table 1). One patient randomized to vitamin A arm did not take the assigned vitamin A, and 2 additional patients who took assigned vitamin A experienced significant delays between dosing and proceeding to HSCT (35 and 63 days, respectively) because of cholecystitis in 1 patient, and septic shock followed by delays in donor availability in the second patient. These patients were included in intent-to-treat analyses but excluded from as-treated analyses.
Patient demographics
| . | Vitamin A (n = 40) . | Placebo (n = 40) . |
|---|---|---|
| Median age (range), y | 6.9 (2-20) | 8.5 (1.1-28) |
| Underlying diagnosis | ||
| Malignancy | 8 | 9 |
| Primary immune deficiency | 8 | 6 |
| Bone marrow failure | 14 | 17 |
| Hemoglobinopathy | 8 | 8 |
| Metabolic disorder | 2 | 0 |
| Conditioning regimen | ||
| Myeloablative | 25 | 27 |
| Reduced intensity | 15 | 13 |
| Serotherapy in conditioning regimen | 24 | 28 |
| Radiation in conditioning regimen | 4 | 2 |
| HLA match | ||
| ≥2 antigen mismatch | 5 | 2 |
| 9 of 10 | 11 | 6 |
| 10 of 10 | 24 | 32 |
| Donor relation | ||
| Related (excluding ≥2 antigen mismatch) | 8 | 15 |
| Related (≥2 antigen mismatch) | 4 | 1 |
| Unrelated | 28 | 24 |
| Stem cell source | ||
| Unmanipulated PBSCs | 5 | 1 |
| PBSCs with stem cell manipulation | 11 | 11 |
| Cord blood | 1 | 0 |
| Bone marrow | 23 | 28 |
| GVHD prophylaxis | ||
| Calcineurin inhibitor + MMF | 9 | 6 |
| Calcineurin inhibitor + MTX | 1 | 5 |
| Calcineurin inhibitor + prednisone | 2 | 2 |
| T-cell depletion | 12 | 10 |
| Abatacept to standard prophylaxis | 15 | 14 |
| αβ-CD19+ TCR depletion | 0 | 2 |
| Posttransplant cyclophosphamide | 1 | 1 |
| . | Vitamin A (n = 40) . | Placebo (n = 40) . |
|---|---|---|
| Median age (range), y | 6.9 (2-20) | 8.5 (1.1-28) |
| Underlying diagnosis | ||
| Malignancy | 8 | 9 |
| Primary immune deficiency | 8 | 6 |
| Bone marrow failure | 14 | 17 |
| Hemoglobinopathy | 8 | 8 |
| Metabolic disorder | 2 | 0 |
| Conditioning regimen | ||
| Myeloablative | 25 | 27 |
| Reduced intensity | 15 | 13 |
| Serotherapy in conditioning regimen | 24 | 28 |
| Radiation in conditioning regimen | 4 | 2 |
| HLA match | ||
| ≥2 antigen mismatch | 5 | 2 |
| 9 of 10 | 11 | 6 |
| 10 of 10 | 24 | 32 |
| Donor relation | ||
| Related (excluding ≥2 antigen mismatch) | 8 | 15 |
| Related (≥2 antigen mismatch) | 4 | 1 |
| Unrelated | 28 | 24 |
| Stem cell source | ||
| Unmanipulated PBSCs | 5 | 1 |
| PBSCs with stem cell manipulation | 11 | 11 |
| Cord blood | 1 | 0 |
| Bone marrow | 23 | 28 |
| GVHD prophylaxis | ||
| Calcineurin inhibitor + MMF | 9 | 6 |
| Calcineurin inhibitor + MTX | 1 | 5 |
| Calcineurin inhibitor + prednisone | 2 | 2 |
| T-cell depletion | 12 | 10 |
| Abatacept to standard prophylaxis | 15 | 14 |
| αβ-CD19+ TCR depletion | 0 | 2 |
| Posttransplant cyclophosphamide | 1 | 1 |
MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; MTX, methotrexate; PBSCs, peripheral blood stem cells; TCR, T-cell receptor.
Intent-to-treat analyses
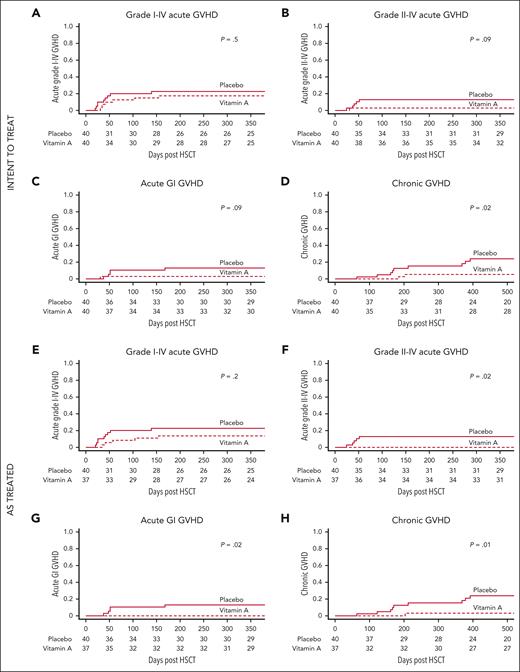
The incidence of grade 1 to 4 acute GVHD by day +100 was 12.5% in the vitamin A cohort and 20% in the placebo cohort (P = .5) (Figure 2A). Cumulative incidence (CI) of acute grade 2 to 4 GVHD by day +180 was 2.5% in the vitamin A arm and 12.5% in placebo (P = .09; Figure 2B). CI of acute GI GVHD by day +180 was 2.5% in the vitamin A arm and 12.5% in placebo (P = .09; Figure 2C). CI of chronic GVHD was 5% in the vitamin A arm and 15.3% in placebo at 1 year (P = .02; Figure 2D; Table 2). Chronic GVHD grades were moderate (n = 2) in the vitamin A arm and moderate (n = 4) or severe (n = 5) in placebo. No patients in either cohort had mild chronic GVHD. There were no significant differences in incidences of bloodstream infections, transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy, and viremias (supplemental Table 2). Nonrelapse mortality at 1 year was 10% in the vitamin A cohort and 7% in placebo (P = .6). Overall survival was 87.5% in the vitamin A arm and 86.9% in placebo (P = 1.0; supplemental Table 2)
Recipients of vitamin A have lower cumulative incidence of GVHD compared to placebo. Intent-to-treat analyses: (A) CI of grade acute 1 to 4 GVHD (primary end point). (B) CI of acute grade 2 to 4 GVHD. (C) CI of acute GI GVHD. (D) CI of chronic GVHD (panels B-D: secondary end points). As-treated analyses: (E) CI of grade 1 to 4 acute GVHD (primary end point). (F) CI of grade 2 to 4 GVHD. (G) CI of acute GI GVHD. (H) CI of chronic GVHD (panels F-H: secondary end points).
Recipients of vitamin A have lower cumulative incidence of GVHD compared to placebo. Intent-to-treat analyses: (A) CI of grade acute 1 to 4 GVHD (primary end point). (B) CI of acute grade 2 to 4 GVHD. (C) CI of acute GI GVHD. (D) CI of chronic GVHD (panels B-D: secondary end points). As-treated analyses: (E) CI of grade 1 to 4 acute GVHD (primary end point). (F) CI of grade 2 to 4 GVHD. (G) CI of acute GI GVHD. (H) CI of chronic GVHD (panels F-H: secondary end points).
Summarized intent-to-treat and as-treated analyses for patients who received high-dose vitamin A or placebo
| . | CI . | P value . | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A . | Placebo . | ||
| Intent-to-treat analyses | |||
| Primary end point | |||
| Acute grade 1-4 GVHD at day +100 | 0.125 | 0.2 | .5 |
| Secondary end point | |||
| Acute grade 2-4 GVHD at day +180 | 0.025 | 0.125 | .09 |
| Steroid refractory acute GVHD at day +180 | 0.025 | 0.1 | .17 |
| Acute GI GVHD at day +180 | 0.025 | 0.125 | .09 |
| Chronic GVHD at 1 y | 0.05 | 0.15 | .02 |
| As-treated analyses | |||
| Primary end point | |||
| Acute grade 1-4 GVHD at day +100 | 0.08 | 0.20 | .27 |
| Secondary end points | |||
| Acute grade 2-4 GVHD at day +180 | 0 | 0.125 | .02 |
| Steroid refractory acute GVHD at day +180 | 0 | 0.1 | .049 |
| Acute GI GVHD at day +180 | 0 | 0.125 | .02 |
| Chronic GVHD at 1 y | 0.027 | 0.15 | .01 |
| . | CI . | P value . | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A . | Placebo . | ||
| Intent-to-treat analyses | |||
| Primary end point | |||
| Acute grade 1-4 GVHD at day +100 | 0.125 | 0.2 | .5 |
| Secondary end point | |||
| Acute grade 2-4 GVHD at day +180 | 0.025 | 0.125 | .09 |
| Steroid refractory acute GVHD at day +180 | 0.025 | 0.1 | .17 |
| Acute GI GVHD at day +180 | 0.025 | 0.125 | .09 |
| Chronic GVHD at 1 y | 0.05 | 0.15 | .02 |
| As-treated analyses | |||
| Primary end point | |||
| Acute grade 1-4 GVHD at day +100 | 0.08 | 0.20 | .27 |
| Secondary end points | |||
| Acute grade 2-4 GVHD at day +180 | 0 | 0.125 | .02 |
| Steroid refractory acute GVHD at day +180 | 0 | 0.1 | .049 |
| Acute GI GVHD at day +180 | 0 | 0.125 | .02 |
| Chronic GVHD at 1 y | 0.027 | 0.15 | .01 |
As-treated analyses
Three patients who were randomized to the vitamin A arm were excluded from this analysis because of documented failure to take study drug, or delay in HSCT after ingestion of study drug.
The incidence of grade 1 to 4 acute GVHD by day +100 was 8% in the vitamin A cohort and 20% in recipients of placebo (P = .2) (Figure 2E). CI of acute grade 2 to 4 GVHD was 0% in the vitamin A arm and 12.5% in placebo (P = .02) at day +180 (Figure 2F). CI of acute GI GVHD by day +180 was 0% in the vitamin A arm and 12.5% in placebo (P = .02; Figure 2G). CI of steroid refractory acute GVHD by day +180 was 0% in the vitamin A arm and 10% in placebo (P = .049). CI of chronic GVHD was 2.7% in the vitamin A arm and 15.3% in placebo at 1 year (P = .01; Figure 2H; Table 2). There were no differences in bloodstream infections, transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy, and viremias. Nonrelapse mortality at 1 year was 5% in the vitamin A cohort and 7% in placebo (P = .7). Overall survival was 91.9% in the vitamin A arm and 86.9% in placebo (P = .5; supplemental Table 2).
On adjustment for multiple comparisons of all secondary end points, analyses of acute GVHD lost significance, but chronic GVHD remained statistically significant.
Adverse effects
Asymptomatic grade 3 hyperbilirubinemia occurred at day +30 after HSCT in 1 recipient of vitamin A, possibly attributable to therapy, and resolved without treatment or adverse consequence. This patient did not receive additional doses of vitamin A. No other attributable toxicities occurred. Notably, the 7 patients who received an additional vitamin A dose did not experience toxicities. One patient who received an additional vitamin A dose experienced grade 1 skin GVHD on day +34 after HSCT, which responded to topical and systemic steroids (supplemental Table 1).
Vitamin A and D levels
Serum vitamin A levels measured before conditioning chemotherapy, weekly after oral dosing until day +30, day +60, and day +100 after HSCT were not statistically different between the vitamin A and placebo arms, reflecting the complex nature of vitamin A absorption, storage, and tissue delivery (supplemental Figure 2A). Serum vitamin D levels measured before conditioning chemotherapy, and at day +30, day +60, and day +100 after HSCT were similar between both arms (supplemental Figure 2B).
Correlative studies
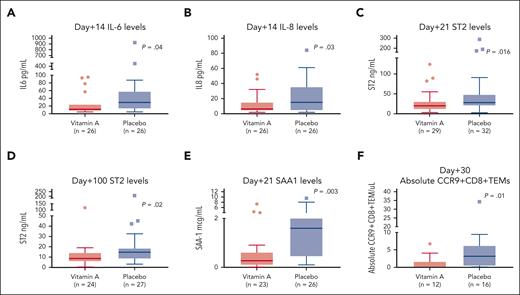
Vitamin A may modulate dendritic cells to produce lower proinflammatory cytokines. Median plasma IL-6 levels were lower at day +14 in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm (Figure 3A; P = .04). Similarly, median plasma IL-8 levels were lower on day +14 (Figure 3B; P = .03; supplemental Table 3).
Correlative studies. (A) Day +14 plasma IL-6 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (B) Day +14 plasma IL-8 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (C) Day +21 plasma ST-2 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (D) Day +100 plasma ST-2 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (E) Day +21 SAA1 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (F) Day +30 absolute CCR9+CD8+ TEM cells are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm.
Correlative studies. (A) Day +14 plasma IL-6 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (B) Day +14 plasma IL-8 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (C) Day +21 plasma ST-2 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (D) Day +100 plasma ST-2 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (E) Day +21 SAA1 levels are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm. (F) Day +30 absolute CCR9+CD8+ TEM cells are lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm.
We then wanted to assess whether ST-2, known to be associated with acute GVHD, was lower in the vitamin A arm. Median plasma ST-2 levels at day +21 and day +100 were lower in the vitamin A arm than in the placebo arm (Figure 3C-D; P = .016 and P = .02, respectively).
In our previous study, we observed higher CCR9+CD8+ effector memory T (TEM) cells in patients with vitamin A levels below the median, which prompted us to characterize these cells in this study. Median absolute CCR9+CD8+ TEM cells at day +30 were lower at 0.1 cells per μL in the vitamin A arm than the placebo arm at 3.1 cells per μL (Figure 3F; P = .01). T-cell characterization at day +100 did not show differences in absolute values of Th17 cells, Th2 or Th1 cells in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (supplemental Figures 4A-E). Median absolute naïve regulatory T cells at day +100 were higher in the vitamin A arm (supplemental Figure 4I; P = .08).
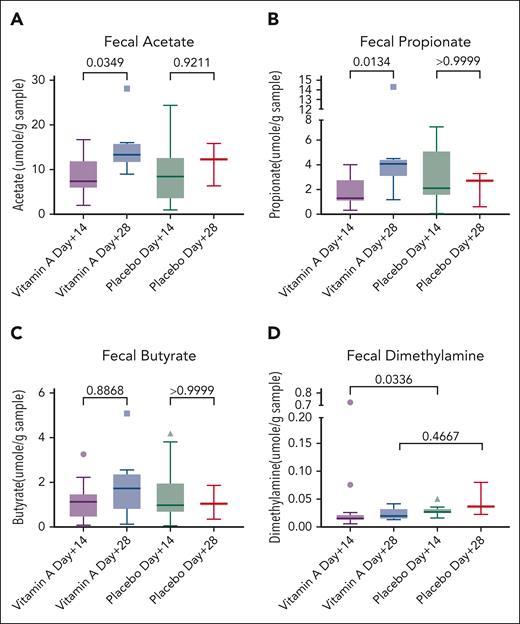
Vitamin A supports beneficial gut microbiome, prompting microbiome and metabolome studies in our patients on study. Fecal acetate increased from day +14 to day +28 in the vitamin A arm (P = .03; Figure 4A), as did fecal propionate (P = .01; Figure 4B) although fecal butyrate was not significantly changed (P = .8; Figure 4C). SCFAs did not increase significantly in the placebo arm (Figures 4A-C). Fecal dimethylamine was lower in the vitamin A arm at day +14 than in the placebo arm (P = .03; Figure 4D).
Fecal metabolomics. (A) Fecal acetate rising in the vitamin A arm over time. (B) Fecal propionate rising in the vitamin A arm over time. (C) Fecal butyrate not statistically significant. (D) Fecal dimethylamine higher in the placebo arm at day +14 than in the vitamin A arm.
Fecal metabolomics. (A) Fecal acetate rising in the vitamin A arm over time. (B) Fecal propionate rising in the vitamin A arm over time. (C) Fecal butyrate not statistically significant. (D) Fecal dimethylamine higher in the placebo arm at day +14 than in the vitamin A arm.
Metagenomic shotgun sequencing of stool did not reveal significant differences in principal component analyses or Shannon diversity index between study arms (data not shown). However, the vitamin A arm showed significant changes in relative abundance of pathogenic species, including lower detection of Candida (P = .049), Aspergillus (P = .018), and Prevotella (P = .006; supplemental Figures 5A-C) and higher potentially beneficial bacteria including Faecalibacteria (P = .048). Zero-inflated generalized linear mixed model analyses (supplemental Methods) showed a statistically significant effect size at species and genus levels at day +14 and day +28 of known beneficial gut microbes in the vitamin A arm (supplemental Figures 6 and 7; supplemental Data set 1 and 2).
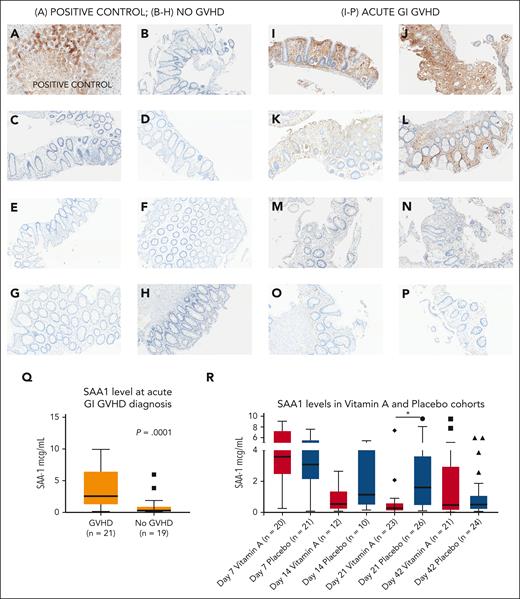
We then wished to examine differences in known vitamin A transport proteins in both cohorts. SAA1 is a retinol transport protein25 that is proinflammatory in some contexts.29 SAA1 levels were significantly lower in the vitamin A arm at day +21 than in the placebo arm (Figure 3E; P = .003; Figure 5R). Additional time points of SAA1 in study patients on day +7 and day +42 did not show differences between study arms (Figure 5R; supplemental Figure 3D,F). Serum SAA1 at day +14 was higher in the placebo arm but not statistically significant, possibly because of small sample size (P = .1; Figure 5R; supplemental Figure 3E). RBP4 and SAA2 levels at days +7, +21, and +42 were similar between arms (supplemental Figure 3A-C, G-I).
Serum amyloid A1 in acute GI GVHD and SAA1 levels in the vitamin A and placebo cohorts. (A) Liver (positive control); SAA1 is strongly expressed in hepatocytes as expected. (B-H) No GVHD: immunohistochemical stain for SAA1 in human colon tissue sections; no SAA1 staining observed. (I-P) Acute GI GVHD: immunohistochemical stain for SAA1 in human GVHD colonic tissue sections. (I-J) Strong SAA1 staining of intestinal epithelium and lamina propria. (K-L) Increased SAA1 superficial density and staining of crypts, lamina propria, and stroma. (M-N) Patchy epithelial SAA1 staining of lamina propria and intestinal epithelial cells. (O-P) Weak focal to patchy SAA1 staining of lamina propria. (Q) SAA1 levels in an independent cohort of 21 patients with acute GI GVHD at time of diagnosis (median day of onset of acute GI GVHD was day +42 after HSCT) and 19 recipients of allogeneic HSCT without acute GVHD at ∼day +42 after HSCT. (R) SAA1 levels at day +7, day +14, day +21, and day +42 after HSCT the vitamin A and placebo study arms. ∗P < .05.
Serum amyloid A1 in acute GI GVHD and SAA1 levels in the vitamin A and placebo cohorts. (A) Liver (positive control); SAA1 is strongly expressed in hepatocytes as expected. (B-H) No GVHD: immunohistochemical stain for SAA1 in human colon tissue sections; no SAA1 staining observed. (I-P) Acute GI GVHD: immunohistochemical stain for SAA1 in human GVHD colonic tissue sections. (I-J) Strong SAA1 staining of intestinal epithelium and lamina propria. (K-L) Increased SAA1 superficial density and staining of crypts, lamina propria, and stroma. (M-N) Patchy epithelial SAA1 staining of lamina propria and intestinal epithelial cells. (O-P) Weak focal to patchy SAA1 staining of lamina propria. (Q) SAA1 levels in an independent cohort of 21 patients with acute GI GVHD at time of diagnosis (median day of onset of acute GI GVHD was day +42 after HSCT) and 19 recipients of allogeneic HSCT without acute GVHD at ∼day +42 after HSCT. (R) SAA1 levels at day +7, day +14, day +21, and day +42 after HSCT the vitamin A and placebo study arms. ∗P < .05.
SAA1 levels in an independent cohort of patients with and without acute GI GVHD, not part of randomized controlled trial
To further explore a possible role for SAA1 in acute GI GVHD, we examined SAA1 levels at time of diagnosis of GVHD in an independent cohort of recipients of allogeneic HSCT with acute GI GVHD (n = 21) and controls who did not develop acute GVHD (n = 19; supplemental Table 4; supplemental Methods). SAA1 levels were significantly higher in patients with acute GI GVHD than in controls (Figure 5Q; P = .0001).
Furthermore, we obtained GI biopsies of recipients of allogeneic HSCT with acute GI GVHD and patients without GVHD and performed immunohistochemistry for SAA1 (supplemental Methods). GI biopsies were not available in meaningful numbers in participants in our randomized trial, thus necessitating this independent cohort of patients. Compared with controls, SAA1 staining was increased in gut epithelium but not crypts in GI GVHD cases (Figures 5B-P).
Finally, we studied SAA1 levels longitudinally in an independent cohort of 130 consecutive recipients of allogeneic HSCT, for whom serum samples were available in our institutional biorepository (supplemental Table 5; supplemental Methods). Day +21 SAA1 levels were higher in the chronic GVHD group than in recipient of allogeneic HSCT who did not develop chronic GVHD; hazard ratio, 1.57; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-2.42; P = .04.
Pertinent negative correlative studies of randomized controlled trial
Levels of IL-6 receptor, glycoprotein-130, IL-22, IL-23, regenerating islet 3α, lipopolysaccharide binding protein, neutrophil extracellular traps, epidermal growth factor, IRAK-1, and neuregulin-1 were not different between arms (supplemental Figures 8A-H; supplemental Figures 9A-H; supplemental Table 3).
Discussion
We conducted a randomized phase 2 study and observed no significant differences in the incidence of acute grade 1 to 4 GVHD between recipients of vitamin A and placebo. The lack of statistical significance was largely driven by the incidence of grade 1 skin GVHD in both cohorts, which was responsive to topical or systemic steroids. Most acute GVHD clinical trials do not consider grade 1 acute GVHD to be relevant and our future planned studies do not plan to include grade 1 GVHD in our analyses.
Our randomized phase 2 study found that a high dose of oral vitamin A given before HSCT reduces chronic GVHD in pediatric recipients of allogeneic HSCT in intent-to-treat and as-treated analyses, and additionally reduces acute GI GVHD in an as-treated analysis. The intervention had no clinically significant adverse effects and cost ∼$1.25 per patient. This strategy is potentially practice changing, particularly in low-resource environments.
Murine studies demonstrate a potentiating effect of vitamin A on acute GVHD.30 We believe that crucial aspects of our strategy allowed safe reduction of GVHD without exacerbation, as might be predicted by a number of preclinical studies.31-33 We gave vitamin A before HSCT when the recipient is in a presumed noninflammatory homeostatic state, favoring the anti-inflammatory regulatory role of vitamin A on resident host gut dendritic cells,9 in contrast to published studies in which vitamin A is given during inflammation and is proinflammatory.34 We hypothesize that the large dose of vitamin A replenished vitamin A stores in the liver, which could later be mobilized during periods of inflammation-drive transient hyporetinolemia.35 Moreover, an immediate local effect of the high dose enteral vitamin A on GI-resident dendritic cells before absorption may have established a more tolerogenic phenotype.
We did consider that, with the large vitamin A dose we were administering, we might see an increase in circulating level, but this was not the case. Vitamin A is absorbed from the intestine via lymphatics and travels to the liver for storage, bypassing the circulation, and is later distributed via transporter proteins when needed.36 Vitamin A levels in the blood are a poor marker of total body vitamin A content because absorption bypasses the circulation,36-38 which further explains the lack of difference in vitamin A levels between the 2 cohorts despite vitamin A supplementation in 1 arm.
Out of an abundance of caution we only treated children with vitamin A levels below the 75th centile of normal range for age. Vitamin A was well tolerated, and we observed generally good compliance despite the large dose, likely because of administration before HSCT, before conditioning chemotherapy-induced nausea and emesis began.
During the initial phases of this study, 7 patients received additional doses of vitamin A at half the initial dose, if vitamin A level dropped below the baseline vitamin A levels. After observing a possible adverse effect at day +30 in 1 patient (transient hyperbilirubinemia) and observing that vitamin A blood levels were not reflective of treatment administered, we chose to omit any further additional half doses of vitamin A to patients even if they met criteria for supplementation. Notably, the patient who experienced a possible adverse effect due to vitamin A had not received an additional dose of vitamin A. Importantly review of vitamin A levels collected in this study after this possible attributable toxicity showed only modest change despite the large dose of vitamin A given, which was confirmed in the levels collected throughout the entire study (supplemental Figure 2). We appreciated this relatively early in the study and review of the literature showed us that enteral vitamin A in entirely absorbed via GI lymphatics. Vitamin A travels via the lymphatics to the liver and is stored there for controlled release into the circulation, explaining why we did not see a boost in blood levels of vitamin A. We, therefore, reduced our focus on blood levels and continued with 1-time dosing only.
Moreover, 2 patients were excluded from as-treated analyses because of significant delays between dosing and proceeding to HSCT (35 days and 63 days from oral vitamin A dose, respectively). We did not know how to safely redose patients with vitamin A in a clinical situation of significant delays between dosing and starting conditioning chemotherapy. To ensure safety, we recommend administering vitamin A within a range of 0 to 7 days before starting chemotherapy. Additionally, in a separate broad analysis of all consecutive recipients of allogeneic HSCT from 2018 to 2020, vitamin A levels were elevated in a quarter of recipients of allogeneic HSCT at baseline, making them ineligible to receive oral vitamin A. Most of these children had prior or ongoing inflammation due to hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), and did not receive vitamin A.
Serendipitously, we were able to avoid administering vitamin A to patients with baseline inflammation, such as children with HLH, because these patients had elevated pre-HSCT vitamin A levels and did not meet criteria for study enrollment. In our recent unpublished work (P. Khandelwal, May 2023), we have observed that patients with HLH have high SAA1 levels at baseline, perhaps reflecting underlying inflammation. We, therefore, postulate that baseline vitamin A levels could be an indirect measure of underlying inflammation and caution against administering high-dose vitamin A to patients with elevated levels at baseline.
We observed favorable changes in the gut microbiome and metabolome in recipients of vitamin A compared with recipients of placebo, in line with published studies demonstrating vitamin A–modulated changes in the gut microbiome. In published work, the gut microbiome and metabolome are modulated via indirect effects of vitamin A on barrier function and gut immune responses,39 prompting our interest in conducting microbiome and metabolome studies. Microbiome studies were corrected for multiple comparisons and the zero-inflated generalized linear mixed model analyses added strength to our findings because it factors antibiotic exposure along with HSCT variables in the analyses, but microbiome studies in general must be interpreted with caution. We believe that the fecal metabolome is a better functional readout of the gut microbiome and found these to be favorable in the vitamin A cohort compared with the placebo arm. Future studies investigating gut barrier function would shed light onto the mechanism by which vitamin A improves the gut metabolome and microbiome. We performed a broad range of hypothesis–driven correlative studies because this, to our knowledge, is the first study of its kind. We found that lower plasma IL-6 levels in vitamin A recipients would be an expected consequence of a more tolerogenic phenotype of gut-resident dendritic cells, supporting our original hypothesis.12 CCR9+CD8+ TEM cells were also lower in the vitamin A arm, similar to our previously published findings,10 likely representing a reduction in the subset of T cells trafficking to the intestinal tract. Rising SCFAs over time support a possible role of microbiome modulation by vitamin A.8 Fecal dimethylamine may be a precursor of trimethylamine, which has a known proinflammatory role in acute GVHD40 (supplemental Figure 10).
In an interesting and unexpected finding, SAA1 levels were significantly lower in the vitamin A arm. SAA1 is a retinol-binding protein produced in the liver and locally in intestinal epithelial cells, and is systemically upregulated during inflammation.29 SAA1 is upregulated by IL-641 and has been implicated in Th17-mediated colitis in inflammatory bowel disease.29 Of note, levels of another better recognized retinol-binding protein, RBP4, typically drop during sepsis,24 whereas SAA1 is upregulated, suggesting that SAA1 might replace the retinol delivery activity of RBP4 during sepsis. RBP4 levels did not differ between study arms, in contrast to SAA1. We compared SAA1 levels in a separate group of children with and without GI GVHD to further investigate this finding, finding elevated SAA1 in those with GVHD. Immunohistochemistry of GI biopsies from children with and without GVHD showed local increase in SAA1 in the biopsies from children with GVHD, further supporting our hypothesis that SAA1 may be playing an active role in promoting GVHD rather than being an acute-phase reactant. SAA-1 levels increase under the influence of IL-6,41 further supporting our proposed mechanism that lower IL-6 levels secreted by tolerogenic dendritic cells led to lower SAA1 levels at day +21. Furthermore, increased SAA1 levels at day +21 was associated with chronic GVHD in an independent cohort of patients, perhaps shedding light onto our observed lower incidence of chronic GVHD. Increased levels of SAA1 may be a response to try to deliver additional retinol to rescue inflamed tissues in GVHD, but it is also possible that higher SAA1 levels in recipients of placebo reflects a direct proinflammatory effect of SAA1 in GVHD, which was more frequent in the placebo arm. Studies are underway to elucidate the role of SAA1 in acute GI GVHD in more detail.
Our finding of reduced chronic GVHD in recipients of vitamin A was surprising and encouraging because progress in identifying effective prophylaxis against chronic GVHD has been slow. We recognize that additional larger studies with correlative studies are needed to understand the precise mechanism of reduction of GVHD. These studies are being planned in adult recipients of HSCT.
We did not observe differences in the incidences of relapse of primary malignancy in either cohort, but our sample size of patients with malignancy was small. Larger studies in adults with underlying malignancies are being planned to address this concern.
Our study has strengths and weaknesses. Importantly, this is, to our knowledge, the first study to address clinical use of vitamin A in this setting, and in a relatively small study we saw significant effects on outcomes with essentially no toxicity. We recognize that survival was excellent in both arms, likely reflecting the outstanding ability of young children to heal after GVHD. However, both acute and chronic GVHD cause important organ injury and reduce quality of life, even in children, and are an important target for improvement. Incomplete availability of biospecimens to perform correlative studies is a limitation of our work. Despite this, we found significant differences between the 2 study arms in several key analyses, providing clear mechanistic hypotheses to be tested in a planned adult study. The effect of vitamin A on gut-resident dendritic cells is central to our hypothesis, and it is a further limitation in that we cannot study these cells directly. We plan to have GI biopsy tissue available for analyses in our adult study as well as further studies of surrogate markers in stool and blood.
We analyzed several end points in this early-stage first study and considered the relevance of correction for multiple comparisons. We believe it is reasonable and usual to compartmentalize considerations of multiple comparisons for the clinical observations and corelative studies. The clinical analyses were analyzed as prespecified in the protocol. We further appreciated that there are different statistical viewpoints on when and how such adjustments should be applied, without a universally accepted standard approach. In the absence of a clear standard, we have chosen to present the data without adjustment but to also show secondary end points with adjustment for multiple comparisons and, with these additional stringent criteria, show that chronic GVHD in the as-treated group remains significant, suggesting a biological signal in this early phase 2 study. In a subsequent larger trial in adults, we will perform focused analyses based on the data generated from this study.
We performed numerous exploratory analyses and corelative studies because of the novelty of our study in an attempt to assess biological signals to study in future studies, but these could increase type 1 error and false positive associations. Additionally, our study has a heterogeneous patient population with varied acute GVHD prophylactic regimens, inherent to pediatric studies. We recognize the correlative findings of our study are several and hypothesis-generating and we have not adjusted biology studies for multiple comparisons. Our data will need to be confirmed in future studies before firm conclusions are drawn. Finally, we did not have a planned interim analysis defined in our study protocol but performed a blinded interim analysis after incomplete enrollment because of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, with an intent of a single look at results. After observing a statistically significant difference in the incidence of chronic GVHD in 1 arm, our medical monitor advised us to unblind the study because of patient safety concerns. We proceeded with unblinding and releasing our results early, recognizing that this could inflate the study type I error, a further limitation of this study. We recognize the importance of replicating and extending these studies to adult recipients of HSCT, and this work is underway.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Patrick McGann, who served as the medical monitor for this study. The authors also thank Ormarie Vasquez Silva and Adesuwa Ekunwe, who served as excellent clinical research coordinators for this study. The authors gratefully acknowledge Ashish R. Kumar for his editorial review. This study was made possible, in part, using the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center’s Nuclear Magnetic Resonance–based metabolomics facility (RRID: SCR_022636).
This study was funded by Gateway for Cancer Research (G-17-300).
Authorship
Contribution: P.K. designed the study, obtained consent from, all patients performed study procedures, and wrote the manuscript; L.L. A.B., and N.L. performed experiments on study; K.E.L. assisted with biospecimen procurement from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center biorepository and dissemination for all experiments; K.B. and C.T. helped identify all eligible patients; H.C. and S.V. assisted with study design, and read the manuscript critically; A.T.-C. was the clinical pharmacist supervising drug dosing; K.N.R. performed SAA1 ELISA experiments; L.R.-R. and M.W.-C. performed fecal metabolomics and analyzed data; D.B.H. performed metagenomic shotgun sequencing and analyzed data; A.L. performed all statistical analyses on study; J.K. assessed baseline vitamin A level in consecutive recipients of allogeneic HSCT over 2 years; G.W. assisted with study design; S.M.D. oversaw the entire study and study design; and all authors reviewed the manuscript critically and approved the final version.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.M.D. has consulted for Novartis, AlloVir, Anthem, and Prolacta. P.K. has consulted for Incyte. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Pooja Khandelwal, Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Immune Deficiency, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, 3333 Burnet Ave, Cincinnati, OH 45229; email: pooja.khandelwal@cchmc.org.
References
Author notes
Deidentified clinical trial data and study protocol will be available, on request, from the corresponding author, Pooja Khandelwal (pooja.khandelwal@cchmc.org).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal