Key Points
Hereditary angioedema is associated with venous thromboembolism in Swedish families with HAE.
A high familial risk for VTE is observed in especially younger patients with HAE.
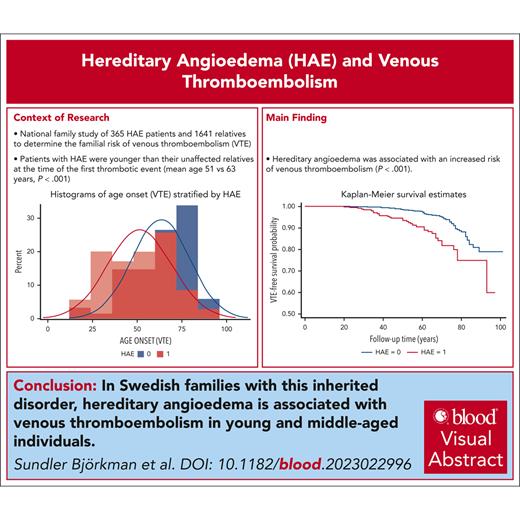
Visual Abstract
Hereditary angioedema (HAE), caused by C1 inhibitor protein deficiency, was recently shown to be associated with an increased risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE). To our knowledge, this is the first national family study of HAE, which aimed to determine the familial risk of VTE. The Swedish Multi-Generation Register was linked to the Swedish National Patient Register for the period of 1964 to 2018. Only patients with HAE with a validated diagnosis were included in the study and were linked to their family members. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for VTE were calculated for patients with HAE in comparison with relatives without HAE. Among 2006 individuals (from 276 pedigrees of 365 patients with HAE), 103 individuals were affected by VTE. In total, 35 (9.6%) patients with HAE were affected by VTE, whereas 68 (4.1%) non-HAE relatives were affected (P < .001). The adjusted HR for VTE among patients with HAE was 2.51 (95% CI, 1.67-3.77). Patients with HAE were younger at the first VTE than their non-HAE relatives (mean age, 51 years vs 63 years; P < .001). Before the age of 70 years, the HR for VTE among patients with HAE was 3.62 (95% CI, 2.26-5.80). The HR for VTE for patients with HAE born after 1964 was 8.29 (95% CI, 2.90-23.71). The HR for VTE for patients with HAE who were born in 1964 or earlier was 1.82 (95% CI, 1.14-2.91). HAE is associated with VTE among young and middle-aged individuals in Swedish families with HAE. The effect size of the association is in the order of other thrombophilias. We suggest that HAE may be considered a new rare thrombophilia.
Introduction
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a serious cardiovascular disease that affects ∼1 to 2 individuals per 1000 per year.1 The existence of familial thrombophilia, that is the aggregation of VTE in families, was recognized at the beginning of the 20th century.2 VTE is a complex disorder influenced by several genetic and environmental factors.3-5 Inherited deficiencies in the natural anticoagulants antithrombin, protein C, and proteins S and the activated protein C resistance because of the factor V Leiden (rs6025) and the prothrombin 20210A (rs1799963) polymorphisms have been associated with familial thrombophilia and are called inherited thrombophilias.3-8 Although a number of other rare genetic defects have been suggested to be linked to VTE, they are not routinely considered as thrombophilias.9-13
C1-inhibitor (C1-INH) is a multifunctional plasma serine protease inhibitor that negatively regulates components of the kallikrein-kinin, contact, and complement systems, including plasma kallikrein, activated factor XII (FXIIa), FXIa, complement C1 components, and mannose associated serine protease (MASP) 1 and 2.14-16 Congenital C1-INH deficiency (type I) or dysfunction (type II) is associated with hereditary angioedema (HAE), a rare disorder characterized by unpredictable episodes of cutaneous and submucosal swelling. Swelling episodes in HAE are driven by excessive bradykinin production caused by incomplete inhibition of plasma kallikrein and FXIIa owing to impaired C1-INH activity.14,17 Bradykinin is a vasoactive peptide generated by plasma kallikrein-mediated proteolysis of high molecular weight kininogen.14,17
Patients with HAE have previously been reported to have increased circulating markers of activation of coagulation at baseline when compared with controls.18-22 This indicates that C1-INH deficiency leads to systemic activation of coagulation that could predispose patients with HAE to a higher risk for VTE. Indeed, in a Swedish case-control study, HAE was associated with a significantly increased risk for VTE.23,24 Complementary studies in mouse models have demonstrated that C1-INH deficiency is sufficient to induce a procoagulant state and to support enhanced venous thrombosis.22
This family study aimed to determine if HAE is associated with VTE, similar to family studies of thrombophilia.25-28 This was a nationwide study that leveraged the Swedish Multi-Generation Register for establishing familial relationships and the Swedish National Patient Register (NPR) for VTE diagnosis.29-32
Materials and methods
Registers used
Linked data from multiple nationwide Swedish registries and health care data were used for the period of 1964 to 2018.29-35 Linking was achieved using the unique individual 10-digit personal identification number that is assigned at birth or immigration to all Swedish residents. To preserve confidentiality, this identification number was replaced by a serial number by Statistics Sweden. The following sources were used to create our database: the Total Population Register; The longitudinal integrated database for health insurance and labor market studies (LISA); Multi-Generation Register, providing information on family relations; the Swedish Cause of Death Register, containing all causes of death; the Prescribed Drug Register; and the NPR, which covers the Swedish Hospital Discharge Register and outpatient specialist care.29-35 The Swedish Hospital Discharge Register contains hospitalizations for all Swedish inhabitants from 1964, the Outpatient Care Register contains information from outpatient specialist clinics from 2001, and the Prescribed Drug Register contains prescription information from July 2005.29-35 However, we had access to information about the full 7-figure Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) code only between July 2005 and December 2014.
Validation of HAE in the NPR
Cases of HAE were identified based on the World Health Organization International Classification of Diseases, 9th and 10th Revision (ICD-9 and ICD-10) codes. HAE was identified by the following ICD codes using the NPR main and supplementary diagnoses: ICD-10 D84.1 and ICD-9 277G. However, ICD-10 D84.1 may also code for other complement defects, and ICD-9 277G codes for both HAE and α1-antitrypsin (A1AT) deficiency. A validation using a previously published case-control study of 239 patients with HAE with biochemically verified HAE type I (n = 216, 90.4%) or type II (n = 23, 9.6%) and 2383 unrelated controls was therefore performed (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website).23,24 ICD-10 D84.1 code was assigned to 226 (94.6%) verified patients with HAE and not to any (0%) matched controls. Moreover, the ICD-9 277G code was assigned to 35 (14.6%) patients with HAE and not to any (0%) controls. Among patients with HAE, 211 (88.3%) were prescribed HAE medicine or had an ICD code for angioedema (supplemental Table 1). Only 3.6% of healthy controls were prescribed HAE medicine or had an ICD code for angioedema (supplemental Table 1). This gives a sensitivity of 88.3% and a specificity of 96.4% for HAE. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ATC codes C09A [C09AA01-C09AA16] or C09B [C09BA01-C09BX05]) had been used by 20 patients with HAE (8.4%) and by 255 controls (10.7%).
Ascertainment of HAE cases
Patients with HAE were identified by the ICD-10 D84.1 and ICD-9 277G codes. To obtain a high validity for included HAE cases, patients who used angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors were excluded (supplemental Figure 1). Moreover, patients with HAE were only included if they had either been prescribed HAE medicine or had at least 1 episode of angioedema (supplemental Figure 1; supplemental Table 1). One patient that emigrated from Sweden was excluded. Moreover, patients with only an ICD-9 277G code without an ICD-10 D84.1 code were also excluded if they had an ICD-10 code for A1AT deficiency or ICD (7-10) codes for chronic obstructive bronchitis or bronchiectasis, liver disease, or vasculitis (supplemental Table 2). A total of 365 patients fulfilled these criteria. Of these patients with HAE, 318 (87.12%) were only assigned the ICD-10 D84.1 code, 7 (1.92%) were only assigned the ICD-9 277G code, and 40 (10.96%) were assigned both ICD-10 D84.1 and ICD-9 277G codes. With the current study design, the included cases were expected to be >96% correct (ie, >96% specificity) (supplemental Table 1).
Study population and pedigree construction
In total, 365 HAE cases were identified that were distributed across 276 separate pedigrees (supplemental Table 3). Some pedigrees were found to contain multiple HAE cases (supplemental Table 4). First-degree relatives (siblings, parents, and children) of index cases were identified. Spouses were included to reflect shared family environment, however, familial risks were also determined by excluding spouses. A total of 1641 non-HAE relatives were identified. Relatives who died before 1964 were not included in the study because the Swedish Hospital Register started in 1964.
Ascertainment of VTE cases
Cases of VTE were classified according to ICD (7-10) codes. VTE was defined using the NPR for the period between 1964 and 2018 by ICD codes for all types of VTE diagnoses36-38 (supplemental Table 5). In total, 103 unique individuals were affected by VTE. In supplemental Table 6, the distribution of VTE in the pedigrees is shown. The ICD codes used to identify provoked VTE cases with cancer, fractures, trauma, surgery, and pregnancy are shown in supplemental Table 7. The major transient provoking factors (fractures, trauma, surgery, and pregnancy) must have occurred within 3 months before VTE. Cancer was considered a permanent provoking factor that must have occurred within 5 years before the first VTE. The distribution of major VTE risk factors is presented in supplemental Table 8 with surgery being the most common.
Because of the low autopsy rate in Sweden, we did not use the National Cause of Death Register for VTE diagnoses.39 The autopsy rate has decreased from almost 40% in 1969 to less than 5% in 2016.39 However, the National Cause of Death Register was also checked. Only 1 patient with VTE as underlying cause of death was identified, and this patient was also registered in the NPR with a VTE. Thus, it is unlikely that any diagnosed VTE events were missed by excluding the Swedish Cause of Death Register for VTE diagnoses.
The Swedish Hospital Discharge Register has 85% to 95% overall validity or positive predictive value for most diagnoses.30 In a Swedish study of males with VTE, hospital records were available for 304 cases (1970-1998),40 and 289 of the 304 (95%) cases with diagnosed VTE were judged to be diagnosed correctly.40 Only 12 cases (3.9%) were not diagnosed with an objectively verified method but were treated with oral anticoagulation because of strong clinical probability. In total, 277 cases (91%) were objectively diagnosed with methods such as phlebography, ultrasonography, computed tomography scans, or pulmonary scintigraphy.40 A quality control of 118 patients with VTE in the Malmö Diet and Cancer cohort has also been performed,12 and in 106 (90%) of the cases, the diagnosis was found to be correct.12
Statistical methods
The risk for VTE was determined in agreement with previous family studies of thrombophilia.25-28 Incidence rates were calculated as a measure of absolute risk and incidence rate ratios were also presented as a robust measure of relative risk. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to examine the crude and adjusted association between HAE and incident VTE.41 Time was given as the number of years from birth until death, emigration, incident VTE, or end of follow-up, whichever occurred first. Model 1 is a univariate model. Model 2 was adjusted for sex, education, birth year, and country of birth. In an additional analysis, adjustment was also made for an environmental socioeconomic indicator, that is, neighborhood deprivation index (NDI) in model 3.42,43 Model 4 was further adjusted for thrombophilia, obesity, coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and cancer (supplemental Table 5). The assumption of proportional hazards was determined by introducing an interaction term with time and HAE. The assumption of proportionality for a period of time was violated. Time interacted with HAE regarding VTE (P < .018). Moreover, the log of negative log of survival plot without adjusting for other covariates in supplemental Figure 2 showed that the survival curves diverged after 70 years of age. The graphical approach indicates that the assumption of proportionality over time is violated. We therefore considered time-dependent variables for VTE and used an extended Cox proportional hazards regression model (Heaviside functions).44 By using this function, the hazard ratio (HR) formula yielded constant HRs for different time intervals.44
Patients with major VTE provoking factors (supplemental Table 7) were excluded to estimate the risk for unprovoked events. A sensitivity analysis was performed in which nonvalidated HAE cases with the ICD-10 D84.1 code was classified as HAE in the identified 276 HAE pedigrees. The HR for HAE was calculated with the exclusion of patients with a first event related to major provoking VTE risk factors (supplemental Tables 7 and 8). Using the Prescribed Drug Register, which contained prescription information from July 2005, a sensitivity analysis was conducted with the exclusion of patients with a prescription for HAE medicine within a year before the first VTE event with the exception of the time period between 2015 and 2018, because we had no access to information about the full 7-figure ATC codes between 2015 and 2018.
A birth-year stratified analysis was also performed because only 4 cases had their first VTE before 1980. The subjects were categorized based on HAE type and Kaplan-Meier plots were calculated for VTE. For curve comparisons, the log-rank test was used. The following significance levels are indicated: ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001.
The Swedish registers used in this study were maintained by Statistics Sweden and the National Board of Health and Welfare. This study was approved by the regional ethical review board in Lund, Sweden (registration number 2012/795 and later amendments). Informed consent was waived as a requirement by the ethics committee.
Results
Descriptive findings of Swedish families with HAE
Descriptive data for 365 HAE cases and 1641 non-HAE controls from 276 different pedigrees are shown in Table 1. When compared with non-HAE controls, HAE cases had a significantly higher proportion of individuals of female sex, a significantly later birth year, a significantly higher proportion of individuals born outside of Sweden, and were significantly younger at the end of the follow-up period (Table 1). The absolute incidence of VTE was significantly higher in HAE cases than in non-HAE controls (Table 1). Patients with HAE were younger at the first VTE than their non-HAE relatives (mean age, 51 vs 63 years; P < .001; Table 2; supplemental Figure 3).
Characteristics of the study population of patients with HAE and their relatives
| . | Participants, n (%) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (2006) . | HAE (n = 365) . | Non-HAE (n = 1641) . | P value . | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 1017 (50.70) | 152 (41.64) | 865 (52.71) | <.001∗ |
| Female | 989 (49.30) | 213 (58.36) | 776 (47.29) | |
| Birth year | ||||
| Mean (SD) (min-max) | 1964 (27) (1892-2018) | 1966 (22) (1914-2009) | 1963 (27) (1892-2018) | .022† |
| Median (Q1-Q3) | 1964 (1945-1984) | 1966 (1951-1984) | 1963 (1944-1984) | |
| Education | ||||
| Unknown or <10 y | 472 (23.53) | 61 (16.71) | 411 (25.05) | |
| 10-11 y | 834 (41.58) | 180 (49.32) | 654 (39.85) | <.001∗ |
| >11 y | 700 (34.90) | 124 (33.97) | 576 (35.10) | |
| Country of birth outside Sweden | 184 (9.17) | 45 (12.33) | 139 (8.47) | .021∗ |
| Age at HAE onset | ||||
| Mean (SD) (min-max) | NA | 40 (22) (0-94) | NA | |
| Median (Q1-Q3) | NA | 39 (24-56) | NA | |
| Age at end of follow-up | ||||
| Mean (SD) (min-max) | 49 (24) (0-101) | 40 (22) (0-94) | 51 (24) (0-101) | |
| Median (Q1-Q3) | 51 (31-68) | 39 (24-56) | 53 (33-70) | <.001† |
| VTE | 103 (5.13) | 35 (9.59) | 68 (4.14) | <.001∗ |
| . | Participants, n (%) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (2006) . | HAE (n = 365) . | Non-HAE (n = 1641) . | P value . | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 1017 (50.70) | 152 (41.64) | 865 (52.71) | <.001∗ |
| Female | 989 (49.30) | 213 (58.36) | 776 (47.29) | |
| Birth year | ||||
| Mean (SD) (min-max) | 1964 (27) (1892-2018) | 1966 (22) (1914-2009) | 1963 (27) (1892-2018) | .022† |
| Median (Q1-Q3) | 1964 (1945-1984) | 1966 (1951-1984) | 1963 (1944-1984) | |
| Education | ||||
| Unknown or <10 y | 472 (23.53) | 61 (16.71) | 411 (25.05) | |
| 10-11 y | 834 (41.58) | 180 (49.32) | 654 (39.85) | <.001∗ |
| >11 y | 700 (34.90) | 124 (33.97) | 576 (35.10) | |
| Country of birth outside Sweden | 184 (9.17) | 45 (12.33) | 139 (8.47) | .021∗ |
| Age at HAE onset | ||||
| Mean (SD) (min-max) | NA | 40 (22) (0-94) | NA | |
| Median (Q1-Q3) | NA | 39 (24-56) | NA | |
| Age at end of follow-up | ||||
| Mean (SD) (min-max) | 49 (24) (0-101) | 40 (22) (0-94) | 51 (24) (0-101) | |
| Median (Q1-Q3) | 51 (31-68) | 39 (24-56) | 53 (33-70) | <.001† |
| VTE | 103 (5.13) | 35 (9.59) | 68 (4.14) | <.001∗ |
Min, minimum; max, maximum; NA, not applicable; Q, quartile; SD, standard deviation.
P value was determined using the Pearson χ2 test, 2-sided.
P value was determined using the independent samples t test, 2-tailed.
Comparison of age at onset of VTE for patients with and without HAE
| . | All (n = 103) . | HAE (n = 35) . | Non-HAE (n = 68) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at onset (VTE) | ||||
| Mean (SD) (min-max) | 59 (18) (17-93) | 51 (18) (20-93) | 63 (16) (17-89) | <.001∗ |
| Median (Q1-Q3) | 61 (46-74) | 52 (35-67) | 66 (51-76) |
| . | All (n = 103) . | HAE (n = 35) . | Non-HAE (n = 68) . | P value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at onset (VTE) | ||||
| Mean (SD) (min-max) | 59 (18) (17-93) | 51 (18) (20-93) | 63 (16) (17-89) | <.001∗ |
| Median (Q1-Q3) | 61 (46-74) | 52 (35-67) | 66 (51-76) |
P value was determined using an independent samples t test, 2-tailed.
Descriptive data for VTE cases and non-VTE controls were also compiled (supplemental Table 9). In total, 103 individuals had at least 1 VTE episode. Of the 103 individuals who had a VTE event, 35 (33.98%) had HAE, whereas of the 1903 family members without VTE, 330 (17.34%) had HAE (P < .001). Patients with VTE were more likely to be of female sex than individuals without VTE. Furthermore, patients with VTE were older and had lower educational attainment than individuals without VTE.
VTE risk
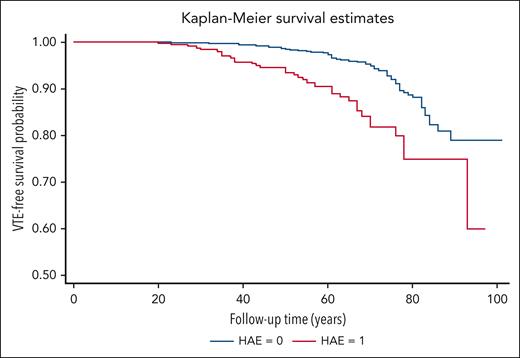
The cumulative follow-up time was 18 130 person-years for patients with HAE and 82 911 years for non-HAE pedigree members. The VTE incidence rate was 1.93 per 1000 person-years (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.39-2.69) for patients with HAE and 0.82 per 1000 person-years (95% CI, 0.65-1.04) for non-HAE relatives (Table 3). The incidence rate ratio for patients with HAE was 2.35 (95% CI, 1.57-3.54) when compared with family members without HAE (Table 3). A significant difference in thrombosis-free survival was observed between patients with HAE and their non-HAE relatives (Figure 1).
Risk of VTE for patients with HAE in comparison with their nonaffected relatives
| Variable . | Person-years, no. . | Cases, no./persons at risk, no. . | Incidence rate, cases per 1000 person-years . | Incidence rate ratio (95% CI) . | HR (95% CI) . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 . | Model 2 . | |||||
| Non-HAE | 82 911 | 68/1641 | 0.82 (0.65-1.04) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| HAE | 18 130 | 35/365 | 1.93 (1.39-2.69) | 2.35∗∗∗ (1.57-3.54) | 2.71∗∗∗ (1.80-4.07) | 2.51∗∗∗ (1.67-3.77) |
| Variable . | Person-years, no. . | Cases, no./persons at risk, no. . | Incidence rate, cases per 1000 person-years . | Incidence rate ratio (95% CI) . | HR (95% CI) . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 . | Model 2 . | |||||
| Non-HAE | 82 911 | 68/1641 | 0.82 (0.65-1.04) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| HAE | 18 130 | 35/365 | 1.93 (1.39-2.69) | 2.35∗∗∗ (1.57-3.54) | 2.71∗∗∗ (1.80-4.07) | 2.51∗∗∗ (1.67-3.77) |
Model 1 is the univariate model. Model 2 is the multivariate model of HAE adjusted for sex, education, birth year, and country of birth. The significance levels are indicated as follows: ∗∗∗P < .001.
VTE-free survival in HAE cases vs controls. Kaplan-Meier curves for VTE-free survival according to HAE in family members are shown. Log-rank test P value <.001.
VTE-free survival in HAE cases vs controls. Kaplan-Meier curves for VTE-free survival according to HAE in family members are shown. Log-rank test P value <.001.
HAE was associated with VTE both in the univariate model 1 and the multivariate model 2 (Table 3). Multivariate HRs in model 2 for VTE among patients with HAE was 2.51 (95% CI, 1.67-3.77; Table 3). However, there was an interaction between time and HAE for VTE (P < .018), thereby violating the proportional hazards assumption. Although HAE was associated with an overall risk for VTE (Table 3), HAE was associated with VTE risk only before the age of 70 years (HR, 3.62; 95% CI, 2.26-5.80) but not thereafter (HR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.30-2.02; Table 4). However, there were only a few HAE cases with VTE in the follow-up >70 years cohort (Table 4).
Risk of VTE for patients with HAE stratified for age below or above 70 years in comparison with their nonaffected relatives
| . | Variable . | Person-years, no. . | Cases, no./persons at risk, no. . | Incidence rate, cases per 1000 person-years . | Incidence rate ratio (95% CI) . | HR (95% CI) . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 . | Model 2 . | ||||||
| Follow-up ≤70 y | Non-HAE | 52 540 | 39/1259 | 0.74 (0.54-1.02) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| HAE | 12 814 | 31/298 | 2.42 (1.70-3.44) | 3.26∗∗∗ (2.03-5.22) | 3.97∗∗∗ (2.50-6.30) | 3.62∗∗∗ (2.26-5.80) | |
| Follow-up >70 y | Non-HAE | 30 371 | 29/382 | 0.95 (0.66-1.37) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| HAE | 5 316 | 4/67 | 0.75 (0.28-2.00) | 0.79 (0.28-2.24) | 0.81 (0.31-2.13) | 0.78 (0.30-2.02) | |
| . | Variable . | Person-years, no. . | Cases, no./persons at risk, no. . | Incidence rate, cases per 1000 person-years . | Incidence rate ratio (95% CI) . | HR (95% CI) . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 . | Model 2 . | ||||||
| Follow-up ≤70 y | Non-HAE | 52 540 | 39/1259 | 0.74 (0.54-1.02) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| HAE | 12 814 | 31/298 | 2.42 (1.70-3.44) | 3.26∗∗∗ (2.03-5.22) | 3.97∗∗∗ (2.50-6.30) | 3.62∗∗∗ (2.26-5.80) | |
| Follow-up >70 y | Non-HAE | 30 371 | 29/382 | 0.95 (0.66-1.37) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| HAE | 5 316 | 4/67 | 0.75 (0.28-2.00) | 0.79 (0.28-2.24) | 0.81 (0.31-2.13) | 0.78 (0.30-2.02) | |
Time divided HRs (95% CI) were determined using extended Cox proportional hazards regression model (Heaviside functions). Model 1 is the univariate model. Model 2 is the multivariate model for HAE adjusted for sex, education, birth year, and country of birth.
The significance levels are indicated as follows: ∗∗∗P < .001.
Unprovoked VTE
Provoked first VTE occurred in 16 patients with HAE and in 31 non-HAE pedigree members (supplemental Table 8). After excluding individuals with provoking events within 3 months before the VTE occurred or cancer within 5 years before first VTE (supplemental Table 7), the risk for VTE was determined for patients with HAE with unprovoked VTE with an HR in the multivariate model 2 of 2.62 (95% CI, 1.51-4.56) (supplemental Table 10).
Sensitivity analysis
In a sensitivity analysis, family members with a D84.1 diagnosis who were not validated were counted as patients with. For nonvalidated cases, the multivariate HR for VTE in model 2 was 2.43 (95% CI, 1.62-3.64) (supplemental Table 11). In supplemental Table 12, the prescribed HAE medicines the year before the first VTE are shown. In total, 11 individuals were excluded; 9 patients with HAE and 2 patients who were prescribed HAE medicine (supplemental Table 1) without having a diagnosis code for HAE. Two patients with HAE were prescribed 2 different medicines. One patient without HAE was prescribed a C1-INH (B06AC01), and 1 was prescribed danazol (G03XA01) and was therefore likely to have been misclassified as non-HAE instead of HAE.
The Prescribed Drug Register contains prescription information from 2005. We therefore also performed several sensitivity analyses with a start of the follow-up from 2005 and with exclusion of family members with HAE medicine within 1 year before first the VTE event and of individuals who died, emigrated, or had a VTE before the new baseline of 2005. Exclusion of patients who were prescribed tranexamic acid (supplemental Table 13), C1-INH concentrate (supplemental Table 14), or any HAE medicine (supplemental Table 15) within 1 year before the first VTE event did not change the results to any major degree. The HRs in the multivariate model 2 were as follows: 2.49 (95% CI, 1.35-4.61; supplemental Table 13), 2.70 (95% CI, 1.55-4.73; supplemental Table 14), and 2.08 (95% CI, 1.09-3.97; supplemental Table 15).
Manifestations of VTE
Among patients with HAE, venous thrombosis of the legs (n = 20, 57%) and pulmonary embolism (n = 8, 23%) were the most common manifestations (supplemental Table 16). In comparison, among their nonaffected relatives, venous thrombosis of the legs occurred in 36 patients (53%) and pulmonary embolism in 15 patients (22%) (supplemental Table 16). Recurrent VTE was present among 19 (54%) of the patients with HAE and 38 (56%) of their nonaffected relatives (supplemental Table 17). All manifestations of VTE are inherited in families in Sweden (Zöller et al36-38). Moreover, manifestations at sites other than the lower extremities and lungs are common in familial thrombophilia (Allaart et al,25 Zöller et al,26,27 and van Boven et al28).
Additional analysis
In an additional analysis, the 263 spouses were excluded (supplemental Table 18). The HR was similar. In the adjusted model, the HR was 2.24 (95% CI, 1.47-3.39) with P < .001.
A birth-year stratified analysis was performed because only 4 cases had their first VTE before 1980 (supplemental Table 19). The HR for VTE for patients with HAE born after 1964 was 8.29 (95% CI, 2.90-23.71). The HR for VTE for patients with HAE born in 1964 or earlier was 1.82 (95% CI, 1.14-2.91; supplemental Table 19).
Additional analyses were conducted with adjustments for NDI (model 3) and, in model 4, additionally adjustments for several common comorbidities, namely thrombophilia, obesity, coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, liver disease, and cancer (supplemental Table 20). In model 3, HAE was associated with an increased risk for VTE with an odds ratio of 3.18 (95% CI, 2.02-5.02) (supplemental Table 20). In the multivariate model 4, including NDI and comorbidities, the odds ratio for VTE for patients with HAE was 2.70 (95% CI, 1.65-4.42; supplemental Table 20).
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first family-based study to show that HAE is associated with a high risk for VTE among young and middle-aged individuals within the approximate range of thrombophilias.8 C1-INH, encoded by the SERPING1 gene, functions as a key negative regulator of the C1 components of the classical pathway, of MASP-1 and 2 of the lectin pathway, and prekallikrein, FXIIa, and FXI of the contact pathway.14-17,45-49 Consistent with the important anticoagulant function of C1-INH, patients with C1-INH deficiency–associated HAE have increased plasma levels of markers of activation of coagulation.18-22 Elevations in systemic markers of activation of coagulation, such as those reported in patients with HAE, have also been observed in patients with thrombophilias.50,51 The greater apparent incidence of VTE in patients with HAE at a younger age is also consistent with C1-INH deficiency functioning as a thrombophilia given that this is frequently observed in studies of thrombophilias.25-28 Moreover, around half of patients with HAE with VTE had a major provoking factor, common among families with thrombophilias.25-28
When comparing C1-INH deficiency–associated HAE with other thrombophilias, the effect size observed for VTE was slightly lower than that observed for thrombophilias in comparable family studies.25-28,52,53 However, the effect size for HAE and VTE was similar to that of factor V Leiden (rs6025) and the prothrombin G20210A variant (rs1799963) in recent population-based genome wide association studies.5,54,55 Interestingly, in the Swedish Malmö Diet and Cancer cohort study, a markedly lower effect was reported for factor V Leiden (rs6025), the prothrombin G20210A variant (rs1799963), and high-risk variants in SERPINC1, PROC, and PROS1 than for those observed for HAE in this study.8
It is interesting to note that the association between HAE and VTE was retained when individuals who had received HAE medicines were excluded, albeit with a slightly reduced effect size. This reduction in effect size may be attributed to the exclusion of patients with HAE with more severe disease presentation and/or C1-INH deficiency who were most likely to receive HAE medicines. Markers of activation of coagulation are further increased in patients with HAE during attacks, suggesting that there may be an association with the severity of disease presentation and a VTE predisposing procoagulant state.19,21 The procoagulant state associated with HAE has also been found to be more pronounced in patients with severe deficiency.22 Although we did not have access to C1-INH antigen and activity data in this study, it is interesting to consider the effect of severity of deficiency on VTE events. Alternatively, the reduced effect size observed could be the consequence of procoagulant effects of HAE medicines, in particular tranexamic acid and C1-INH preparations. Case reports and case series have reported episodes of VTE in patients with HAE who received C1-INH preparations, which led to speculation that the preparations might have prothrombotic properties.56,57 However, available evidence from controlled studies does not support any significant association between tranexamic acid or C1-INH preparations and VTE.58,59 In fact, in a controlled study, C1-INH preparations were associated with a 10-fold lower incidence of VTE in patients with HAE.59 The persistence of the association with HAE in medicine naive cohorts suggests that the association between HAE and VTE is not a treatment artifact.
A recent prospective case-control study in the general population also supports a role for plasma C1-INH in modulating VTE risk.60 Patients with elevated plasma levels of C1-INH were found to have a significantly lower risk for VTE than those with lower levels of C1-INH.60 Furthermore, increasing plasma level of C1-INH were found to significantly reduce contact pathway–initiated thrombin generation.60 This association in the general population complements that reported in this study for C1-INH deficiency–associated HAE and VTE. This finding was recently confirmed in a Mendelian randomization–based study in which higher genetically inferred levels of C1-INH were associated with a significantly lower risk for VTE.61
In viewing C1-INH deficiency as a thrombophilia, it is useful to consider the extent to which inhibitory targets of C1-INH in the contact pathway are involved in the pathogenesis of VTE. To date, there is no clear epidemiologic evidence supporting a role for either plasma kallikrein or FXII in the pathogenesis of VTE. However, congenital FXI deficiency has been associated with a reduced risk for VTE.62,63 Furthermore, elevated plasma levels of FXI have been associated with an increased risk for VTE.64,65 The contribution of FXI to VTE is further highlighted by the emergence of promising, novel anticoagulant FXI inhibitors.66
Although it has been proposed that dysregulation of the contact pathway may contribute to the association between HAE and VTE, a contribution of the complement system to the observed association cannot be discounted. C1-INH is the major endogenous negative regulator of C1 components of the classical pathway and MASP-1 and 2 of the lectin pathway. Epidemiologic studies indicate that increased plasma levels of numerous complement components are associated with an increased risk for VTE.67-70 High plasma levels of C3 and C5 have been associated with an increased risk for VTE.67,68 Furthermore, high plasma MASP-2 levels have also been causally associated with risk for future VTE.69 Interestingly, MASP-1 and MASP-2 have the ability to activate prothrombin to generate thrombin.45-49 Although MASP-1 has several substrates in the hemostatic system, the activity of MASP-2 seems to be specific for prothrombin.45-49 Consistent with systemic complement activation, patients with HAE often present with low plasma levels of complement C4.71 Further mechanistic studies are required to determine the relative contribution of the contact and complement systems to VTE in the setting of HAE.
There are a number of potential limitations with the approach used. Although the use of a nationwide sample likely minimized the risk of selection bias in variance partition studies, the interpretation of the results is constrained by time (1964-2018) and geographical location (Sweden). Inclusion and exclusion criteria were set to ensure that the diagnosis of HAE had high validity. However, as a result some patients with HAE among family members with VTE may have been missed and this may have diluted the association with VTE, leading to a reduction in power. It is also possible that some VTE events may have been missed. Another limitation is that 7-figure ATC code data were not available for the period between 1987 and 2005 and after 2015. Some individuals and families with HAE diagnosed during these periods may therefore have been missed. However, including individuals based on the presence of a D84.1 code alone did not change the results (supplemental Table 11), indicating that the lack of ATC code data did not affect the results to any major degree. The inpatient register was not complete before 1987.30 Outpatient data were only available from 2001, although outpatient treatment of VTE before this date was not as common as today. Moreover, because VTE is a recurrent disease,1 these outpatients are likely to be affected later and found in the register in 2001 or later. Moreover, severe cases with VTE are more likely to be hospitalized than less severe cases and it might be an advantage when studying inherited disorders to focus on the most severe phenotypes.72 Major advances have been made in the diagnosis of VTE during the study period,73 which, together with the incomplete inpatient register before 1987, explains why only 4 VTE cases were diagnosed before 1980. This is most likely a register effect caused by the advancement of diagnostic methods and the inpatient register not being complete before 1987.28,64 The birth-year stratified analysis also suggests that an even higher VTE risk may exist among those born after 1964 (supplemental Table 19). It is expected that the relative risk for a genetic factor is higher at younger ages in complex traits such as VTE.72 Heritability for VTE has also been shown to be higher in younger individuals.36 The lack of an association between HAE and VTE among the elderly above 70 years of age may also be because of the low statistical power (few VTE cases). Another possible explanation is dilution owing to the accumulation of environmental factors or comorbidities in the elderly, which is why heritability for complex traits usually are higher at younger ages.36,72
It was not possible to control for several VTE risk factors that may have changed in frequency during the study period, such as overweight, height, smoking, hormone replacement therapy, and oral contraceptives use. However, adjustments for obesity, thrombophilia, coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic kidney diseases, liver disease, and cancer did not change the results to any major degree (supplemental Table 20). Moreover, education as a proxy for socioeconomic status, which is related to VTE risk and lifestyle factors, was controlled for.74,75 Education may be the best socioeconomic predictor of good health.75 We also adjusted for being born outside Sweden, that is, country of birth. Being born in Sweden is associated with higher VTE risk.76 Moreover, neighborhood deprivation, as assessed by the NDI, is a common risk factor for VTE.42 However, adjustment for NDI42,43 did not change the association between HAE and VTE to any major degree (supplemental Table 20).
There are a number of key strengths to the approach used. The nationwide design of this study allowed for the inclusion of all available validated patients with HAE in Sweden, thereby increasing its power. Furthermore, this study was able to leverage well-validated hospital discharge data. The positive predictive value is generally 85% to 95%.30 The validity of these data is high for cardiovascular disorders, such as VTE, stroke, and myocardial infarction, approaching 95%.12,30,40 Another advantage is that the use of objective clinical hospital diagnoses and the multigeneration register data allows for the elimination of any recall bias.77 Recall and self-report bias are common problems in many family studies of VTE.77 Swedish registers, such as the Swedish Total Population Register and the Swedish Hospital Discharge Register, have high completion rates.29-35 The Swedish register on prescribed drugs is regulated under a legislation issued by the Swedish government (Svensk författningssamling [Swedish Code of Statutes] 2005:363).78 The register contains data with unique patient identifiers for all dispensed prescriptions to the whole population of Sweden78; these identifiers were replaced by pseudonymized serial numbers to preserve people’s integrity.
In conclusion, this study reports a significant association between HAE and VTE among young and middle-aged individuals in Swedish families. The effect size of the association is similar to that of several thrombophilias. We suggest that HAE may be classified a new rare thrombophilia caused by congenital C1-INH deficiency.
Acknowledgments
The registers used in this study are maintained by Statistics Sweden and the National Board of Health and Welfare.
This work was supported by Avtal om läkarutbildning och forskning (agreement on medical education and research) funding from Region Skåne (B.Z. and K.S.), the Swedish Research Council (B.Z. and K.S.), and the Swedish Heart Lung Foundation (K.S.).
Authorship
Contribution: J.S. and K.S. contributed to the acquisition of data; L.S.B. and B.Z. drafted the manuscript; M.P. and B.Z. had full access to all of the data (including statistical reports and tables) and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of their analysis; and all authors contributed to the conception and design of the study, to the analysis and interpretation of the data, revised the manuscript critically, and approved the final version.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: L.S.B. has received an unrestricted grant from CSL Behring; and honoraria from CSL Behring, BioCryst, and Takeda. A.E. has received honoraria from BioCryst. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Bengt Zöller, Center for Primary Health Care Research, Skåne University Hospital, CRC, Building 28, Floor 11, Jan Waldenströms gata 35, S-205 02 Malmö, Sweden; email: bengt.zoller@med.lu.se.
References
Author notes
Data may be obtained from a third party and are not publicly available. We are not allowed to share our data as the data are drawn from registries owned by a third party, that is, the Swedish authorities. The reason behind this is that public availability could potentially compromise patient confidentiality or privacy. Permission to use the data is issued to researchers (if certain conditions are fulfilled) by the National Board of Health and Welfare and by Statistics Sweden. Request to use the data can be applied for from the Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare (https://www.socialstyrelsen.se/en/statistics-and-data/statistics/statistical-database/) and Statistics Sweden (https://www.scb.se/en/About-us/contact-us/). An application for use of the same minimal data set that we have used in this study should include a motivation, a referral to the present study and an addition of a list of variables, before submission of a data request to the Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare and Statistics Sweden using the contact addresses above. Then, the authorities will coordinate the handling of the request and do a special review.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal