Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
EVIDENCE meta-analysis: evaluating minimal residual disease as an intermediate clinical end point for multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this Plenary Paper, Landgren and colleagues present the EVIDENCE meta-analysis of randomized trials in multiple myeloma (MM), designed to test whether minimal residual disease (MRD)–negativity at 12 months is a valid surrogate for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival. The authors demonstrate that MRD-negativity is prognostic and that the treatment effect on MRD correlates with the effect on PFS. Treatments with higher rates of MRD-negativity at 12 months are likely to predict improved meaningful clinical outcomes and should be an acceptable end point for accelerated approvals in MM.
REVIEW ARTICLE
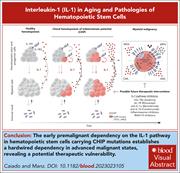
IL-1 in aging and pathologies of hematopoietic stem cells
Caiado and Manz review current knowledge about inflammaging of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and highlight the potential of targeting the interleukin-1 (IL-1) signaling pathway in stem cell disorders. Early premalignant IL-1 pathway activity in HSCs carrying mutations common in clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) may establish a hardwired dependency in advanced myeloid malignancy states. As well as explaining how CHIP can evolve during inflammation, this proposal may also reveal a potential therapeutic vulnerability for secondary myeloid malignancies.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
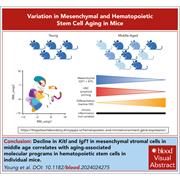
Variation in mesenchymal KITL/SCF and IGF1 expression in middle age underlies steady-state hematopoietic stem cell aging
To what extent age-related changes in hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) function are cell intrinsic or instructed by environmental signals is unknown. Young and colleagues conducted a single-cell analysis of age-related changes in the bone marrow, analyzing both bone marrow–derived HSCs and cells of the HSC niche. The authors’ data reveal that a reduction in growth signals from mesenchymal stromal cells to HSCs underlies impaired lymphoid differentiation and increased transcriptional heterogeneity of HSCs in aging mice.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Ibrutinib as part of risk-stratified treatment for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: the phase 2 TIDaL trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Antigen escape as a shared mechanism of resistance to BCMA-directed therapies in multiple myeloma
Brief Report
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Standardized indolent systemic mastocytosis evaluations across a health care system: implications for screening accuracy
Clinical Trials & Observations
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
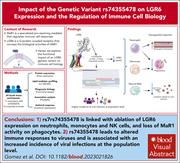
An LGR6 frameshift variant abrogates receptor expression on select leukocyte subsets and is associated with viral infections
Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein–coupled receptor 6 (LGR6) is the receptor for the soluble mediator maresin 1, which favors resolution of inflammation. Gomez et al found that naturally occurring human variants that reduce LGR6 expression corresponded with altered activities of myeloid cells and a reduced antiviral response from natural killer cells. Population-based studies demonstrate that this deficiency leaves people to be more susceptible to viral disease, uncovering a subtle dysregulation of the host immunity.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
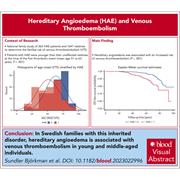
Increased risk of venous thromboembolism in young and middle-aged individuals with hereditary angioedema: a family study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Most patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE) have either a congenital deficiency or dysfunction of the C1 esterase inhibitor, which has important functions in the complement and kinin-kallikrein systems and acts as a natural anticoagulant. Sundler Björkman et al present linked registry data on patients with HAE that indicate for the first time that family members with HAE have a 2.5-times higher risk of venous thromboembolism than relatives without HAE, and that this phenotype is penetrant at early ages. This report identifies HAE as a rare thrombophilia.
TRANSPLANTATION
Does IPSS-R downstaging before transplantation improve the prognosis of patients with myelodysplastic neoplasms?
Clinical Trials & Observations
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is the only curative therapy for myelodysplastic neoplasms, but whether to use conventional therapies before HCT is controversial. Scheid et al present a retrospective analysis examining whether changes in the revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R), with or without treatment before HCT, influence outcomes. In the absence of therapy, changes in IPSS-R did not alter outcomes. While downstaging IPSS-R by chemotherapy correlated with improved transplant outcome, that was not the case for hypomethylating therapies, and stable or worse IPSS-R after therapy correlated with worse outcome. The created model can inform decisions by patients and physicians and suggests that pre-HCT therapy is not appropriate for many patients.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Glofitamab stimulates immune cell infiltration of CNS tumors and induces clinical responses in secondary CNS lymphoma
Godfrey and colleagues report the first case series of patients with central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma treated with CD3-CD20 bispecific-based therapy. The authors found that glofitamab partially penetrated the blood brain barrier and that responses could be seen. These preliminary results prompt the need for formal clinical trials with larger numbers of patients to assess whether higher doses of glofitamab may have a role in care for patients with CNS lymphomas.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A confocal microscopy image of the bone marrow from a mouse femur, with megakaryocytes (Gp1Bβ) in magenta and nuclei in blue (DAPI). See the article by Young et al on page 378.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals