Key Points
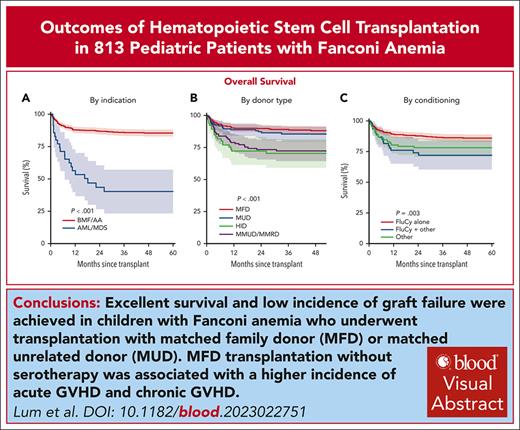
Excellent survival and low incidence of graft failure was obtained in children with FA given HSCT using MFD and MUD.
MFD transplant without serotherapy was associated with higher incidence of acute GVHD and chronic GVHD.
Visual Abstract
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the only established curative option for Fanconi anemia (FA)–associated bone marrow failure (BMF)/aplastic anemia (AA) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML)/myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). We performed a retrospective multicenter study on 813 children with FA undergoing first HSCT between 2010 and 2018. Median duration of follow-up was 3.7 years. Median age at transplant was 8.8 years (IQR, 6.5-18.1). Five-year overall survival (OS), event-free survival (EFS), and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)-free, relapse-free survival (GRFS) were 83% (95% confidence interval [CI], 80-86), 78% (95% CI, 75-81), and 70% (95% CI, 67-74), respectively. OS was comparable between matched family donor (MFD; n = 441, 88%) and matched unrelated donor (MUD; n = 162, 86%) and was superior to that of mismatched family donor (MMFD) or mismatched unrelated donor (MMUD; n = 144, 72%) and haploidentical donor (HID; n = 66, 70%; P < .001). In multivariable analysis, a transplant indication of AML/MDS (vs AA/BMF), use of MMFD/MMUD and HID (vs MFD), and fludarabine-cyclophosphamide (FluCy) plus other conditioning (vs FluCy) independently predicted inferior OS, whereas alemtuzumab vs antithymocyte globulin was associated with better OS. Age ≥10 years was associated with worse EFS and GRFS. Cumulative incidences (CINs) of primary and secondary graft failure were 2% and 3% respectively. CINs of grade 3 to 4 acute GVHD and chronic GVHD were 12% and 8% respectively. The 5-year CIN of secondary malignancy was 2%. These data suggest that HSCT should be offered to patients with FA with AA/BMF at a younger age in the presence of a well-matched donor.
Medscape Continuing Medical Education online

In support of improving patient care, this activity has been planned and implemented by Medscape, LLC and the American Society of Hematology. Medscape, LLC is jointly accredited with commendation by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), to provide continuing education for the healthcare team.
Medscape, LLC designates this Journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
Successful completion of this CME activity, which includes participation in the evaluation component, enables the participant to earn up to 1.0 MOC points in the American Board of Internal Medicine's (ABIM) Maintenance of Certification (MOC) program. Participants will earn MOC points equivalent to the amount of CME credits claimed for the activity. It is the CME activity provider's responsibility to submit participant completion information to ACCME for the purpose of granting ABIM MOC credit.
All other clinicians completing this activity will be issued a certificate of participation. To participate in this journal CME activity: (1) review the learning objectives; (2) study the education content; (3) take the post-test with a 75% minimum passing score and complete the evaluation at https://www.medscape.org/journal/blood; and (4) view/print certificate. For CME questions, see page 1350.
Disclosures
CME questions author Laurie Barclay, freelance writer and reviewer, Medscape, LLC, declares no competing financial interests.
Learning objectives
Upon completion of this activity, participants will:
Describe survival outcomes and secondary malignancy at 5 years for children with Fanconi anemia (FA) undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) from various donor sources, based on a retrospective multicenter study
Determine factors associated with survival outcomes and incidence of graft-versus-host disease in children with FA undergoing HSCT from various donor sources, based on a retrospective multicenter study
Identify clinical implications of outcomes at 5 years for children with FA undergoing HSCT from various donor sources, based on a retrospective multicenter study
Release date: September 19, 2024; Expiration date: September 19, 2025
Introduction
Fanconi anemia (FA) is an inherited DNA repair disorder with an estimated incidence of 1 in 200 000 to 400 000 live births.1 It is a genetically and clinically heterogeneous, rare disorder characterized by congenital and developmental abnormalities, progressive bone marrow failure (BMF), and increased susceptibility to malignancy. Affected patients can present at any age with a severe phenotype in need of complex medical care for multiple congenital malformations and malignant complications early in life, or a more subtle phenotype with hematological and neoplastic complications in their third and fourth decades of life.2 FA is due to mutations of 1 of the at least 22 genes identified starting from 1992, coding for the proteins of the FA pathway that are involved in cytokine overproduction and crosslinker hypersensitivity to DNA repair.2FANCA mutations account for almost two-thirds of cases, FANCC and FANCG for 25%, FANCE and FANCF for a further 8%, and the remaining cases are distributed among the other genes.3 The pattern of inheritance of these mutations is mainly autosomal recessive.
FA has been recognized as the most common cause of inherited BMF or aplastic anemia (AA). The reported cumulative incidence (CIN) of BMF/AA is 90% by the age of 40 years, with a median age of onset at 7 years, and 33% hematological malignancy at a median age of 40 years.4 BMF/AA in FA is strongly associated with the emergence of premalignant clonal aberrations and can transform into myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), which occur in later childhood and in the second or even third decade of life. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the only established potentially curative therapy for hematological abnormalities in FA. The largest retrospective multicenter study conducted by the Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party (SAAWP) and the Pediatric Disease Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) in 795 consecutive adult and pediatric patients with FA who underwent first HSCT between 1972 and 2010 reported that the overall survival (OS) at 5 and 20 years after HSCT was 65% (95% confidence interval [CI], 61-68) and 36% (95% CI, 28-47), respectively. A more recent EBMT SAAWP study, which examined transplant outcomes in adults with FA, demonstrated a poorer transplant outcome in adult patients compared with younger patients, with an OS in the modern era (2009-2014) of 50%.5
There are few studies that examined the outcome of HSCT in children with FA, and published series are mostly single-center experiences. In the large single-center reports by MacMillan et al (n = 130 children and adults with FA, 1995-2012) and Locatelli et al (n = 64 children with FA, 1989-2005), 5-year OS ranged between 38% and 65%.5-9 Therefore, the SAAWP and Pediatric Disease Working Party of the EBMT conducted a multicenter retrospective analysis of data from 813 children with FA undergoing first HSCT between 2010 and 2018.
Methods
Data source
This retrospective study was approved by the scientific review board of the SAAWP of the EBMT (study number 8409081). The EBMT registry provided demographic, laboratory, and clinical data, and a questionnaire was sent to all centers with patients with FA aged <18 years at diagnosis to obtain additional details for the study analyses; 137 centers participated in this study. In accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, all patients and/or their legal guardians gave informed consent for data entry into the EBMT registry database and for its use in analyses.
Study participants
All patients with FA who were aged <18 years at HSCT and received their first allogeneic HSCT between January 2010 and December 2018 were eligible for inclusion. There was a total of 849 pediatric patients with FA in the EBMT database; 36 of them were excluded from the study because of missing donor HLA data.
Definition and end points
The primary end points were OS; event-free survival (EFS); and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)-free, relapse-free survival (GRFS). EFS was defined as survival without graft failure (GF), relapse, and posttransplant malignancy. GRFS was defined as survival without grade 3 to 4 acute GVHD (aGVHD), extensive chronic GVHD (cGVHD), GF, relapse, and posttransplant malignancy. Secondary end points were GF, aGVHD, and cGVHD (overall, limited, and extensive) occurrence.
Statistical analysis
OS, EFS, and GRFS were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier product limit estimation method, and differences in subgroups were assessed by the log-rank test. Median follow-up was determined using the reverse Kaplan-Meier method. Competing risks methods were used for estimating the CINs of grade 2 to 4 and 3 to 4 aGVHD, cGVHD, and secondary malignancies, the competing events being death, GF, relapse, and second transplant. Subgroup differences in aGVHD and cGVHD were evaluated by the Gray test.
Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression was applied to investigate the simultaneous impact of multiple covariates on OS, EFS, and GRFS. All multivariable analysis (MVA) models included the same covariates: donor type (matched unrelated donor [MUD], 10/10 HLA match; mismatched family or unrelated donor [MMFD/MMUD], 9/10 HLA match; and haploidentical donor [HID], ≤8/10 HLA match vs matched family donor [MFD]), age at transplant (in decades), indication for transplant (MDS/AML vs AA/BMF), conditioning (fludarabine-cyclophosphamide [FluCy] + others, non-FluCy vs FluCy), serotherapy (alemtuzumab, none vs antithymocyte globulin [ATG]), total body irradiation (TBI; yes vs no), and ex vivo T-cell depletion (TCD; yes vs no).
Continuous variables are presented in the text summarized as median and interquartile range (IQR), and categorical variables as percentages within the group of patients with available data. All estimates and hazard ratios (HRs) are reported with corresponding 95% CIs in parentheses. All P values were 2-sided and P <.05 was considered significant. Statistical analyses were performed in R version 3.6.0 (R Development Core Team, Vienna, Austria), using packages “survival,” “prodlim,” and “cmprsk.”
Results
Patient and transplantation characteristics
Patient and HSCT characteristics are summarized in Table 1 and supplemental Tables 1 and 2, available on the Blood website. The median duration of follow-up was 3.7 years (IQR, 3.4-4.0). The indications for transplantation were BMF/AA (n = 778, 96%) and AML/MDS (n = 35, 4%; AML, n = 17; MDS, n = 18). Of note, donor type, conditioning, serotherapy, TBI, and ex vivo TCD graft differed significantly between these 2 indications of HSCT. Conditioning regimens used in AML/MDS are listed in supplemental Table 3.
Patient and transplant characteristics
| Variables . | Missing data, n (%) . | All (N = 813) . | BMF/AA (n = 778) . | AML/MDS (n = 35) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year of transplant, n (%) | 0 | .03 | |||
| Before 2014 | 396 (49) | 372 (48) | 24 (79) | ||
| After 2014 | 417 (51) | 406 (52) | 11 (32) | ||
| Median age at transplant, y (IQR) | 0 | 8.8 (6.5-11.5) | 8.8 (6.5-11.4) | 9.9 (7.4-14.0) | .12 |
| Median interval between diagnosis and transplant, y (IQR) | 0 | 2.1 (0.8-4.5) | 2.1 (0.8-4.4) | 1.3 (0.4-5.9) | .27 |
| Male, n (%) | 4 (0.5) | 415 (51) | 396 (51) | 19 (54) | .85 |
| Donor, n (%) | 0 | .007 | |||
| MFD | 441 (54) | 431 (55) | 11 (31) | ||
| MUD | 162 (20) | 154 (20) | 20 (57) | ||
| MMFD/MMUD | 144 (18) | 133 (17) | 11 (31) | ||
| HID (≤ 8/10 HLA matching) | 66 (8) | 60 (8) | 6 (17) | ||
| Stem cell source, n (%) | 3 (0.4) | .503 | |||
| Marrow | 526 (65) | 506 (65) | 20 (57) | ||
| Peripheral blood | 226 (28) | 215 (30) | 11 (31) | ||
| CB | 51 (6) | 47 (6) | 4 (11) | ||
| Marrow + CB | 7 (1) | 7 (1) | 0 (0) | ||
| Ex vivo TCD, n (%) | 14 (2) | 87 (11) | 77 (10) | 10 (31) | <.001 |
| Conditioning regimen, n (%) | 6 (0.7) | ||||
| FluCy | 611 (75.7) | 591 (77) | 20 (57) | <.001 | |
| FluCy + other chemotherapy | 63 (7.8) | 53 (7) | 10 (29) | ||
| Non-FluCy conditioning | 133 (16.5) | 128 (17) | 5 (14) | ||
| Serotherapy, n (%) | 4 (0.5) | .03 | |||
| ATG | 620 (76) | 596 (77) | 24 (71) | ||
| Alemtuzumab | 86 (11) | 78 (10) | 8 (24) | ||
| None | 103 (13) | 101 (13) | 2 (6) | ||
| TBI | 29 (4) | <.001 | |||
| None | 688 (88) | 666 (89) | 22 (65) | ||
| 2-4 Gy | 90 (11) | 79 (11) | 11 (32) | ||
| >8 Gy | 6 (1) | 5 (1) | 1 (3) |
| Variables . | Missing data, n (%) . | All (N = 813) . | BMF/AA (n = 778) . | AML/MDS (n = 35) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year of transplant, n (%) | 0 | .03 | |||
| Before 2014 | 396 (49) | 372 (48) | 24 (79) | ||
| After 2014 | 417 (51) | 406 (52) | 11 (32) | ||
| Median age at transplant, y (IQR) | 0 | 8.8 (6.5-11.5) | 8.8 (6.5-11.4) | 9.9 (7.4-14.0) | .12 |
| Median interval between diagnosis and transplant, y (IQR) | 0 | 2.1 (0.8-4.5) | 2.1 (0.8-4.4) | 1.3 (0.4-5.9) | .27 |
| Male, n (%) | 4 (0.5) | 415 (51) | 396 (51) | 19 (54) | .85 |
| Donor, n (%) | 0 | .007 | |||
| MFD | 441 (54) | 431 (55) | 11 (31) | ||
| MUD | 162 (20) | 154 (20) | 20 (57) | ||
| MMFD/MMUD | 144 (18) | 133 (17) | 11 (31) | ||
| HID (≤ 8/10 HLA matching) | 66 (8) | 60 (8) | 6 (17) | ||
| Stem cell source, n (%) | 3 (0.4) | .503 | |||
| Marrow | 526 (65) | 506 (65) | 20 (57) | ||
| Peripheral blood | 226 (28) | 215 (30) | 11 (31) | ||
| CB | 51 (6) | 47 (6) | 4 (11) | ||
| Marrow + CB | 7 (1) | 7 (1) | 0 (0) | ||
| Ex vivo TCD, n (%) | 14 (2) | 87 (11) | 77 (10) | 10 (31) | <.001 |
| Conditioning regimen, n (%) | 6 (0.7) | ||||
| FluCy | 611 (75.7) | 591 (77) | 20 (57) | <.001 | |
| FluCy + other chemotherapy | 63 (7.8) | 53 (7) | 10 (29) | ||
| Non-FluCy conditioning | 133 (16.5) | 128 (17) | 5 (14) | ||
| Serotherapy, n (%) | 4 (0.5) | .03 | |||
| ATG | 620 (76) | 596 (77) | 24 (71) | ||
| Alemtuzumab | 86 (11) | 78 (10) | 8 (24) | ||
| None | 103 (13) | 101 (13) | 2 (6) | ||
| TBI | 29 (4) | <.001 | |||
| None | 688 (88) | 666 (89) | 22 (65) | ||
| 2-4 Gy | 90 (11) | 79 (11) | 11 (32) | ||
| >8 Gy | 6 (1) | 5 (1) | 1 (3) |
Of 87 patients (11%) who received an ex vivo TCD graft, 13 (15%) were received transplantation from MFD, 16 (19%) from MUD, 9 (10%) from MMFD/MMUD, and 49 (56%) from HID. The TCD methods were CD34+ cell selection (n = 15, 18%), CD3+ cell depletion (n = 8, 9%), T-cell receptor αβ (TCRαβ)–positive TCD (n = 25, 29%), and unknown in 37 (44%). Of 96 patients (12%) who received TBI, the donors were MFD (n = 19, 20%), MUD (n = 26, 27%), MMFD/MMUD (n = 18, 19%), and HID (n = 33, 34%).
Engraftment and GF
The median time to neutrophil engraftment was 15 days (95% CI, 14-15) and the CIN of neutrophil recovery by day 100 was 95% (93-96). The median time to platelet engraftment was 20 days (IQR, 19-20 days) and the CIN by day 100 was 88% (86-91).
The CINs of primary and secondary GF were 2% (95% CI, 1-3) and 3% (95% CI, 2-4), respectively. Of 38 patients with primary (n = 17) and secondary (n = 21) GF, 7 patients (19%) received TBI. The use of TBI did not correlate with the CIN of GF. Without TBI, 5-year GF rate was 5% (95% CI, 3-6), compared with 7% (2%-13%) with TBI (P = .2).
OS
The 1-year and 5-year OS after transplant was 87% (95% CI, 84-89) and 83% (95% CI, 80-86), respectively, for the entire cohort.
In univariable analysis (Table 2), OS was significantly inferior in patients aged ≥10 years (P = .009) and in patients who received transplantation for AML/MDS (P < .001; Figure 1A). OS was comparable between MFD and MUD and it was superior to that of MMFD/MMUD and HID (P < .001; Figure 1B). OS was also influenced by stem cell source (P = .02), conditioning regimen (P = .003; Figure 1C), serotherapy (P = .05; Figure 1D), and TBI (P = .004). In MVA, a transplant indication of AML/MDS compared with AA/BMF (HR, 4.47; 95% CI, 2.58-7.74; P < .001), and MMFD/MMUD (HR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.26-3.26; P = .004) and HID (HR 2.48; 95% CI, 1.14-5.40; P = .02) compared with MFD and FluCy plus other conditioning compared with FluCy (HR, 1.81;95% CI, 1.00-3.31; P = .05), were independent predictors of worse OS, whereas alemtuzumab compared with ATG was associated with a better OS (HR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.14-0.77; P = .01; Table 3).
Univariable analysis of OS, EFS, GVHD, GRFS, grade 2 to 4 aGVHD, and cGVHD, stratified by baseline characteristics
| . | OS (95% CI) . | EFS (95% CI) . | GRFS (95% CI) . | aGVHD grade 2-4 (95% CI) . | aGVHD grade 3-4 (95% CI) . | cGVHD (95% CI) . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-y OS . | P value . | 5-y EFS . | P value . | 5-y GRFS . | P value . | Day-100 aGVHD . | P value . | Day-100 aGVHD . | P value . | 5-y cGVHD . | P value . | |
| Year of transplant | .6 | .5 | .3 | .03 | .9 | .2 | ||||||
| Before 2014 (n = 396) | 83% (79-87) | 78% (73-82) | 69% (64-74) | 26% (22-30) | 12% (9-15) | 14% (10-18) | ||||||
| After 2014 (n = 417) | 84% (80-88) | 78% (74-83) | 72% (67-77) | 20% (16-24) | 13% (9-16) | 10% (7-13) | ||||||
| Age at transplant | .009 | <.001 | .2 | .07 | .09 | |||||||
| <10 y (n = 507) | 86% (83-89) | 83% (79-86) | 76% (72-80) | <.001 | 21% (18-25) | 11% (8-13) | 10% (7-13) | |||||
| ≥10 y (n = 306) | 78% (73-83) | 70% (65-76) | 61% (55-67) | 26% (21-31) | 15% (11-19) | 15% (10-20) | ||||||
| Interval between diagnosis and transplant | .6 | .7 | .7 | .2 | .3 | >.99 | ||||||
| <12 mo (n = 242) | 81% (75-86) | 78% (72-83) | 69% (63-76) | 20% (15-25) | 10% (6-14) | 11% (7-13) | ||||||
| 12-24 mo (n = 143) | 87% (90-93) | 81% (74-88) | 74% (65-82) | 21% (14-28) | 11% (6-17) | 13% (6-20) | ||||||
| >24 mo (n = 428) | 83% (80-87) | 77% (73-81) | 70% (65-75) | 26% (21-30) | 14% (11-17) | 12% (8-16) | ||||||
| Sex | .6 | .3 | .4 | .7 | .8 | .9 | ||||||
| Male (n = 415) | 84% (80-88) | 80% (75-84) | 72% (67-77) | 24% (20-28) | 12% (9-15) | 12% (8-15) | ||||||
| Female (n = 394) | 83% (79-87) | 76% (72-81) | 69% (64-74) | 23% (18-27) | 13% (9-16) | 12% (8-16) | ||||||
| Indication for transplant | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | .03 | >.99 | .4 | ||||||
| BMF/AA (n = 778) | 85% (83-88) | 80% (77-83) | 72% (69-76) | 22% (19-25) | 12% (10-15) | 12% (10-15) | ||||||
| AML/MDS (n = 35) | 40% (23-57) | 33% (17-49) | 32% (15-49) | 38% (22-55) | 12% (1-23) | 7% (0-15) | ||||||
| Donor | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | .12 | ||||||
| MFD (n = 441) | 88% (85-91) | 85% (81-89) | 80% (76-85) | 17% (14-21) | 8% (5-11) | 10% (7-14) | ||||||
| MUD (n = 162) | 86% (80-91) | 80% (73-86) | 69% (62-77) | 29% (22-36) | 15% (10-21) | 15% (9-21) | ||||||
| MMFD/MMUD (n = 144) | 72% (64-80) | 62% (54-71) | 49% (39-58) | 36% (28-44) | 24% (17-32) | 16% (9-23) | ||||||
| HID (n = 66) | 70% (59-82) | 62% (50-74) | 58% (46-70) | 19% (9-28) | 8% (1-15) | 8% (1-14) | ||||||
| Stem cell source | .02 | .3 | .6 | .3 | .7 | .08 | ||||||
| Marrow (n = 526) | 86% (83-89) | 80% (76-83) | 72% (68-76) | 22% (18-26) | 13% (10-16) | 10% (7-13) | ||||||
| Peripheral blood (n = 226) | 79% (74-85) | 77% (71-83) | 68% (62-75) | 26% (20-32) | 12% (7-16) | 16% (10-22) | ||||||
| CB (n = 58) | 76% (65-88) | 73% (61-85) | 67% (54-80) | 18% (8-28) | 9% (1-16) | 17% (6-29) | ||||||
| Ex vivo TCD | .1 | .05 | .2 | .3 | .13 | .2 | ||||||
| Yes (n = 87) | 76% (67-86) | 71% (62-81) | 65% (54-76) | 19% (10-27) | 7% (2-12) | 8% (2-15) | ||||||
| No (n = 712) | 84% (81-87) | 79% (76-82) | 72% (68-76) | 23% (20-27) | 13% (10-15) | 13% (10-16) | ||||||
| Conditioning | .003 | .029 | .029 | <.001 | .06 | .013 | ||||||
| FluCy (n = 611) | 86% (83-89) | 80% (77-84) | 73% (69-77) | 17% (14-20) | 10% (8-13) | 10% (7-13) | ||||||
| FluCy + other chemotherapy (n = 63) | 72% (60-84) | 66% (54-78) | 56% (42-70) | 37% (25-49) | 17% (7-26) | 15% (5-25) | ||||||
| Non-FluCy conditioning (n = 133) | 78% (71-86) | 76% (68-84) | 69% (60-77) | 41% (32-50) | 17% (10-24) | 21% (12-29) | ||||||
| Serotherapy | .05 | .2 | .016 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | ||||||
| ATG (n = 620) | 82% (79-85) | 76% (72-93) | 69% (64-73) | 23% (20-27) | 13% (11-16) | 12% (9-15) | ||||||
| Alemtuzumab (n = 86) | 93% (88-98) | 86% (79-93) | 85% (77-93) | 7% (2-13) | 0% | 4% (0-8) | ||||||
| None (n = 103) | 82% (74-90) | 81% (73-89) | 68% (57-79) | 35% (26-45) | 17% (9-24) | 24% (14-35) | ||||||
| TBI | .004 | <.001 | .004 | .9 | >.99 | .9 | ||||||
| Yes (n = 96) | 73% (64-82) | 65% (55-75) | 56% (45-67) | 23% (14-32) | 12% (6-19) | 11% (4-18) | ||||||
| No (n = 688) | 85% (82-88) | 80% (77-83) | 73% (69-76) | 23% (20-27) | 12% (10-15) | 12% (9-15) | ||||||
| . | OS (95% CI) . | EFS (95% CI) . | GRFS (95% CI) . | aGVHD grade 2-4 (95% CI) . | aGVHD grade 3-4 (95% CI) . | cGVHD (95% CI) . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-y OS . | P value . | 5-y EFS . | P value . | 5-y GRFS . | P value . | Day-100 aGVHD . | P value . | Day-100 aGVHD . | P value . | 5-y cGVHD . | P value . | |
| Year of transplant | .6 | .5 | .3 | .03 | .9 | .2 | ||||||
| Before 2014 (n = 396) | 83% (79-87) | 78% (73-82) | 69% (64-74) | 26% (22-30) | 12% (9-15) | 14% (10-18) | ||||||
| After 2014 (n = 417) | 84% (80-88) | 78% (74-83) | 72% (67-77) | 20% (16-24) | 13% (9-16) | 10% (7-13) | ||||||
| Age at transplant | .009 | <.001 | .2 | .07 | .09 | |||||||
| <10 y (n = 507) | 86% (83-89) | 83% (79-86) | 76% (72-80) | <.001 | 21% (18-25) | 11% (8-13) | 10% (7-13) | |||||
| ≥10 y (n = 306) | 78% (73-83) | 70% (65-76) | 61% (55-67) | 26% (21-31) | 15% (11-19) | 15% (10-20) | ||||||
| Interval between diagnosis and transplant | .6 | .7 | .7 | .2 | .3 | >.99 | ||||||
| <12 mo (n = 242) | 81% (75-86) | 78% (72-83) | 69% (63-76) | 20% (15-25) | 10% (6-14) | 11% (7-13) | ||||||
| 12-24 mo (n = 143) | 87% (90-93) | 81% (74-88) | 74% (65-82) | 21% (14-28) | 11% (6-17) | 13% (6-20) | ||||||
| >24 mo (n = 428) | 83% (80-87) | 77% (73-81) | 70% (65-75) | 26% (21-30) | 14% (11-17) | 12% (8-16) | ||||||
| Sex | .6 | .3 | .4 | .7 | .8 | .9 | ||||||
| Male (n = 415) | 84% (80-88) | 80% (75-84) | 72% (67-77) | 24% (20-28) | 12% (9-15) | 12% (8-15) | ||||||
| Female (n = 394) | 83% (79-87) | 76% (72-81) | 69% (64-74) | 23% (18-27) | 13% (9-16) | 12% (8-16) | ||||||
| Indication for transplant | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | .03 | >.99 | .4 | ||||||
| BMF/AA (n = 778) | 85% (83-88) | 80% (77-83) | 72% (69-76) | 22% (19-25) | 12% (10-15) | 12% (10-15) | ||||||
| AML/MDS (n = 35) | 40% (23-57) | 33% (17-49) | 32% (15-49) | 38% (22-55) | 12% (1-23) | 7% (0-15) | ||||||
| Donor | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | .12 | ||||||
| MFD (n = 441) | 88% (85-91) | 85% (81-89) | 80% (76-85) | 17% (14-21) | 8% (5-11) | 10% (7-14) | ||||||
| MUD (n = 162) | 86% (80-91) | 80% (73-86) | 69% (62-77) | 29% (22-36) | 15% (10-21) | 15% (9-21) | ||||||
| MMFD/MMUD (n = 144) | 72% (64-80) | 62% (54-71) | 49% (39-58) | 36% (28-44) | 24% (17-32) | 16% (9-23) | ||||||
| HID (n = 66) | 70% (59-82) | 62% (50-74) | 58% (46-70) | 19% (9-28) | 8% (1-15) | 8% (1-14) | ||||||
| Stem cell source | .02 | .3 | .6 | .3 | .7 | .08 | ||||||
| Marrow (n = 526) | 86% (83-89) | 80% (76-83) | 72% (68-76) | 22% (18-26) | 13% (10-16) | 10% (7-13) | ||||||
| Peripheral blood (n = 226) | 79% (74-85) | 77% (71-83) | 68% (62-75) | 26% (20-32) | 12% (7-16) | 16% (10-22) | ||||||
| CB (n = 58) | 76% (65-88) | 73% (61-85) | 67% (54-80) | 18% (8-28) | 9% (1-16) | 17% (6-29) | ||||||
| Ex vivo TCD | .1 | .05 | .2 | .3 | .13 | .2 | ||||||
| Yes (n = 87) | 76% (67-86) | 71% (62-81) | 65% (54-76) | 19% (10-27) | 7% (2-12) | 8% (2-15) | ||||||
| No (n = 712) | 84% (81-87) | 79% (76-82) | 72% (68-76) | 23% (20-27) | 13% (10-15) | 13% (10-16) | ||||||
| Conditioning | .003 | .029 | .029 | <.001 | .06 | .013 | ||||||
| FluCy (n = 611) | 86% (83-89) | 80% (77-84) | 73% (69-77) | 17% (14-20) | 10% (8-13) | 10% (7-13) | ||||||
| FluCy + other chemotherapy (n = 63) | 72% (60-84) | 66% (54-78) | 56% (42-70) | 37% (25-49) | 17% (7-26) | 15% (5-25) | ||||||
| Non-FluCy conditioning (n = 133) | 78% (71-86) | 76% (68-84) | 69% (60-77) | 41% (32-50) | 17% (10-24) | 21% (12-29) | ||||||
| Serotherapy | .05 | .2 | .016 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | ||||||
| ATG (n = 620) | 82% (79-85) | 76% (72-93) | 69% (64-73) | 23% (20-27) | 13% (11-16) | 12% (9-15) | ||||||
| Alemtuzumab (n = 86) | 93% (88-98) | 86% (79-93) | 85% (77-93) | 7% (2-13) | 0% | 4% (0-8) | ||||||
| None (n = 103) | 82% (74-90) | 81% (73-89) | 68% (57-79) | 35% (26-45) | 17% (9-24) | 24% (14-35) | ||||||
| TBI | .004 | <.001 | .004 | .9 | >.99 | .9 | ||||||
| Yes (n = 96) | 73% (64-82) | 65% (55-75) | 56% (45-67) | 23% (14-32) | 12% (6-19) | 11% (4-18) | ||||||
| No (n = 688) | 85% (82-88) | 80% (77-83) | 73% (69-76) | 23% (20-27) | 12% (10-15) | 12% (9-15) | ||||||
Kaplan-Meier estimates are given for OS, EFS, and GRFS, with group differences tested by log-rank tests, and CINs are given for all other outcomes, with group differences tested by the Gray test. All estimates are reported with 95% CIs in parentheses.
Overall survival of 813 children with FA undergoing HSCT. OS stratified by transplant indication (A), donor type (B), conditioning regimen (C), and use of serotherapy (D).
Overall survival of 813 children with FA undergoing HSCT. OS stratified by transplant indication (A), donor type (B), conditioning regimen (C), and use of serotherapy (D).
Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models of OS, EFS, GVHD, and GRFS
| . | OS . | EFS . | GRFS . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) . | P value . | HR (95% CI) . | P value . | HR (95% CI) . | P value . | |
| Donor | ||||||
| MFD | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| MUD | 1.10 (0.62-1.95) | .8 | 1.33 (0.81-2.17) | .3 | 1.80 (1.20-2.70) | .004 |
| HID | 2.48 (1.14-5.40) | .02 | 4.29 (2.11-8.70) | <.001 | 3.67 (1.99-6.77) | <.001 |
| MMFD/MMUD | 2.03 (1.26-3.26) | .004 | 2.7 (1.83-4.12) | <.001 | 3.35 (2.37-4.74) | <.001 |
| Age at transplant (decades) | 1.66 (0.98-2.79) | .06 | 1.87 (1.18-2.95) | .007 | 1.62 (1.1-2.39) | .01 |
| Transplant indication | ||||||
| AA/BMF | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| AML/MDS | 4.47 (2.58-7.74) | <.001 | 3.66 (2.22-6.04) | <.001 | 2.42 (1.51-3.88) | <.001 |
| Conditioning | ||||||
| FluCy alone | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| FluCy + other | 1.81 (1.00-3.31) | .05 | 1.52 (0.90-2.55) | .12 | 1.59 (1.02-2.47) | .04 |
| Other | 1.51 (0.93-2.44) | .09 | 1.02 (0.64-1.62) | .9 | 1.26 (0.86-1.84) | .2 |
| Serotherapy | ||||||
| ATG | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Alemtuzumab | 0.33 (0.14-0.77) | .01 | 0.62 (0.34-1.14) | .12 | 0.42 (0.23-0.74) | .003 |
| No serotherapy | 1.13 (0.63-2.05) | .7 | 0.92 (0.53-1.61) | .8 | 0.99 (0.63-1.55) | >.99 |
| TBI | ||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.27 (0.74-2.17) | .4 | 1.19 (0.74-1.89) | .5 | 1.12 (0.75-1.68) | .6 |
| Ex vivo TCD | ||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 0.76 (0.38-1.52) | .4 | 0.62 (0.33-1.16) | .14 | 0.6 (0.35-1.03) | .06 |
| . | OS . | EFS . | GRFS . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) . | P value . | HR (95% CI) . | P value . | HR (95% CI) . | P value . | |
| Donor | ||||||
| MFD | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| MUD | 1.10 (0.62-1.95) | .8 | 1.33 (0.81-2.17) | .3 | 1.80 (1.20-2.70) | .004 |
| HID | 2.48 (1.14-5.40) | .02 | 4.29 (2.11-8.70) | <.001 | 3.67 (1.99-6.77) | <.001 |
| MMFD/MMUD | 2.03 (1.26-3.26) | .004 | 2.7 (1.83-4.12) | <.001 | 3.35 (2.37-4.74) | <.001 |
| Age at transplant (decades) | 1.66 (0.98-2.79) | .06 | 1.87 (1.18-2.95) | .007 | 1.62 (1.1-2.39) | .01 |
| Transplant indication | ||||||
| AA/BMF | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| AML/MDS | 4.47 (2.58-7.74) | <.001 | 3.66 (2.22-6.04) | <.001 | 2.42 (1.51-3.88) | <.001 |
| Conditioning | ||||||
| FluCy alone | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| FluCy + other | 1.81 (1.00-3.31) | .05 | 1.52 (0.90-2.55) | .12 | 1.59 (1.02-2.47) | .04 |
| Other | 1.51 (0.93-2.44) | .09 | 1.02 (0.64-1.62) | .9 | 1.26 (0.86-1.84) | .2 |
| Serotherapy | ||||||
| ATG | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Alemtuzumab | 0.33 (0.14-0.77) | .01 | 0.62 (0.34-1.14) | .12 | 0.42 (0.23-0.74) | .003 |
| No serotherapy | 1.13 (0.63-2.05) | .7 | 0.92 (0.53-1.61) | .8 | 0.99 (0.63-1.55) | >.99 |
| TBI | ||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.27 (0.74-2.17) | .4 | 1.19 (0.74-1.89) | .5 | 1.12 (0.75-1.68) | .6 |
| Ex vivo TCD | ||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 0.76 (0.38-1.52) | .4 | 0.62 (0.33-1.16) | .14 | 0.6 (0.35-1.03) | .06 |
Patient age at transplant are in decades. Effect estimates are given with 95% CIs. Corresponding P values are calculated using the Wald test.
A total of 123 patients died during follow-up, with 120 deaths occurring in the first 5-years after transplant. The causes of death were transplant-related mortality in 93 patients (76%; GVHD [n = 40, 33%], infection [n = 34, 28%], organ failure [n = 7, 6%], toxicity [n = 4, 3%], and other [n = 8, 6%]), relapse (n = 14, 11%), secondary malignancy (n = 4, 3%), other causes (n = 6, 5%) and missing in 6 (5%). The 5-year CIN of death due to GVHD is 5% (95% CI, 3-7) with serotherapy, and 9% (95% CI, 3-15) without serotherapy (P = .045). The 5-year CIN of death due to infection was 5% (95% CI, 3-7) and 2% (95% CI, 0-5) in patients who did or did not receive serotherapy, respectively (P = .2).
EFS
One-year EFS and 5-year EFS were 82% (95% CI, 79-84) and 78% (95% CI, 75-81), respectively, for the entire cohort. EFS was also influenced by age of ≥10 years at transplant (P < .001; Figure 2A), indication of transplant (P < .001), donor type (P < .001), and use of TBI (P < .001). MVA confirmed that age of ≥10 years (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.18-2.95; P = .007), AML/MDS compared with AA/BMF (HR, 3.66; 95% CI, 2.22-6.04; P < .001), MMFD/MMUD (HR, 2.75; 95% CI, 1.83-4.12; P < .001), and HID compared with MFD (HR, 4.29; 95% CI, 2.11-8.70; P < .001) were significant risk factors for EFS.
Event-free survival and GVHD rates of 813 children with FA undergoing HSCT. EFS stratified by age at transplant (A) and GRFS by use of serotherapy (B). CINs of grade 2 to 4 aGVHD (C) and of cGVHD (D).
Event-free survival and GVHD rates of 813 children with FA undergoing HSCT. EFS stratified by age at transplant (A) and GRFS by use of serotherapy (B). CINs of grade 2 to 4 aGVHD (C) and of cGVHD (D).
GVHD
The CIN of grade 2 to 4 and 3 to 4 aGVHD were 23% (95% CI, 20-26) and 12% (95% CI, 10-15) by day 100 after transplant (Figure 2C).
Day-100 grade 2 to 4 aGVHD was 17% (95% CI, 14-21), 29% (95% CI, 22-36), 36% (95% CI, 28-44), and 19% (95% CI, 9-28) in MFD, MUD, MMFD/MMUD, and HID transplants, respectively (P < .001). In the same groups, the CINs of grade 3 to 4 aGVHD were 8% (95% CI, 5-11), 15% (95% CI, 10-21), 24% (95% CI, 17-32), and 8% (95% CI, 1-15), respectively (P < .001).
The use of alemtuzumab was associated with lowest aGVHD (grade 2-4, 7% [95% CI, 2-13]; none had grade 3-4) compared with ATG (grade 2-4, 23% [95% CI, 20-27]; grade 3-4, 13% [95% CI, 11-16]) and no serotherapy (grade 2-4, 35% [95% CI, 26-45]; grade 3-4, 17% [95% CI, 9-24]). The effects of serotherapy on aGVHD grade 2 to 4 and grade 3 to 4 were both significant at P < .001.
The 1-year and 5-year CINs of cGVHD were 8% (95% CI, 6-10) and 12% (95% CI, 9-15); 4% (95% CI, 3-6) and 6% (95% CI, 4-8) for limited cGVHD; and 4% (95% CI, 2-5) and 5% (95% CI, 3-7) for extensive cGVHD (Figure 2D). Alemtuzumab was significantly associated with lower 5-year cGVHD (4%; [95% CI, 0-8]) compared with ATG (12% [95% CI, 9-15]) and no serotherapy (24% [95% CI, 14-35]; P < .001).
GRFS
GRFS for the entire cohort was 73% (95% CI, 69-76) at 1 year, and 70% (95% CI, 67-74) at 5 years after transplant. Age of ≥10 years at transplant (P < .001), indication of transplant (P < .001), donor type (P < .001), serotherapy (P = .015), and use of TBI (P = .004) had a significant influence on GRFS. In MVA, age of ≥10 years (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.1-2.39; P = .01), AML/MDS compared with BMF/AA (HR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.51-3.88; P < .001), donor types other than MFD (MUD [HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.20-2.70; P = .004]; MMFD/MMUD [HR, 3.35; 95% CI, 2.37-4.74; P < .001]; and HID [HR, 3.67; 95% CI, 1.99-6.77; P < .001]) were associated with worse GRFS, whereas alemtuzumab compared with ATG correlated with a better GRFS (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.23-0.74; P = .003; Figure 2B).
Secondary malignancy
The CIN of secondary malignancy was 2% (95% CI, 1-3) by 5 years, and 3 patients developed secondary malignancy 5 years after transplant. Of 14 secondary cancers, 4 had leukemia, 1 MDS, 2 lymphoma, 1 histiocytic disorder, 5 solid tumors, and unspecified in 1 patient. Of 7 who had lymphohematopoietic malignancies, 1 patient with non-Hodgkin lymphoma was reported to be donor in origin, 5 were host in origin, and 1 was unknown. Five had received TBI during the preparation, 1 had grade 2 to 4 aGVHD and progressed to cGVHD, and 1 had cGVHD.The total duration of follow-up in the 16 cases who developed secondary malignancies is 60.1 months (unadjusted median IQR, 23.7-67.0).
Transplant outcomes for BMF/AA
In subgroup analysis for 778 patients who received transplantation for BMF/AA, 5-year OS, EFS, and GRFS were 85% (95% CI, 83-88), 80% (95% CI, 77-83), and 72% (95% CI, 69-76) respectively (supplemental Table 4; supplemental Figure 1A-B). On MVA for OS, MMUD/MMFD (HR, 2.34; 95% CI, 1.40-3.91; P = .001) and HID (HR 2.73; 95% CI, 1.40-3.91; P = .03) compared with MFD, FluCy plus other chemotherapy (HR, 2.17; 95% CI, 1.11-4.24; P = .02) and other conditioning (HR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.11-3.04 P = .02) compared with FluCy were independent negative predictors, whereas alemtuzumab (HR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.12-0.89) compared with ATG was an independent positive predictor (supplemental Table 4). EFS was only independently influenced by donor type. Compared with MFD, MUD (HR, 4.83; 95% CI, 2.15-10.86; P < .001), MMFD/MMUD (HR, 2.34; 95% CI, 1.40-3.91; P < .001), and HID (HR, 2.73; 95% CI, 1.10-6.79; P = .003) were associated with lower EFS. On MVA for GRFS, age of ≥10 years (HR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.16-2.65; P = .008), MUD (HR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.28-3.00; P = .002), MMFD/MMUD (HR, 3.85; 95% CI, 1.95-7.59; P < .001), and HID (HR ,3.74; 95% CI, 2.60-5.38; P < .001) were independent negative predictors, and alemtuzumab (HR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.16-0.64) was an independent positive predictor. Similar to the observation in the entire cohort, grade 2 to 4 aGVHD was significantly influenced by donor (P < .001), conditioning (P = .001), and serotherapy (P < .001). For cGVHD, FluCy (10% [7-13] vs FluCy plus others, 15% [95% CI, 4-27] vs non-FluCy, 21% [95% CI, 12-29]; P = .01) and alemtuzumab (4% [95% CI, 0-9] vs ATG, 12% [95% CI, 9-15] vs none, 24% [95% CI, 14-36]; P = .002) was significantly associated with lower 5-year cGVHD.
Impact of serotherapy in MFD transplant
Of 441 patients who received MFD transplant, 74% (n = 324) had ATG, 7% had alemtuzumab (n = 33), and 19% (n = 83) did not receive any serotherapy. Five-year OS was 97% (95% CI, 91-100) after alemtuzumab, 88% (95% CI, 84-92) after ATG, and 87% (95% CI, 80-95) after no serotherapy (P = .3; Figure 3A). CIN of grade 2 to 4 aGVHD was significantly higher in transplant without serotherapy (34% [95% CI, 23-44]) compared with 14% (95% CI, 10-18) after ATG and 7% (95% CI, 0-16) after alemtuzumab (P < .001; Figure 3B). Again, transplant without serotherapy had the highest grade 3 to 4 aGVHD at 16% (95% CI, 8-24) compared with 6% (95% CI, 4-9) after ATG and 0% after alemtuzumab (P = .003). A similar observation was found in cGVHD: 25% (95% CI, 13-37) after transplant without serotherapy, 8% (95% CI, 4-11) after ATG, and 6% (95% CI, 0-15) after alemtuzumab (P < .001; Figure 3C). In MFD transplant, GRFS was 96% (95% CI, 90-100) after alemtuzumab, 81% (95% CI, 75-86) after ATG, and 72% (95% CI, 61-84) in transplant without serotherapy (P = .017; Figure 3D).
Outcomes in MFD transplants, stratified by serotherapy. (A) OS, (B) CINs of grade 2 to 4 aGVHD, (C) cGVHD, and (D) GRFS.
Outcomes in MFD transplants, stratified by serotherapy. (A) OS, (B) CINs of grade 2 to 4 aGVHD, (C) cGVHD, and (D) GRFS.
CB transplant in FA
Of 58 cord blood (CB) transplants, 25 (43%) were MFD (19 CB only; 6 CB plus marrow), 6 (10%) were MUD and 27 (47%) MMUD. Two of 6 MUD CB recipients died before 6 months; 1 died of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease, and 1 died of infection. Five-year OS after CB transplant was 91% (95% CI, 78-100) and 66% (95% CI, 49-84) in MFD and MMUD, respectively (P = .05). EFS was significantly lower in MMUD (59% [95% CI, 41-78]), compared with 91% (95% CI, 78-100) in MFD (P = .012). Similar results were observed in GRFS with 54% (95% CI, 34-74) and 88% (95% CI, 73-100) in MMFD and MFD, respectively (P = .008). Grade 2 to 4 and 3 to 4 aGVHD were higher in MMUD compared with MFD (31% [95% CI, 13-49] compared with 4% [95% CI, 0-12], P = .015; and 19% [95% CI, 4-34] compared with 0%, P = .025, respectively). Five-year cGVHD was higher in MMUD at 23% (95% CI, 5-40), compared with 6% (95% CI, 0-16) in MFD (P = .12).
HID transplant in FA
In 66 HID transplants, 47 (71%) had ex vivo TCD, 14 (21%) had in vivo TCD with posttransplant cyclosphosphamide (PTCY), 2 (3%) had both ex vivo TCD and PTCY, and TCD method was unspecified in 3 patients (5%). The indications of HID transplant were AA/BMF (n = 60, 91%) and AML/MDS (n = 6, 9%). One-year OS was 72% (95% CI, 59-85) in ex vivo TCD, compared with 79% (95% CI, 57-100) in PTCY (P = .6; supplemental Figure 2A). EFS was similar between ex vivo TCD and PTCY (61% [95% CI, 47-75] vs 79% [95% CI, 57-100]; P = .2). Similar results were observed in GRFS, with 61% (95% CI, 47-75) and 58% (95% CI, 30-86) in ex vivo TCD and PTCY, respectively (P = .9). CIN of primary/secondary GF at 12 months was 15% (95% CI, 7-24). GF was 15% (95% CI, 3-27) in TBI recipients and 17% (95% CI, 2-32) in patients conditioned without TBI (P = .9). Grade 2 to 4 and 3 to 4 aGVHD were higher with PTCY, but this was not statistically significant (31% (95% CI, 6-56) compared with ex vivo TCD 15% (95% CI, 5-26; P = .2) and 17% (95% CI, 0-38) compared with 9% (95% CI, 1-17; P = .4; supplemental Figure 2B), respectively). One-year cGVHD was higher with PTCY at 21% (95% CI, 0-43), compared with 2% (95% CI, 0-6) with ex vivo TCD (P = .011; supplemental Figure 2C).
Focusing on HID transplant for BMF/AA, OS was 76% (95% CI, 63-89; n = 42) after ex vivo TCD, and 79% (95% CI, 57-100; n = 14) after PTCY (P = .80; supplemental Figure 3A). There was no significant difference in CIN of grade 3 to 4 aGVHD between ex vivo TCD (7% [95% CI, 0-15]) and PTCY (17% [95% CI, 0-38]; P = .32; supplemental Figure 3B). A higher CIN of cGVHD was observed in PTCY (21% [95% CI, 0-43]) compared with ex vivo TCD (2% [95% CI, 0-7]; P = .017; supplemental Figure 3C).
Discussion
A number of important observations emerge from this largest multicenter study of HSCT in pediatric FA. In these registry data, OS and EFS after MFD (OS, 88%; EFS, 85%) and MUD (OS 85%; EFS 80%) are comparable. Outcomes after HID HSCT (OS, 70%; EFS, 62%) are encouraging and significantly better than those historically reported. Even in this pediatric cohort, younger age (<10 years) at HSCT is an important predictor of EFS and GRFS. FluCy without TBI is the best conditioning regimen for MFD and MUD HSCT in pediatric FA. Further studies are required to assess the role of TBI in mismatched/HID HSCT. Although the number of patients analyzed is small, alemtuzumab was associated with favorable OS and GVHD rate. Among MFD donor transplants, the use of either ATG or alemtuzumab has improved GRFS and reduced the rates of aGVHD and cGVHD without compromising OS. CB is a safe and effective alternative only in the presence of a MFD.
The use of minimal intensity conditioning is 1 of the main contributing factors that has led to the improvement in transplant survival in FA. Standard doses of Cy (100-200 mg/kg) was associated with dismal outcomes because of the marked hypersensitivity of FA cells to alkylating agents in vitro and radiation in vivo.10-13 Low-dose Cy and TBI led to improved survival of >80% and a low rate of GF (<10%) after matched sibling donor (MSD), but GF (24%-30%) and poor survival (16%-29%) remained the limiting factors for MUD HSCT.14,15 Additional fludarabine to a Cy-TBI backbone in MFD and then MUD HSCT by the Minnesota group demonstrated superior neutrophil (>89%) and platelet (74%) engraftment in MUD HSCT.16 Chemotherapy-only conditioning using a higher dose of Cy (60 mg/kg) was first reported by Bonfim et al, which showed OS of 93% and 12% of GF in 42 MSD HSCTs.17 A subsequent study by the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research, comparing an irradiation-containing regimen (n = 77) and chemotherapy-only regimen (n = 71) in MSD HSCT, showed that both regimens had comparable OS, neutrophil engraftment, and GVHD.18 In this largest pediatric FA study, TBI has no impact on GF in the whole cohort (at 5 years, 5% in no TBI vs 7% in TBI group; P = .2) and, in univariable analysis, because the absence of TBI in the preparative regimen correlated with better OS, EFS, and GRFS. This confirms that TBI can be avoided in MFD transplants and indicate that MUD HSCTs also may benefit of lack of irradiation. The small number of HID HSCTs and the different ex vivo TCD methods used do not enable the elucidation of the role of irradiation in this setting.
Although FluCy-based minimal intensity conditioning improved OS, GVHD remained an issue and has been associated with an increased risk of posttransplant malignancy, particularly squamous cell carcinomas.14,15 Various strategies have been explored to reduce GVHD in FA HSCT, including in vivo TCD using various serotherapies and ex vivo TCD. Historically, serotherapy was not used in MFD because of a perceived lower risk of GVHD and the use of serotherapy has been associated with increased risk of viral infection and mortality. This study highlighted the importance of serotherapy in MFD HSCT in reducing aGVHD (P < .001) and cGVHD (P < .001) without compromising OS (P = .30). Although the number of children who received alemtuzumab (n = 86) is relatively small compared with those who received ATG (n = 620), the use of alemtuzumab was associated with excellent GRFS (85%) compared with ATG (69%) and no serotherapy (68%) and low rates of aGVHD and cGVHD. A recent paper on the UK experience of FluCy and alemtuzumab showed excellent survival after matched donor HSCT (MFD, 85% and MUD, 96%), none had severe aGVHD or cGVHD.19 Access to alemtuzumab is unfortunately limited, but the use of ATG can be further optimized by pharmacokinetic studies and individualized dosing. In this study, ex vivo TCD was performed in 29 MFD/MUD, 9 MMFD/MMUD, and 49 HID transplants. The impact of ex vivo TCD in this small number of matched donor HSCT was not evaluated.
HID HSCT has emerged as a promising alternative donor strategy in patients without a matched donor in all indications of HSCT. The main challenge of performing HID HSCT is how to overcome the major HLA barrier with minimal intensity conditioning. TBI-based conditioning has shown promising results in both TCRαβ+/CD19+ depletion and PTCY platforms. Strocchio et al reported an excellent survival of 100% after TCRαβ+/CD19+–depleted HID HSCT after conditioning with FluCy and TBI at 2 Gy in 24 patients with FA. Two patients (8%) had primary GF but were rescued by a subsequent HSCT from the other parent. Of 3 patients who did not receive TBI, 1 patient developed poor graft function but improved after a CD34+ stem cell boost. Despite no posttransplant GVHD prophylaxis being used, only 4 patients developed grade 1/2 aGVHD, and 1 had mild skin cGVHD.20 Bonfim et al published the largest single-center study of using a PTCY strategy on a backbone of Flu and low-dose TBI conditioning in 30 pediatric patients with FA.21 OS was 73%, and 4 (13%) developed GF. The use of ATG (n = 14) improved OS from 50% to 79% and reduced severity of aGVHD (grade 3-4: ATG 14% vs no ATG 50%) and cGVHD (moderate to severe: ATG, 7% vs no ATG, 75%). Mild cGVHD occurred in 42% of patients receiving ATG-containing conditioning. Xu et al (n = 56) and Wang et al (n = 15) reported the outcomes of irradiation-free, T-cell–replete HID HSCT using intensive GVHD prophylaxis (calcineurin inhibitor plus mycophenolate mofetil plus methotrexate) in FA.22,23 Both studies demonstrated successful engraftment and favorable survival, but high rates of grade 2 to 4 aGVHD up to 60%, and cGVHD of 16% to 40% despite using either ATG or alemtuzumab.21,22 There is an ongoing clinical trial (NCT04784052) to study the outcome of TCRαβ+/CD19+–depleted HID using briquilimab (JSP191) in combination with FluCy and rituximab without TBI. Briquilimab is a first-in-class monoclonal antibody that inhibits stem cell factor binding to CD117 (c-kit) to deplete hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and is being trialed in HSCT for severe combined immunodeficiency (NCT02963064), chronic granulomatous disease (NCT05600907), GATA2 deficiency (NCT059077546), and MDS/AML (NCT04429191) and hemoglobinopathy (NCT05357482).
For patients with FA who developed AML/MDS before HSCT, unsolved questions include the need of pretransplant chemotherapy and the best chemotherapy regimen. Pretransplant cytoreductive chemotherapy in patients with FA is associated with significant toxicity because of their sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents. In patients with MDS but <10% BM leukemia blasts, classical strategy using reduced intensity conditioning regimen (RIC) HSCT has been recommended.24 For patients with MDS with >10% blast cells or AML, sequential strategy using a reduced intensity chemotherapy, followed by RIC has been used successfully.25-27 A French-Brazilian study recently published the outcome of 18 patients with FA with MDS/AML using FLAG-sequential regimen (Flu 30 mg/m2 daily and Cy 1 g/m2 twice daily for 5 days with granulocyte colony–stimulating factor), followed 3 weeks later by RIC (Flu 30 mg/m2 daily for 4 days, Cy 10 mg/kg for 4 days, and TBI 2 Gy) without waiting for myeloid recovery.28 Engraftment was achieved in 17 (94%) patients. The 3-year progression-free survival, OS, and CIN of relapse were 53% (95% CI, 32-89), 53% (95% CI, 32-89), and 13% respectively. In a recent EBMT study on transplant outcomes of 74 patients with FA who received transplantation for MDS and acute leukemia, patients who received transplantation in complete remission had a better OS (71% [95% CI, 48-95]) compared with patients with an active malignant disease (37% [95% CI, 24-50]; P = .04).29 Relapse rate for the entire cohort was 21% (95% CI, 11-30). Various pre-HSCT cytoreductive therapies were used in 22 (30%) of patients.
Although HSCT is a curative therapy for Fanconi–associated hematological abnormalities and BMF, it does not modify the risk of cancer. In the German FA registry analysis of 181 patients, the CIN by age 49 years was 33.6% for solid tumor and 23.7% for AML.30 Patients with FA at a high risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma in the head and neck, esophagus, or the ano-genital region.3,30,31 The CIN of squamous cell carcinoma at 15 and 30 years from the HSCT was 14.2% and 71.2%, respectively32 In the EBMT registry study on 795 patients with FA who received transplantation between 1972 to 2010, the 15-year CIN of secondary malignancies was 15% (95% CI, 11-20) for the entire cohort, and the CIN was 21% (95% CI, 14-28) in patients who survived >1 year (n = 509) and increased to 34% (95% CI, 23-46) at 20 years.6 This study identified that 89% of secondary malignancies were solid tumors, and independent risk factors were older age at HSCT, clonal evolution as an indication for HSCT, use of peripheral blood stem cells, and previous cGVHD. The potential reasons of the low CIN of secondary malignancies of 2% in the study are shorter duration of follow-up, young study population, and underreported events from a registry study. Because the number of FA transplant survivors is growing, a comprehensive survivorship program is required for FA with a specific focus on surveillance of secondary malignancy as outlined by FA clinical care guidelines.33
Despite the limitations of a retrospective study, these results will contribute to reevaluating the potential role of alternative donors and the timing of HSCT in children with FA. The perceived risk of MUD HSCT is often based on survival data from previous studies. Conventionally transplant is only offered as first-line treatment if a MFD is available and androgen therapy is offered to patients lacking a MFD. Androgen therapy is associated with unwanted side effects, because virilization in female patients and development of liver adenoma have been observed.34 Older age, higher transfusion burden, previous androgen exposure, and development of clonal evolution have been associated with lower survival in patients with FA.15,18,35 The timing of HSCT is critical and better survivals are seen in young patients without clonal evolution and higher transfusion burden. Therefore, transplant from an HLA-matched family or unrelated donor should be offered as first-line treatment in patients with FA with BMF/AA when cytopenia occurs and before the onset of clonal evolution.36 Although outcome after HID HSCT is comparable with that after MFD/MUD HSCT in young children with malignant disorders, constitutional BMF, and immunodeficiency, this multicenter study indicates that there is still an ongoing learning curve for HID HSCT in FA.20,21,37-40 Nevertheless, such an alternative donor strategy should be considered as a feasible option especially in centers with specific programs and robust experience in the field.
In conclusion, the largest study ever conducted on HSCT in FA confirms excellent survival after MFD or MUD HSCT and improved survival after HID HSCT using either ex vivo TCD or PTCY. Although FluCy plus serotherapy without TBI is the preferred and safe conditioning for matched donors, optimization is still required for HID transplant to ensure engraftment with minimal GVHD. Longer follow-up is required to fully assess the risk of second cancer in this young study population.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the contributing centers: Ashrafsadat Mousavi, Shariati Hospital, Tehran, Iran; Serap Aksoylar, Ege University Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplant Centre, Izmir, Turkey; Jerry Stein, Schneider Children’s Medical Center of Israel, Petach-Tikva, Israel; Alexander Kulagin, RM Gorbacheva Research Institute, Pavlov University, St. Petersburg, Russia; Marta Gonzalez Vicent, Niño Jesus Children’s Hospital, Madrid, Spain; Sarah Lawson, Birmingham Children’s Hospital, Birmingham, United Kingdom; Stephan Mielke, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden; Polina Stepensky, Hadassah University Hospital, Jerusalem, Israel; Josu de la Fuente, Division of Paediatrics, London, United Kingdom; Peter von dem Borne, Leiden University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands; Mohsen Al Zahrani, King Abdul Aziz Medical City, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; Antonio Campos, Instituto Português de Oncologia do Porto, Porto, Portugal; Julia Peristeri, Saint Sophia Children’s Hospital, Athens, Greece; Cristina Diaz de Heredia, Hospital Vall d'Hebron, Barcelona, Spain; Amir Ali Hamidieh, Children’s Medical Centre/Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran; Mahmoud Aljurf, King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; Mohamed Bayoumy, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; Caroline Besley, University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHSFT, Bristol, United Kingdom; Tunc Fisgin, Altinbas University, Faculty of Medicine, Bahçelievler Medicalpark Hospital, Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplantation Unit, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey; Tobias Gedde-Dahl, Oslo University Hospital, Rikshospitalet, Oslo, Norway; Krzysztof Kalwak, Fundacja Na Ratunek Dzieciom z Choroba Nowotworowa, Wroclaw, Poland; Nuno Miranda, Instituto Portugues Oncologia, Lisboa, Portugal; Benedicte Neven, Hôpital Necker, Paris, France; Sema Anak, Istanbul Medipol Universit, Istanbul, Turkey; Alessandra Carotti, Sezione di Ematologia, Azienda Ospedaliera Perugia, Perugia, Italy; Musa Karakukcu, Erciyes University, Faculty of Medicine, Kayseri, Turkey; Gérard Michel, Hopital d’Enfants de la Timone, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU) de Marseille, Marseille, France; Henrik Sengeloev, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark; Amos Toren, Edmond and Lily Safra Children’s Hospital, Tel-Hashomer, Israel; Emel Unal, University of Ankara, Ankara, Turkey; Ali Bülent Antmen, Adana Acibadem Hospital, Adana, Turkey; Adriana Balduzzi, Centro Trapianto di Midollo Osseo, Clinica Pediatrica, Monza, Italy; Patrice Chevallier, CHU Nantes, Nantes, France; Virginie Gandemer, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Rennes, Rennes, France; Brenda E. Gibson, Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow, United Kingdom; Jolanta Gozdzik, University Children’s Hospital in Krakow, Krakow, Poland; Gergely Kriván, Central Hospital of Southern Pest, Budapest, Hungary; Petr Sedlacek, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic; Marco Zecca, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, Italy; Peter Bader, Universitaetsklinikum Frankfurt Goethe Universitaet, Frankfurt am Main, Germany; Alessandra Biffi, Clinica di Oncoematologia Pediatrica, Padova, Italy; Bénédicte Bruno, Unité d`Hématologie Pédiatrique, Lille, France; Ben Carpenter, University College London Hospital, London, United Kingdom; Jennifer Clay, Yorkshire Blood & Marrow Transplant Programme, Leeds, United Kingdom; Katarzyna Drabko, Children’s University Hospital, Lublin, Poland; Tayfun Güngör, University Children’s Hospital, Zürich, Switzerland; Concepcion Herrera Arroyo, Hospital Reina Sofia, Córdoba, Spain; Ulker Kocak, Gazi University School of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey; Stig Lenhoff, Skanes University Hospital, Lund, Sweden; Philippe Lewalle, Institut Jules Bordet, Brussels, Belgium; Natalia Maximova, Institute for Maternal and Child Health, Trieste, Italy; Katharine Patrick, Sheffield Childrens NHS Foundation Trust, Sheffield, United Kingdom; Mario Petrini, Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Pisana, Pisa, Italy; Samppa Ryhänen, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland; John Snowden, Sheffield Blood and Marrow Transplant and Cellular Therapy Programme, Sheffield, United Kingdom; Jacek Wachowiak, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland; Olga Aleinikova, Belarussian Federation Research Center for Pediatric Oncology, Hematology and Immunology, Minsk, Belarus; Ali Bazarbachi, American University of Beirut Medical Center, Beirut, Lebanon; Arancha Bermúdez Rodríguez, Marqués de Valdecilla University Hospital, Santander, Spain; Claude Eric Bulabois, CHU Grenoble Alpes, Université Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France; Raffaella Cerretti, Tor Vergata University of Rome, Rome, Italy; Anca Colita, Fundeni Clinical Institute, Bucharest, Romania; Luca De Rosa, Ospedale S. Camillo-Forlanini, Rome, Italy; Eric Deconinck, Hopital Jean Minjoz, Besançon, France; Ronit Elhasid, Tel-Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel; Melissa Gabriel, The Children’s Hospital at Westmead, Sydney, Australia; Soledad González Muñiz, Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias, Oviedo, Spain; Bernd Gruhn, University of Jena, Jena, Germany; Charlotte Jubert, CHU Bordeaux Groupe Hospitalier Pellegrin-Enfants, Bordeaux, France; Nicolaus Kröger, University Hospital Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany; Giorgio La Nasa, Centro Trapianti Unico Di CSE Adulti e Pediatrico AO Brotzu, Cagliari, Italy; Peter Lang, University Hospital Tuebingen, Tuebingen, Germany; Lucía López Corral, Hospital Clínico, Salamanca, Spain; Christine Mauz-Körholz, Justus Liebig University Giessen, Giessen, Germany; Richard Mitchell, Sydney Children’s Hospital, Sydney, Australia; Emma Nicholson, Royal Marsden Hospital, London, United Kingdom; Jakob Passweg, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland; Elisa Sala, Klinik fuer Innere Medzin III, Ulm, Germany; Pascale Schneider, Hôpital Charles Nicolle, Rouen, France; Julia Winkler, University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany; Tsila Zuckerman, Rambam Medical Center, Haifa, Israel; Shashikant Apte, Sahyadri Speciality Hospital, Pune, India; Jacques-Olivier Bay, CHU Estaing, Clermont, France; Yves Beguin, University of Liege, Liege, Belgium; Cristina Belendez Bieler, Hospital Universitario Materno Infantil Gregorio Marañon, Madrid, Spain; Tarek Ben Othman, Centre National de Greffe de Moelle, Tunis, Tunisia; Fabio Benedetti, Policlinico G.B. Rossi, Verona, Italy; Ivana Bodova, Pediatric University Teaching Hospital, Bratislava, Slovak Republic; Franca Fagioli, Ospedale Infantile Regina Margherita, Torino, Italy; Jürgen Finke, University of Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany; Wolfgang Holter, St. Anna Kinderspital, Vienna, Austria; Anna Paola Iori, Universita La Sapienza, Rome, Italy; Jan-Erik Johansson, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Goeteborg, Sweden; Ain Kaare, Tartu University Hospital, Tartu, Estonia; Matthias Klammer, St George’s Hospital, London, United Kingdom; Bruno Lioure, Techniciens d’Etude Clinique Suivi de Patients Greffes, Strasbourg, France; Alexei Maschan, Federal Research Center for Pediatric Hematology, Moscow, Russia; Roland Meisel, Universitaetsklinikum, Duesseldorf, Germany; Giuseppe Milone, Ospedale Policlinico, Catania, Italy; Antonio Perez Martinez, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid, Spain; Xavier Poiré, Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc, Brussels, Belgium; Fulvio Porta, Universitá Degli Studi di Brescia, Brescia, Italy; Arcangelo Prete, Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria, Bologna, Italy; Jelena Rascon, Children’s Hospital, Affiliate of Vilnius University Hospital, Vilnius, Lithuania; Claudia Rössig, Universitaetsklinikum Muenster, Muenster, Germany; Riccardo Saccardi, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Careggi, Florence, Italy; Paul G. Schlegel, University Children’s Hospital, Wuerzburg, Germany; Anne Sirvent, CHU Lapeyronie, Montpellier, France; Jan Styczynski, University Hospital, Collegium Medicum UMK, Bydgoszcz, Poland; Francesco Paolo Tambaro, Azienda Ospedaliera di Rilievo Nazionale, Naples, Italy; Johanna Tischer, Klinikum Grosshadern, Munich, Germany; Estelle Verburgh, University of Cape Town, Faculty of Health Sciences, Cape Town, South Africa; and Radovan Vrhovac, University Hospital Center Rebro, Zagreb, Croatia.
Authorship
Contribution: S.H.L., R.P.d.L., C.D., F.L., A.R., S.S., and R.F.W. conceived and designed the study; B.P. managed the data; D.-J.E. performed the statistical analysis; S.H.L., F.L., C.D., R.P.d.L., and A.R. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; and all authors reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Su Han Lum, Great North Children’s Hospital, Clinical Resource Building, Floor 4, Block 2, Queen Victoria Rd, Newcastle upon Tyne NE1 4LP, United Kingdom; email: nshl5@newcastle.ac.uk.
References
Author notes
Data are available on request from the corresponding author, Su Han Lum (nshl5@newcastle.ac.uk).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.




This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal