Key Points
Kitl and Igf1 in MSCs at middle age correlates with aging-associated molecular programs in HSCs in individual mice.
Elevation of proinflammatory cytokines is not observed in steady-state middle-aged mice.
Visual Abstract
Intrinsic molecular programs and extrinsic factors including proinflammatory molecules are understood to regulate hematopoietic aging. This is based on foundational studies using genetic perturbation to evaluate causality. However, individual organisms exhibit natural variation in the hematopoietic aging phenotypes and the molecular basis of this heterogeneity is poorly understood. Here, we generated individual single-cell transcriptomic profiles of hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cell types in 5 young adult and 9 middle-aged C57BL/6J female mice, providing a web-accessible transcriptomic resource for the field. Among all assessed cell types, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) exhibited the greatest phenotypic variation in expansion among individual middle-aged mice. We computationally pooled samples to define modules representing the molecular signatures of middle-aged HSCs and interrogated, which extrinsic regulatory cell types and factors would predict the variance in these signatures between individual middle-aged mice. Decline in signaling mediated by adiponectin, kit ligand (KITL) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) from mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) was predicted to have the greatest transcriptional impact on middle-aged HSCs, as opposed to signaling mediated by endothelial cells or mature hematopoietic cell types. In individual middle-aged mice, lower expression of Kitl and Igf1 in MSCs was highly correlated with reduced lymphoid lineage commitment of HSCs and increased signatures of differentiation-inactive HSCs. These signatures were independent of expression of aging-associated proinflammatory cytokines including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor α and RANTES. In sum, we find that Kitl and Igf1 expression are coregulated and variable between individual mice at the middle age and expression of these factors is predictive of HSC activation and lymphoid commitment independently of inflammation.
Introduction
Biological aging results in reduced ability of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to robustly regenerate progenitor and mature cells of the hematopoietic system. The bone marrow (BM) microenvironment is an important regulator of HSC function, and several HSC aging phenotypes are linked to microenvironment dysregulation. For example, production of kit ligand/stromal cell-derived factor 1 (KITL/SCF), CXC ligand 12 (CXCL12) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) is altered with aging1-4 and these factors are essential for HSC maintenance5-7 and/or lymphoid production from HSCs.3,5 Chronic low-grade inflammation in aged mice also impairs HSC function. For example, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) produced in the endosteum of aged mice stimulates inflammatory responses in HSCs, mesenchymal and endothelial cells (ECs).8 Interventions to reduce chronic inflammation in aged mice such as blocking IL-1 signaling, knockout of the IL-1 receptor, fetal microbiotas transplantation from young mice, or in vivo antibiotic suppression improve HSC function.8-10 However, the dynamics of and relationship between chronic inflammation relative to the decline in HSC- and lymphoid-supportive factors remains unclear.
Most studies of mammalian aging report average differences between groups of aged vs young individuals.11 However, 1 observed effect of aging is increased variability between individuals. Heterogeneity in health characteristics and biomarkers of tissue function12 has served as the rationale for development of molecular “clocks” that predict biological age.13 In the context of hematopoiesis, however, the extent to which phenotypic variation is observed in biological aging of the BM, and the extent to which this variation can be used to predict HSC and hematopoietic function, is unknown. We recently reported altered HSC function and hematopoiesis in middle-aged C57BL/6J mice.3 Here, we used single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to define the cellular and molecular determinants of variability between middle-aged mice in HSC activation and lymphoid commitment including consideration of HSC-extrinsic changes in the BM microenvironment.
Methods
Mice
Young (2 months) and middle-aged (ranging from 9-14 months, details provided for each experiment in figure legend) C57BL/6J (JAX:000664) female mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory’s aging mouse colony and housed together before experiments. Some, but not all, of the mice within an age group were littermates. B6.129(FVB)-Igf1tm1Dlr/J14 (JAX:016831) were crossed to B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(cre/ERT2)Tyj/J (JAX:008463), B6.129(Cg)-Leprtm2(cre)Rck/J15 (JAX:008320), and B6.Cg-Tg(Prrx1-cre/ERT2,-EGFP)1Smkm/J16 (JAX:029211). Lepr-Cre were crossed to B6.Cg-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm14(CAG-tdTomato)Hze/J17 (JAX:007914). All Igf1 conditional knockout experiments were performed using young adult female mice (2-4 months). Control and experimental mice with CreER received 125 mg/kg tamoxifen for 3 days by oral gavage.
Volumetric confocal imaging
Procedures were performed as described.18 Femurs were fixed in 4% methanol-free formaldehyde for 24 hours (Thermo Fisher) and decalcified in 10% EDTA for 2 weeks before embedding. Sections (220 μm) were blocked/permeabilized for 2 hours (Tris-buffered saline, 20% dimethyl sulfoxide, 0.05% Tween 20, and 10% donkey serum) and serially stained with primary anti-Sca-1 (BioLegend), anti-CD105 (R&D Systems), anti-Gp1Bβ (glycoprotein 1b platelet subunit β, emfret), anti-Opn (osteopontin, R&D Systems), secondary antibodies (488, 555, 680, and 800), BODIPY (Invitrogen) and DAPI (Thermo Fisher). Sections were optically cleared (2,2’-thiodiethanol; Sigma Aldrich) and imaged using a Leica Stellaris equipped with 5 HyD detectors using a 20× multiple-immersion objective (NA 0.75, FWD 0.680 mm) at 400 Hz, 8-bit and 1024 × 1024 resolution. Quantitative image analysis was performed using Imaris 9.9.0. BM volume was defined by the less deep fluorescent channel.
Isolation of BM cells
For hematopoietic isolation, BM was isolated by crushing spine, sternum, and humeri of individual mice. Mononuclear cells were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies CD45 (clone 30-F11), Ter-119 (TER-119), c-Kit (2B8), Sca-1 (D7), mature lineage (Lin) marker mix (B220 [RA3-6B2], CD11b [M1/70], CD4 [RM4-5], CD5 [53-7.3], CD8a [53-6.7], Ter-119 [TER-119], and Gr-1 [RB6-8C5]), and DAPI. For nonhematopoietic cell isolation, BM plugs were flushed from femurs, tibias, and iliac crests. BM plugs and bone chips were digested with collagenase type IV (2 mg/mL) and dispase (1 mg/mL). Digested supernatants were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies CD45 (30-F11), Ter-119 (TER-119), CD41 (MWReg30), CD31 (cMEC13.3), CD71 (R17217), and CD51 (RMV-7). From each mouse, hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic fractions were serially sorted into the same collection tube: mature hematopoietic cells (CD45+Ter119–), committed hematopoietic progenitors (CD45+Ter119–Lin–c-Kit+), and hematopoietic stem and multipotent progenitors (CD45+Ter119–Lin–c-Kit+Sca1+) were sorted on a FACS Aria II (BD) followed by ECs (CD45–Ter119–CD71–CD31+) and mesenchymal cells (CD45–Ter119–CD31–CD71–CD51+) on a FACSymphony S6 (BD). Cells were counted using a Countess II (Thermo Fisher) and 12 000 cells were loaded onto a 10X Chromium microfluidic chip (10X Genomics) for capture, barcoding, and library preparation using version 3.1 chemistry (#CG000315).
scRNA-seq
Libraries were sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq6000 S4 targeting 6000 barcoded cells at 75 000 reads per cell. Base call files were converted to FASTQ using bcl2fastq v2.20.0.422. The Cell Ranger pipeline (10x Genomics, version 6.0.0) aligned reads to the mouse reference GRCm38.p93. Individual count matrices were combined without batch correction using Seurat v4.3.0.19 Quality control filtering used ddqcR.20 First, initial quality control was used as a high-level filter using default parameters. Second, ddqc.metrics performed Seurat clustering (dims: 1:20, k.param = 30, and resolution = 1). Third, cells were filtered whether they were above or below 2 mean absolute deviations from within their cluster based on RNA counts, RNA features, mitochondrial, or ribosomal content using default parameters, with addition of high RNA counts. The filtered data set was then used for Seurat processing, normalization, scaling, and clustering (dims = 1:20, k.param = 30, and resolution = 0.6). Resulting clusters were classified as hematopoietic (Ptprc) or nonhematopoietic (Pecam1 and Itgav). The FindMarkers function and dplyr21 v1.1.1 identified the top 20 marker genes for each cluster (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website). Cluster identities were assigned based on published marker genes.22-25 Partek Flow (version 10.0.22.0428) was used for differential gene expression analysis and gene ontology (GO) term enrichment analysis (supplemental Table 2). Gene set enrichment analysis26,27 was performed using published signatures28-31 and using the Molecular Signatures Database hallmark inflammatory response gene set. Aging signature scores were calculated from averaged normalized gene counts per sample. CellChat32 (v1.6.1) predicted and graphed ligand-receptor interactions classified in the “secreted signaling” category in young and middle-aged groups. Communication probability differences calculated by subtraction were graphed with ggplot233 v3.4.2. For correlation plots, WGCNA v1.72-134 calculated eigengene values for each module (supplemental Table 2), and Pearson correlations between MSC genes and eigengene values in HSCs.
Ex vivo assays
Techniques were adapted from previous article.35 Femurs, tibiae, and iliac crests were isolated from Igf1+/+ Cre-ERT2 mice and Igf1fl/fl Cre-ERT2 mice. Bones were flushed with alpha minimum essential medium/20% fetal bovine serum, and adherent cells cultured at 37°C and 5% CO2. MSCs were used between passage 2 and passage 5. For conditioned media (CM), MSCs were treated with 20 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen for 24 hours, washed, and cultured in fresh media for 7 days. Luminex assays were used to assess mouse IGF1, CXCL12, IL-6, IL-7, IL-1α, IL-1β, interferon gamma (IFN-γ) (R&D Systems), and KITL using a mouse enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (Thermo Fisher). Luminex assays were used to quantitate mouse RANTES, TNF, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-6, IL-7, IL-1α, IFN-γ (R&D Systems) from BM fluid flushed from femurs.
Statistical analysis
No sample group randomization or blinding was performed. All statistical tests were performed using Prism 9 (GraphPad) or R.
All mouse work was approved by the institutional animal care and use committee at The Jackson Laboratory.
Results
Phenotypic variation in composition of the BM microenvironment in middle-aged female mice
First, we performed volumetric multiplexed immunofluorescence of femur sections from 4 young (2 months) and 3 middle-aged (14 months) C57BL/6J female mice to assess high-level morphology and cell composition (Figure 1A). The abundance of megakaryocytes (Gp1Bβ), arteriolar ECs (Sca-1), sinusoidal vascular ECs (CD105), and adipocytes (BODIPY) were not significantly different in middle-aged mice compared with young mice (Figure 1B-E). Adipocyte accumulation was variable between individual middle-aged mice (Figure 1E), consistent with variable accumulation of adipocytes in the BM of old mice.8 These data suggest that high-level composition of the BM is not dramatically altered at middle age, but certain aspects may differ among individual mice of the same chronological age.
Histological assessment of the BM microenvironment in MA mice. (A) Representative 5-color immunostaining of a longitudinal tissue-wide volumetric section from a MA mouse femur (220 μm) stained for Gp1Bβ-680 (MK), Sca1-488 (arterioles), CD105-555 (sinusoids), Opn-800 (extracellular matrix), BODIPY(adipocytes), and DAPI. (B) Representative images of megakaryocytes (Gp1Bβ+) in young (2 months) and MA (14 months) mouse femurs (left) and quantitation of occupied volume (right). (C) Representative images of arterioles (Sca1+) in young (2 months) and MA (14 months) mouse femurs (left) and quantitation of occupied volume (right). (D) Representative images of sinusoids (CD105+) in young (2 months) and MA (14 months) mouse femurs (left) and quantitation of occupied volume (right). (E) Representative images of adipocytes (BODIPY+) in young (2 months) and MA (14 months) mouse femurs (left) and quantitation of occupied volume (right). (B-E) Dots represent individual mice (n = 4). MA, middle-aged; MK, megakaryocytes.
Histological assessment of the BM microenvironment in MA mice. (A) Representative 5-color immunostaining of a longitudinal tissue-wide volumetric section from a MA mouse femur (220 μm) stained for Gp1Bβ-680 (MK), Sca1-488 (arterioles), CD105-555 (sinusoids), Opn-800 (extracellular matrix), BODIPY(adipocytes), and DAPI. (B) Representative images of megakaryocytes (Gp1Bβ+) in young (2 months) and MA (14 months) mouse femurs (left) and quantitation of occupied volume (right). (C) Representative images of arterioles (Sca1+) in young (2 months) and MA (14 months) mouse femurs (left) and quantitation of occupied volume (right). (D) Representative images of sinusoids (CD105+) in young (2 months) and MA (14 months) mouse femurs (left) and quantitation of occupied volume (right). (E) Representative images of adipocytes (BODIPY+) in young (2 months) and MA (14 months) mouse femurs (left) and quantitation of occupied volume (right). (B-E) Dots represent individual mice (n = 4). MA, middle-aged; MK, megakaryocytes.
Comprehensive single-cell transcriptome profiling of nonhematopoietic and hematopoietic compartments in middle-aged female mice
To robustly assess cellular and molecular variation among individual mice of the same chronological age, we performed scRNA-seq using bones from 5 individual young (2 months) and 9 individual middle-aged (14 months) female C57BL/6J mice. From each mouse, we crushed bones without digestion to retrieve hematopoietic cell fractions and, in parallel, flushed a portion of bones followed by digest to retrieve nonhematopoietic cell fractions following established protocols.22 The hematopoietic cell fraction was sorted to enrich mature hematopoietic cells, committed hematopoietic progenitor cells, and hematopoietic stem and multipotent progenitor cells (MPP; Figure 2A). The nonhematopoietic cell fraction was sorted to enrich ECs and mesenchymal cells (Figure 2B). When sorting, we observed that the proportion of ECs was significantly decreased in middle-aged mice and the proportion of mesenchymal cells was increased (Figure 2B). All 5 cell populations were serially sorted and pooled from individual mice at a defined ratio (Figure 2C) and directly used for 10x Chromium capture. 106 852 cells were sequenced generating 55 000 to 100 000 reads per cell and evenly distributed across collection dates, suggesting little to no batch effect (supplemental Figure 1A-B). Filtering thresholds were set on a per-cluster basis using ddqc, a method which considers biological variability across cell types.20 We observed variation in percent mitochondrial and ribosomal genes, as well as number of genes and RNA molecules per cell in different clusters in our data set (supplemental Figure 1C-E). We then used expression of the pan-hematopoietic marker Ptprc (CD45) and erythrocyte marker Tfrc (CD71) to define hematopoietic cells, and the EC marker Pecam1 (CD31) or mesenchymal marker Itgav (CD51) to define nonhematopoietic cells (supplemental Figure 2A). Across individual mice, the proportion of hematopoietic cells ranged from 60% to 80% (supplemental Figure 2B), matching our expected value of ∼68% hematopoietic based on cell proportions sorted.
scRNA-seq of hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic fractions of the BM from young and MA mice. (A-B) Cell surface marker definitions (top) and cell frequency (bottom) in the BM of young (2 months; n = 5) and MA (14 months, n = 9) female C57BL/6J mice. (C) Representative flow cytometry gating for isolation of cell populations from young and MA mice (top) and ratio at which sorted populations were mixed for scRNA-seq (bottom). (D) UMAP projection of pooled data from a subset of young (n = 4; 22 328 cells) and MA (n = 4; 23 093 cells) mice with annotated cell populations denoted by different colors. (E) Frequency and variance of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell populations in young and MA mice identified by cluster annotation. (F) Frequency and variance of mature hematopoietic cell populations in young and MA mice identified by cluster annotation. (G) Frequency and variance of endothelial cell populations in young and MA mice identified by cluster annotation. (H) Frequency and variance of mesenchymal cell populations in young and MA mice identified by cluster annotation. (E-H) Dots represent individual mice. P values were calculated by unpaired t test and F test to compare variances. ∗P < .01; ∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗P < .0001.
scRNA-seq of hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic fractions of the BM from young and MA mice. (A-B) Cell surface marker definitions (top) and cell frequency (bottom) in the BM of young (2 months; n = 5) and MA (14 months, n = 9) female C57BL/6J mice. (C) Representative flow cytometry gating for isolation of cell populations from young and MA mice (top) and ratio at which sorted populations were mixed for scRNA-seq (bottom). (D) UMAP projection of pooled data from a subset of young (n = 4; 22 328 cells) and MA (n = 4; 23 093 cells) mice with annotated cell populations denoted by different colors. (E) Frequency and variance of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell populations in young and MA mice identified by cluster annotation. (F) Frequency and variance of mature hematopoietic cell populations in young and MA mice identified by cluster annotation. (G) Frequency and variance of endothelial cell populations in young and MA mice identified by cluster annotation. (H) Frequency and variance of mesenchymal cell populations in young and MA mice identified by cluster annotation. (E-H) Dots represent individual mice. P values were calculated by unpaired t test and F test to compare variances. ∗P < .01; ∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗P < .0001.
We annotated 19 hematopoietic cell clusters and 6 nonhematopoietic cell clusters based on reference data sets22-25 (Figure 2D; supplemental Table 1). In middle-aged compared with young mice, we observed increased frequency of HSCs and decreased frequencies of HSC and MPP (HSC/MPP), megakaryocyte/erythroid (MkE)-primed MPP (MPP-MkE) and erythroid progenitors (Figure 2E; supplemental Figure 2C-D). Of these, HSCs and MPP-MkE had increased variation between individual middle-aged mice. Within mature hematopoietic cells, we observed increased frequencies of Erythroblast-3, Neutrophil-1, and Neutrophil-3 in middle-aged mice and decreased frequency of PreB cells (Figure 2F; supplemental Figure 2C-D). Of these, Erythroblast-2 and PreB cells had decreased variation between individual middle-aged mice. Within ECs, we observed increased frequency of EC-Arteriolar and decreased frequency of EC-Sinusoidal (Figure 2G; supplemental Figure 2C-D). Within mesenchymal cells, we observed no changes in frequencies of subpopulations, however, MSC-Adipo-2 and MSC-Osteo had increased variation between individual middle-aged mice (Figure 2H; supplemental Figure 2C-D). Together, of all the hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic populations that we captured, HSCs have the most significant changes with respect to altered abundance as well as increased variance among individual middle-aged female mice.
Decline in lymphoid specification signatures and enrichment of differentiation-inactive HSC signatures in middle-aged HSCs in absence of inflammation
In addition to having significant alterations in abundance and variance, HSCs also had the greatest differential gene expression in middle-aged compared with young mice after computationally pooling samples (Figure 3A). We interrogated these pooled data sets to define modules representing molecular signatures of middle-aged HSCs. Middle-aged HSCs had increased expression of 619 genes including Aldh1a1, Sult1a1, Rorb, Cavin2, Nupr1, Selp, Prtn3, and Mt1, and decreased expression of 677 genes, including Lst1 and Lgals1 (Figure 3B; supplemental Table 3). These genes comprise a comprehensive transcriptome signature of murine HSC aging and this HSC aging signature36 was enriched in all middle-aged mice (Figure 3C).
Decline in lymphoid signatures and increased differentiation-inactive signatures in HSCs in MA mice. (A) Bar graph representing the number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) increased (red) and decreased (blue) in hematopoietic cell types in pooled data from MA vs young mice. (B) Volcano plot of DEGs in MA vs young HSCs. Significant differences (P < .01) are indicated by colored dots (increased expression in red and decreased expression in blue). (C) Principal component analysis of HSCs from young (circles) and MA (triangles) individual mice based on a defined HSC AS.36 Colors represent AS score from low (purple) to high (yellow). (D) Enrichment score of top GO terms in genes significantly decreased in expression in MA vs young HSCs. Numbers within the bars indicate genes significantly decreased in expression out of total genes represented in the GO term. (E) Enrichment score of top GO terms in genes increased in MA vs young HSCs. Numbers within the bars indicate genes significantly increased in expression out of total genes represented in the GO term. (F-H) Enrichment score of (F) lymphoid, B-cell, and T-cell relevant GO terms, (G) myeloid-relevant GO terms, and (H) MK/erythroid-relevant GO terms in genes decreased (blue) and increased (red) in expression in MA vs young HSCs plotted against the number of genes in the GO term. The dotted horizontal lines indicate a threshold for significance of enrichment at P < .05. Each triangle represents 1 GO term. Complete data with significance testing can be found in supplemental Table 2. (I) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of signatures representing (left) LPS-induced acute inflammation in HSCs28 and (right) IL-1-induced chronic inflammation in HSCs30 in young vs MA HSCs in our data set. (J) GSEA of a differentiation-inactive HSC signature30 in young vs MA HSCs. AS, aging signature; GMP, granulocyte macrophage progenitor; NK, natural killer, Y, young.
Decline in lymphoid signatures and increased differentiation-inactive signatures in HSCs in MA mice. (A) Bar graph representing the number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) increased (red) and decreased (blue) in hematopoietic cell types in pooled data from MA vs young mice. (B) Volcano plot of DEGs in MA vs young HSCs. Significant differences (P < .01) are indicated by colored dots (increased expression in red and decreased expression in blue). (C) Principal component analysis of HSCs from young (circles) and MA (triangles) individual mice based on a defined HSC AS.36 Colors represent AS score from low (purple) to high (yellow). (D) Enrichment score of top GO terms in genes significantly decreased in expression in MA vs young HSCs. Numbers within the bars indicate genes significantly decreased in expression out of total genes represented in the GO term. (E) Enrichment score of top GO terms in genes increased in MA vs young HSCs. Numbers within the bars indicate genes significantly increased in expression out of total genes represented in the GO term. (F-H) Enrichment score of (F) lymphoid, B-cell, and T-cell relevant GO terms, (G) myeloid-relevant GO terms, and (H) MK/erythroid-relevant GO terms in genes decreased (blue) and increased (red) in expression in MA vs young HSCs plotted against the number of genes in the GO term. The dotted horizontal lines indicate a threshold for significance of enrichment at P < .05. Each triangle represents 1 GO term. Complete data with significance testing can be found in supplemental Table 2. (I) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of signatures representing (left) LPS-induced acute inflammation in HSCs28 and (right) IL-1-induced chronic inflammation in HSCs30 in young vs MA HSCs in our data set. (J) GSEA of a differentiation-inactive HSC signature30 in young vs MA HSCs. AS, aging signature; GMP, granulocyte macrophage progenitor; NK, natural killer, Y, young.
With respect to gene ontology, downregulated genes in middle-aged HSCs were enriched for signatures of lymphocyte activation and differentiation, metabolism, immune system, and B-cell activation and differentiation (Figure 3D). This is consistent with aged HSCs exhibiting downregulation of genes mediating lymphoid specification and function.37 We observed that nearly all assessed lymphoid, B-cell, and T-cell GO terms decreased in enrichment in middle-aged HSCs compared with young HSCs (Figure 3F; supplemental Table 2). Upregulated genes in middle-aged HSCs were enriched for translation, ribosome, peptide and amide metabolic processes, cell junction, and signaling receptor binding (Figure 3E). Although myeloid-biased hematopoiesis is associated with aging,37-39 some evidence suggests this is because of decreased lymphopoiesis and correlates with increased platelet priming in HSCs.40 We observed that nearly all myeloid GO terms were not enriched in middle-aged HSCs (Figure 3G; supplemental Table 2). Only 2 signatures representing granulocyte differentiation and myeloid leukocyte differentiation were modestly enriched in middle-aged HSCs. Overall, the GO terms representing megakaryocyte and erythroid lineages were also not enriched; however, the 2 signatures that were most specific to the platelet lineage were significantly enriched in middle-aged HSCs (Figure 3H; supplemental Table 2). To further interrogate myeloid-biased hematopoiesis, we examined inflammatory signatures given their association with expansion of myeloid-biased HSCs.28,29 We observed that signatures engaged in HSCs after acute lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment29 or chronic IL-1 treatment28 were not enriched in middle-aged HSCs (Figure 3I). These data strongly support a decline in lymphoid priming in HSCs at middle age and increased platelet priming in the absence of myeloid priming transcriptional programs.
Apart from differences in lineage priming, we observed that HSCs were significantly increased in abundance in middle-aged mice (Figure 2E). A recent cellular barcoding study linking single-cell transcriptomics with HSC fate reported a subset of “differentiation-inactive” HSCs that lacked cellular output but were not quiescent.30 Interrogating our data set using this differentiation-inactive HSC fate signature revealed robust enrichment in middle-aged compared with young HSCs (Figure 3J). This is consistent with lineage tracing studies showing that aged HSCs have reduced multilineage differentiation capacity in mice and nonhuman primates.41,42 Together, we have determined that gene modules defining differentiation activity and lymphoid priming represent robust molecular signatures of middle-aged HSCs.
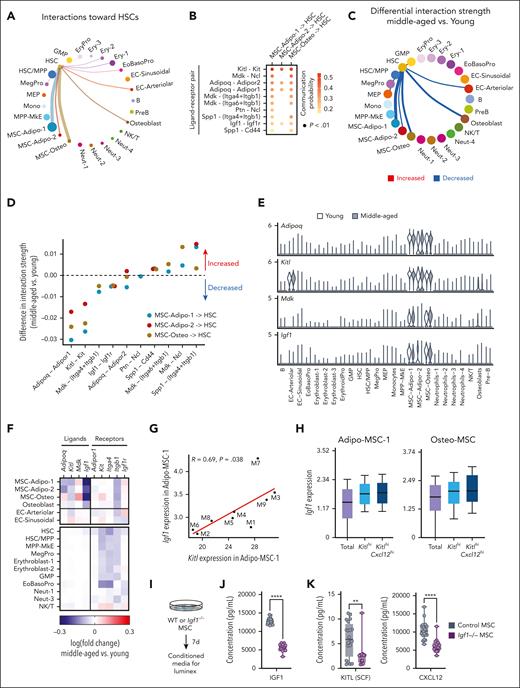
Decline in KITL and IGF1 ligand-receptor interactions between MSCs and HSCs in steady-state middle-aged mice
We next examined which cell types and ligand-receptor interactions would be predicted to affect middle-aged HSCs. We used CellChat32 to quantitatively analyze communication networks in young and middle-aged mice. In young mice, MSCs have the strongest interaction with HSCs (Figure 4A) through ligands including KITL, midkine (MDK), adiponectin (ADIPOQ), pleiotropin, osteopontin (SPP1), and IGF1 (Figure 4B). In middle-aged mice, MSCs had reduced interaction with HSCs (Figure 4C), predicted to be mediated by reduced ADIPOQ, KITL, MDK, and IGF1 signaling (Figure 4D; supplemental Table 4). The transcripts encoding these ligands (Adipoq, Kitl, Mdk, and Igf1) were largely exclusively expressed in MSCs (Figure 4E), apart from Kitl, which was also expressed in arteriolar ECs that are known to secrete KITL.6 Examining ligand and receptor expression more closely, we observed decreased expression of Adipoq, Kitl, and Igf1 in middle-aged MSCs and decreased expression of Adipor1, Kit, and Igf1r in HSCs (Figure 4F). In contrast, the expression of Mdk in middle-aged MSCs was modestly increased, indicating that the predicted decline in MDK signaling is HSC-autonomous by reduced expression of the receptors Itga4 and Itgb1. Thus, decline in engagement of ADIPOQ, KITL, and IGF1 signaling from MSCs to HSCs are the most robust predicted extrinsic changes at middle age.
Reduced engagement of ADIPOQ, KITL, and IGF1 signaling from MSCs to HSCs is predicted to sustain transcriptional changes in MA HSCs. (A) Predicted communication network to HSCs coming from all sampled BM cell types in young mice. Circle size and line weight represent the strength of the connection predicted by CellChat and color represents each cell type. (B) Ligand-receptor pairs with significant communication probability from MSCs (MSC-Adipo-1, MSC-Adipo-2, and MSC-Osteo) to HSCs in young mice. A 1-sided permutation test was used to compute P value. (C) Differential strength of the communication network to HSCs in MA mice. Red lines denote increased interaction strength and blue lines denote decreased interaction strength. Line weight represents the degree of difference between MA and young mice. (D) Differential strength of ligand-receptor interactions from MSCs to HSCs in MA compared with young mice. Dotted line denotes zero (no difference in interaction strength). (E) Expression of Adipoq, Kitl, Mdk, and Igf1 in hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cell clusters in pooled young mice (white) and MA mice (grey). (F) Heat map representing differences in transcript expression of ligands and receptors in MA vs young hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cell clusters. (G) Correlation between Igf1 expression and Kitl expression in Adipo-MSC-1 in individual MA mice. Each dot represents 1 mouse. Pearson correlation, nominal P values. (H) Expression of Igf1 in (left) Adipo-MSC-1, Kitlhi Adipo-MSC-1, and KitlhiCxcl12hi Adipo-MSC-1 and (right) Osteo-MSC-1, Kitlhi Osteo-MSC-1, and Kitlhi Cxcl12hi Osteo-MSC-1. (I) Experimental design to analyze CM from young (2 months) Igf1–/– and control MSCs. (J) Concentration of IGF1 in CM from control (n = 20 individual wells treated with 4-OHT isolated from 3 individual mice) and Igf1–/– (n = 15 individual wells treated with 4-OHT isolated from 3 individual mice) MSCs. (K) Concentration of KITL (left) and CXCL12 (right) in CM from control and Igf1–/– MSCs. 4-OHT, 4-hydroxytamoxifen; GMP, granulocyte macrophage progenitor; NK, natural killer; WT, wild type.
Reduced engagement of ADIPOQ, KITL, and IGF1 signaling from MSCs to HSCs is predicted to sustain transcriptional changes in MA HSCs. (A) Predicted communication network to HSCs coming from all sampled BM cell types in young mice. Circle size and line weight represent the strength of the connection predicted by CellChat and color represents each cell type. (B) Ligand-receptor pairs with significant communication probability from MSCs (MSC-Adipo-1, MSC-Adipo-2, and MSC-Osteo) to HSCs in young mice. A 1-sided permutation test was used to compute P value. (C) Differential strength of the communication network to HSCs in MA mice. Red lines denote increased interaction strength and blue lines denote decreased interaction strength. Line weight represents the degree of difference between MA and young mice. (D) Differential strength of ligand-receptor interactions from MSCs to HSCs in MA compared with young mice. Dotted line denotes zero (no difference in interaction strength). (E) Expression of Adipoq, Kitl, Mdk, and Igf1 in hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cell clusters in pooled young mice (white) and MA mice (grey). (F) Heat map representing differences in transcript expression of ligands and receptors in MA vs young hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cell clusters. (G) Correlation between Igf1 expression and Kitl expression in Adipo-MSC-1 in individual MA mice. Each dot represents 1 mouse. Pearson correlation, nominal P values. (H) Expression of Igf1 in (left) Adipo-MSC-1, Kitlhi Adipo-MSC-1, and KitlhiCxcl12hi Adipo-MSC-1 and (right) Osteo-MSC-1, Kitlhi Osteo-MSC-1, and Kitlhi Cxcl12hi Osteo-MSC-1. (I) Experimental design to analyze CM from young (2 months) Igf1–/– and control MSCs. (J) Concentration of IGF1 in CM from control (n = 20 individual wells treated with 4-OHT isolated from 3 individual mice) and Igf1–/– (n = 15 individual wells treated with 4-OHT isolated from 3 individual mice) MSCs. (K) Concentration of KITL (left) and CXCL12 (right) in CM from control and Igf1–/– MSCs. 4-OHT, 4-hydroxytamoxifen; GMP, granulocyte macrophage progenitor; NK, natural killer; WT, wild type.
These predictions are consistent with the essential role of KITL in steady-state and regenerative hematopoiesis6,7 and our recent report that IGF1 supports lymphopoiesis from HSCs and declines in middle-aged mice.3 However, our previous study functionally assessed IGF1 solely in regenerative hematopoiesis. Thus, we tested the extent to which decline in MSC-produced IGF1 in young (2-4 months) steady-state female mice would replicate middle-aged hematopoietic phenotypes. First, we confirmed that Lepr-Cre and Prx1-CreER models selectively induce recombination in MSCs. Crossing Lepr-Cre with a lox-STOP-lox-tdTomato reporter identified recombination in ∼85% of CD51+ CD31– MSCs, ∼10% of CD51– CD31+ ECs, and <1% of hematopoietic cells (supplemental Figure 3A). Prx1-CreER was expressed in 20% to 50% of MSCs, <1% of ECs, and <1% of hematopoietic cells (supplemental Figure 3C). Using Lepr-Cre or Prx1-CreER to conditionally knockout Igf1 in steady-state mice resulted in decreased frequencies of B cells and increased frequencies of myeloid cells compared with Cre-only controls (supplemental Figure 3B,D). The magnitude of these changes was consistent with alterations in steady-state, middle-aged, and wild-type mice compared with young wild-type controls (supplemental Figure 3B,D). In the BM, Igf1–/– Prx1-CreER mice had reduced cellularity (supplemental Figure 3E) and a decreased proportion of mature cells and increased proportion of HSCs (supplemental Figure 4F) compared with Prx1-CreER control mice. Within the HSC compartment, Igf1–/– Prx1-CreER mice had increased myeloid-biased (CD150hi) and balanced (CD150int) HSCs and decreased lymphoid-biased (CD150lo) HSCs (supplemental Figure 3G). These data support that loss of MSC-produced Igf1 is sufficient to phenocopy aspects of middle age such as expansion of “differentiation-inactive” HSCs resulting in reduced mature cellular output and a decline in lymphoid production from HSCs. CellChat analysis predicted that IGF1 signaling from MSCs predominantly impacts HSCs, EoBasoPro, and Neutrophil-1 populations (supplemental Figure 3H) supporting that the effects of IGF1 on HSCs are through paracrine rather than autocrine mechanisms.
Given that multiple factors were predicted to mediate the decline in intercellular communication from MSCs to HSCs in middle age, we examined the relationship of these factors to one another. Expression of Igf1 and Kitl in MSCs were positively correlated when examining individual middle-aged mice (Figure 4G), whereas Igf1 and Adipoq as well as Kitl and Adipoq were negatively correlated (supplemental Figure 3I). Subsetting MSCs based on expression of Kitl and the key MSC marker Cxcl1243 revealed that Igf1 expression was higher in Kitl(hi) and/or Cxcl12(hi) MSCs (Figure 4H), suggesting that these genes are coexpressed with the same subpopulation(s). To interrogate the extent to which Igf1, Kitl, and Cxcl12 are coregulated, we derived MSCs from Igf1 conditional knockout mice (Igf1fl/fl; Cre-ERT2) and generated CM from these cells (Figure 4I). The CM from Igf1–/– MSCs contained reduced IGF1 as expected (Figure 4J), but also contained reduced KITL and CXCL12 (Figure 4K). These data suggest that a similar subset of MSCs produces IGF1, KITL, and CXCL12 and/or that expression of these key HSC-supportive factors is coregulated in MSCs.
KITL and IGF1 expression in MSCs predict differentiation-inactive and lymphoid priming transcriptional signatures in HSCs in middle-aged mice
Given the naturally occurring variability observed in Igf1 and Kitl in MSCs between middle-aged mice, the predicted decline in paracrine signaling of IGF1 and KITL from MSCs to HSCs, and the decline in differentiation activity and lymphoid priming in middle-aged HSCs, we predicted that Igf1 and Kitl expression in MSCs would correlate with HSC differentiation activity and lymphoid priming on an individual mouse basis. Using individual mice as data points, correlation plots revealed that Igf1 expression in MSCs and Kitl expression in MSCs were negatively correlated with the differentiation-inactive HSC signature (Figure 5A). These results demonstrate that middle-aged mice with lower levels of Igf1 and Kitl expression in MSCs have greater expression of the differentiation-inactive signature in HSCs. In addition, Igf1 expression in MSCs and Kitl expression in MSCs were positively correlated with lymphoid signatures in HSCs including the lymphoid priming transcription factor Ikaros (Ikzf1)44 (Figure 5B). These results demonstrate that middle-aged mice with lower levels of Igf1 and Kitl expression in MSCs have reduced expression of lymphoid signatures in HSCs. In contrast, declining levels of Adipoq expression did not associate with greater expression of the differentiation-inactive signature nor reduced expression of lymphoid signatures in HSCs (supplemental Figure 4A-B), suggesting that decline in Adipoq in MSCs is not predictive of aging-associated HSC expression signatures. Taken together, we have found that decline in Igf1 and Kitl expression in MSCs is naturally variable among individual middle-aged female mice and the level of this decline may be used to predict HSC function with respect to contribution to hematopoiesis and lymphoid production.
Lower expression of Kitl and Igf1 in MSCs correlates with increased expression of differentiation-inactive HSCs and decreased expression of lymphoid signatures in HSCs. (A) Correlation between Igf1 expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and differentiation-inactive HSC signature (left), and Kitl expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and differentiation-inactive HSC signature, in individual MA mice (right). Each dot represents one mouse. (B) Correlation between Igf1 expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and lymphoid progenitor signatures and genes in HSCs in individual MA mice (top). Correlation between Kitl expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and lymphoid progenitor signatures and genes in HSCs in individual MA mice (bottom). Each dot represents 1 mouse. Pearson correlation, nominal P values.
Lower expression of Kitl and Igf1 in MSCs correlates with increased expression of differentiation-inactive HSCs and decreased expression of lymphoid signatures in HSCs. (A) Correlation between Igf1 expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and differentiation-inactive HSC signature (left), and Kitl expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and differentiation-inactive HSC signature, in individual MA mice (right). Each dot represents one mouse. (B) Correlation between Igf1 expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and lymphoid progenitor signatures and genes in HSCs in individual MA mice (top). Correlation between Kitl expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and lymphoid progenitor signatures and genes in HSCs in individual MA mice (bottom). Each dot represents 1 mouse. Pearson correlation, nominal P values.
To test our predictions in independent data sets, we considered studies that have recently reported methods to rejuvenate the aged BM microenvironment and subsequently evaluated HSC function and molecular alterations in MSCs. We predicted that rejuvenation of the BM microenvironment would upregulate Igf1 and Kitl in MSCs, resulting in an increased contribution of aged HSCs to hematopoiesis and lymphoid cell production. In 1 study, HSCs from middle-aged mice (12 months) were rejuvenated using an advanced 3D MSC coculture system.45 This 3D MSC culturing system maintains expression of Igf1 and Kitl more robustly than traditional 2D culturing (supplemental Figure 4C). Middle-aged HSCs rejuvenated by this method had reduced expression of the differentiation-inactive HSC signature and increased expression of lymphoid genes45 (supplemental Figure 4D). In another study, supplementation of Netrin-1 (NTN1) was shown to rejuvenate the BM microenvironment in old mice (18 months) and restore competitive fitness of old HSCs.46 MSCs from NTN1–treated old mice (18 months) had increased expression of Igf1 and Kitl. The expression of Igf1 and Kitl were positively correlated within individual mice supporting their coregulation (supplemental Figure 4E). HSCs from NTN1-treated old mice had lower expression of the differentiation-inactive HSC signature and increased expression of lymphoid genes (supplemental Figure 4F) and NTN1 treatment resulted in an approximately fivefold increase in numbers of long-term repopulating HSCs within the aged BM.46 These data support that Igf1 and Kitl expression in MSCs may be used to predict molecular indicators of HSC function with respect to hematopoietic cell output and lymphoid production.
Decline in production of HSC-supportive factors by MSCs is not associated with proinflammatory cytokines in middle-aged mice
Chronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of aging, and impacts HSCs, MSCs, and ECs in old mice.47 Thus, we investigated the contribution of inflammation to phenotypes observed in middle age. We did not observe increased acute or chronic inflammation signatures in steady-state, middle-aged HSCs (Figure 3I). We also did not observe enrichment of a hallmark inflammatory response signature in nonhematopoietic cells including MSC and EC subsets (Figure 6A). We then interrogated specific genes reported to be increased in mesenchymal (CARc) and sinusoidal ECs in 24-month-old mice and/or in young mice treated acutely with LPS or polyI:C (pI:C).48Il1b and Ccl6 were strongly increased in mesenchymal and ECs in old mice but were not increased in middle-aged MSCs or ECs (Figure 6B). Ccl5, Il6, and Tnf were induced by LPS and/or pI:C in young mice but were not increased in middle-aged MSCs or ECs. The only set of genes increased in all groups (old MSCs, young MSCs treated with LPS or pI:C, and middle-aged MSCs) were the complement genes C4b, Cfb, and C3. In middle-aged mice, the increase in expression of C4b, Cfb, and C3 was restricted to MSCs (Figure 6C). We interrogated a subset of these changes at the protein level in BM fluid from young and middle-aged mice. Consistent with our gene expression data, we only observed an increase in RANTES in middle-aged mice (Figure 6D). Given our observation that decline in IGF1 in MSCs led to decreased production of KITL and CXCL12 (Figure 4J-K), we evaluated levels of inflammatory factors in this same system. CM from Igf1–/– MSCs did not have altered levels of IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ or IL-7 (Figure 6E-F). Using individual mice as data points, the expression of Il1b, Ccl5, Il6, and Tnf in MSCs did not correlate with the differentiation-inactive HSC signature or lymphoid signatures in HSCs (Figure 6G-H; supplemental Figure 5). Thus, expression of inflammatory factors in MSCs are not predictive of aging–associated HSC programs at middle age.
Inflammatory factors associated with stress and old age are not observed in steady-state MA female mice. (A) GSEA of a hallmark inflammatory response signature in young and MA MSC-Adipo-1, MSC-Adipo-2, MSC-Osteo, EC-Arteriolar, and EC-Sinusoidal (SEC) cell clusters. (B) Differential expression of Il1b, Ccl6, Ccl5, Il6, Tnf, C4b, Cfb, and C3 in MA vs young MSC-Adipo-1, MSC-Adipo-2, MSC-Osteo, EC-Sinusoidal (SEC), and EC-Arteriolar (AEC) cell clusters, old (2 years) vs young MSC (CARc) and SECs∗, and young LPS-treated or polyI:C (pI:C)-treated vs young MSC (CARc) and SECs∗. ∗Derived from published data.48 (C) Heat map representing differential expression of Il1b, Ccl6, Ccl5, Il6, Tnf, Ifng, C4b, Cfb, and C3 in all MA vs young cell clusters. (D) Relative protein level of IL-1α, RANTES, IL-6, TNF, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, and IL-7 in BM fluid from young (2 months) and MA (12-14 months) mice. Bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean of n = 5-8 per condition. P values were calculated using 2-way analysis of variance with Sidak multiple comparisons test. ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (E) Experimental design to analyze CM from Igf1–/– and control MSCs. (F) Concentration of IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ, and IL-7 in CM from young control (2 months) and Igf1–/– MSCs. Each dot represents 1 biological replicate. (G) Correlation between Il1b, Ccl5, Il6, and Tnf expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and differentiation-inactive HSC signature in individual MA mice. Each dot represents 1 mouse. (H) Correlation between Il1b, Ccl5, Il6, and Tnf expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and lymphoid progenitor signatures and genes in HSCs in individual MA mice. Each dot represents 1 mouse. WT, wild type.
Inflammatory factors associated with stress and old age are not observed in steady-state MA female mice. (A) GSEA of a hallmark inflammatory response signature in young and MA MSC-Adipo-1, MSC-Adipo-2, MSC-Osteo, EC-Arteriolar, and EC-Sinusoidal (SEC) cell clusters. (B) Differential expression of Il1b, Ccl6, Ccl5, Il6, Tnf, C4b, Cfb, and C3 in MA vs young MSC-Adipo-1, MSC-Adipo-2, MSC-Osteo, EC-Sinusoidal (SEC), and EC-Arteriolar (AEC) cell clusters, old (2 years) vs young MSC (CARc) and SECs∗, and young LPS-treated or polyI:C (pI:C)-treated vs young MSC (CARc) and SECs∗. ∗Derived from published data.48 (C) Heat map representing differential expression of Il1b, Ccl6, Ccl5, Il6, Tnf, Ifng, C4b, Cfb, and C3 in all MA vs young cell clusters. (D) Relative protein level of IL-1α, RANTES, IL-6, TNF, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, and IL-7 in BM fluid from young (2 months) and MA (12-14 months) mice. Bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean of n = 5-8 per condition. P values were calculated using 2-way analysis of variance with Sidak multiple comparisons test. ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (E) Experimental design to analyze CM from Igf1–/– and control MSCs. (F) Concentration of IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ, and IL-7 in CM from young control (2 months) and Igf1–/– MSCs. Each dot represents 1 biological replicate. (G) Correlation between Il1b, Ccl5, Il6, and Tnf expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and differentiation-inactive HSC signature in individual MA mice. Each dot represents 1 mouse. (H) Correlation between Il1b, Ccl5, Il6, and Tnf expression in Adipo-MSC-1 and lymphoid progenitor signatures and genes in HSCs in individual MA mice. Each dot represents 1 mouse. WT, wild type.
Discussion
This study provides reference scRNA-seq data sets of BM cells from individual female C57BL/6J mice at young adult and middle age. To our knowledge, this is the first study sampling hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic fractions from the same individual mice at middle age. This design enabled evaluation of the molecular basis of variation in HSC and hematopoietic aging from an HSC-intrinsic and HSC-extrinsic standpoint. Our data reveal naturally occurring variability between individual middle-aged mice in the decline of lymphopoiesis programs and functional HSC signatures that can be predicted by the expression of Kitl and Igf1 in MSCs, and that this can occur independently from, or potentially before, emergence of aging-associated chronic inflammation. We evaluated our prediction in 2 independent data sets in which rejuvenation of the BM microenvironment was shown to have a beneficial effect on aged HSC function.45,46 In these data sets, Kitl and Igf1 expression were increased or restored in MSCs with evidence of coregulation, and this correlated with improved expression of lymphopoiesis programs and functional HSC signatures.
Identifying important roles for KITL and IGF1 in HSC function and lymphopoiesis is not surprising as this is well understood from genetic knockout experiments.3,6,49,50 However, our observations that Igf1 and Kitl in MSCs exhibit variability in expression between individual mice of the same chronological age and are coregulated in their expression suggests that cross talk between multiple factors underlies maintenance of HSC and lymphoid niches at middle age. By using 2 Cre driver strains to knockout Igf1 at varying efficiencies within MSCs, we observed that more robust Cre expression (Lepr-Cre) had a stronger aging-associated phenotype of reduced B-cell lymphopoiesis compared with milder Cre expression (Prx1-Cre). Interestingly, we did not observe strong evidence of inflammation in contrast to recent evidence that heightened production of inflammatory cytokines in the BM originates from a subset of MSCs in old mice.8 In that study, reducing inflammation by Il1r1 knockout did not result in increased expression of Igf1 in MSCs.8 Thus, blocking inflammatory processes may be insufficient to prevent the decline of Igf1 in MSCs with aging.
A limitation of our study is that we may have missed acute or chronic inflammatory events earlier in life by evaluating a single time point at middle age. In addition, we focused on female mice although C57BL/6J mice are known to have sex–dependent inflammatory responses.51,52 It remains unknown whether our observations are attributed to sex–based biological aging vs generalizable biological aging. Further, because we enriched for sorted rare cell populations, we have not interrogated the entirety of the niche and there may be other relevant factors and cell types that were not sampled in this analysis.
Despite these limitations, we observed increased expression of the complement genes C3, C4b, and Cfb in middle-aged MSCs, which is observed in old mice as well as young mice treated with inflammatory stimuli. Upregulation of complement impacts hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell mobilization during stress hematopoiesis;53 however, little is known about complement in steady-state aging hematopoiesis. In general, complement is associated with aging and linked to degenerative disease.54 Whether complement activation is an initiating change that seeds an inflammatory environment later in aging, and how complement activation relates to Igf1 and Kitl expression, are interesting questions for further investigation.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all members of the Trowbridge laboratory for experimental support and manuscript editing. They thank The Jackson Laboratory’s Single Cell Biology and Genome Technologies Scientific Services and Research IT for support in publishing the R Shiny web application. They thank Carl Mitchell, Oakley Olson, and Emmanuelle Passegue for sharing their processed data and thank Louise Purton, Mick Milsom, and Simon Haas for their critical input into this work.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (grant R01DK118072), NIH, National Institute on Aging (grants R01AG069010, and U01AG077925), and a grant from the Edward P. Evans Foundation (J.J.T.). This work was supported in part by the NIH/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center support grant (P30CA034196). J.J.T. was supported by a Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Scholar Award and The Dattels Family Endowed Chair. J.J.M. was supported by a Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Career Development Program Fellow Award and The Jackson Laboratory Scholar Award. J.H. and K.D.K. were supported by the Mildreed-Scheel-Nachwuchszentrum Frankfurt and Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung.
Authorship
Contribution: K.A.Y. and J.J.T. conceptualized the project and designed experiments; K.A.Y., and J.J.M. performed experiments; K.A.Y., J.J.M., and M.A.T., analyzed data; J.H. and K.D.K. performed imaging experiments and quantitative image analysis; M.A.T. designed and created the web portal; K.A.Y. and J.J.T. wrote the manuscript; and all authors edited the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.J.T. has received research support from H3 Biomedicine, Inc and patent royalties from Fate Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Jennifer J. Trowbridge, The Jackson Laboratory, 600 Main St, Bar Harbor, ME 04609; email: jennifer.trowbridge@jax.org.
References
Author notes
Raw and processed single-cell RNA sequencing data are publicly available in the Gene Expression Omnibus database (accession number GSE210584).
Data can be accessed online at https://thejacksonlaboratory.shinyapps.io/hematopoietic-and-microenvironment-gene-expression.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.








This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal