Key Points
Cancer imprints a disease-specific “immune scar” that persists for years despite clinical remission.
The DLBCL-induced scar shows high IL6, high myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and low immature T cell counts and impairs adaptive immunity.
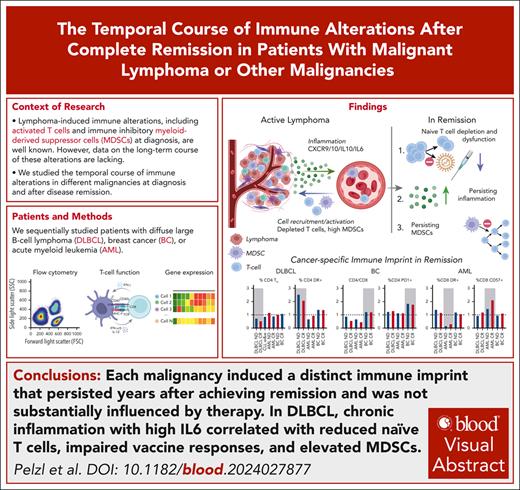
Visual Abstract
Immunotherapy has become standard of care in the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Changes in immunophenotypes observed at first diagnosis predict therapy outcome but little is known about the resolution of these alterations in remission. Comprehensive characterization of immune changes from fresh, peripheral whole blood revealed a functionally relevant increase of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, reduced naïve T cells, and an increase of activated and terminally differentiated T cells before treatment, which aggravated after therapy. Suggesting causal relation, injection of lymphoma in mice induced similar changes in the murine T cells. Distinct immune imprints were found in those who have survived breast cancer and acute myeloid leukemia. Identified alterations persisted beyond 5 years of ongoing complete remission and correlated with increased proinflammatory markers such as interleukin-6, β2-microglobulin, or soluble CD14 in DLBCL. The chronic inflammation was associated with functionally blunted T-cell immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2–specific peptides, and reduced responses correlated with reduced naïve T cells. Persisting inflammation was confirmed by deep sequencing and by cytokine profiles, together pointing toward a compensatory activation of innate immunity. The persisting, lymphoma-induced immune alterations in remission may explain long-term complications, have implications for vaccine strategies, and are likely relevant for immunotherapies.
Introduction
The therapeutic landscape of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) has been revolutionized by the introduction of novel targeted and immune-mediated therapies. Thereby, response rates to first-line therapy have increased, resulting in more patients with lasting complete remission (CR).1,2 Nowadays immunotherapies including bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells are standard of care in later lines but will rapidly advance toward use in earlier treatment settings.3-6 Because of improved therapeutic efficacy, the number of survivors of DLBCL will further grow, which may be challenged by previously underappreciated disease- and treatment-related complications. Such challenges were identified in data from large registry studies that show that survivors of DLBCL are distinct from survivors of other cancers including those with breast cancer (BC), with higher rates of infectious complications and autoimmune phenomena for at least 10 years after achieving remission independently of rituximab treatment.7 Although all survivors of cancer have a generally higher risk of secondary primary malignancies (SPM),8 the risk in DLBCL is among the highest with relative enrichment of skin cancer and of squamous cell carcinoma including lung cancer.9,10 This “high-risk” status and potential immune dysfunction in remission, together with elevated rates of autoimmunity, infections, and SPMs, remains unexplained as of today.
Distinct from long-term complications in remission, the initial high-risk status predicting relapse probability is defined by basic clinical parameters such as the revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) before first-line therapy and will likely be combined with genomic risk-prediction in the future.1,11-15 Biopsy-derived immune profiles underscore high inflammation in DLBCL as a common feature with clinical relevance.16-18 In line with DLBCL-induced inflammation, elevated monocytic myeloid–derived suppressor cells (M-MDSCs) have been reported before first-line immunochemotherapy or in relapsed/refractory (R/R) DLBCL.19-21 Because of the physiological task of MDSCs of resolving inflammation, a high fraction of MDSCs is a typical observation in all states of chronic and unresolved inflammation including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and chronic infections.22,23 Accordingly, inflammatory cytokines are commonly elevated in the serum of patients with DLBCL.24,25
Despite frequently reported inflammation at first diagnosis, surprisingly little is known about the immune system in patients in CR after first-line therapy and their immunological fitness. To better understand distinct patterns of long-term complications and possibly to develop a tool to predict response to immunotherapies in the future, we set forth to comprehensively and mechanistically analyze the immune system of patients in CR after chemoimmunotherapy.
Methods
Patients
Patients with newly diagnosed (ND) DLBCL, BC, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), or chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), as well as patients in CR and healthy controls (HCs) were enrolled. Detailed patient characteristics are described in supplemental Tables 1-3, available on the Blood website. Patients in CR were sampled at indicated time points during routine follow-ups. This project was approved by the Ethics Department of the University of Erlangen (approval no. 513-20) according to the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants gave written informed consent. The SAL-AML biobank was approved by the ethics committee of Technische Universität Dresden (EK98032010).
Sample preparation, phenotyping, and serum cytokines
Fresh whole blood was stained using TruCount technology and analyzed by flow cytometry within 4 hours after blood draw. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated using Pancoll. Individual serum cytokines were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (R&D Systems) and serum proteomics using Olink technology.26,27 Reagents, detailed procedures, and hardware used are described in the supplemental Methods. Representative gating strategies are shown in supplemental Figure 1.
T-cell assays
For proliferation, CD3+ T cells, M-MDSCs (Lin−/CD16−/CD11b+/CD14+/human leukocyte antigen type DR [HLA-DR)−/low]) and myeloid controls (Lin−/CD16/CD11b+/CD14+/HLA-DRhigh) were sorted from freshly isolated PBMCs. T cells were stained with carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester; stimulated with anti-CD2, anti-CD3, and anti-CD28; and cocultured with respective myeloid cells. Proliferation was analyzed after 7 days by flow cytometry. For antigen-specific T-cell stimulation, cryopreserved PBMCs were cocultured with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike peptides, as described in the supplemental Materials. Surface and intracellular cytokines were measured using Attune Nxt (ThermoFisher), and secreted cytokines were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
RNA and TCR sequencing
MDSCs (CD14+/HLA-DRlow) and activated CD4+/HLA-DR+ T cells were sorted from freshly isolated PBMCs. RNA was extracted with RNeasy kit (Qiagen). Bulk RNA was sequenced at Eurofins Genomics (Constance, Germany) using an Illumina platform (Illumina NovaSeq6000, PE150 mode). For T-cell receptor (TCR) sequencing, the library was prepared using QIAseq Targeted RNA Panel TCR Library kit (Qiagen) and sequenced on Illumina NextSeq at the local next-generation sequencing core facility. Detailed methods and the bioinformatic pipelines used for analysis are described in the supplemental Materials.28
Animal model
A systemic, syngeneic C57BL/6 lymphoma model was used as previously described and further detailed in the supplemental Methods.29 Animal studies were approved by the institutional animal care and use committee. Animals were handled according to institutional guidelines.
Statistical analysis
A principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to identify immunophenotypic patterns using “FactoMineR” in R version 4.3.2 as detailed in the supplemental Materials. Difference in means and correlation analyses were evaluated with parametric tests (unpaired or paired t test, ordinary 1-way analysis of variance, or linear regression). Results are shown as median and 95% confidence interval as indicated. All statistics were performed using GraphPad Prism, version 9.0.2. (GraphPad Prism Software Inc, San Diego, CA), with assumed significance from P < .05.
Results
Patient characteristics
Peripheral blood samples of 67 patients with ND DLBCL, 32 with R/R DLBCL, 70 patients in CR after DLBCL, and 60 HCs were collected between September 2021 and March 2025. Patient characteristics are presented in Table 1. Of 70 patients in CR, 62 patients had been diagnosed with de novo DLBCL (89%), and 8 patients (11%) had a transformation, 7 from follicular lymphoma (FL) and 1 from marginal zone lymphoma. The median time interval in CR from the last treatment to measurement was 15.8 months (3.0-196). Comparison of these characteristics between the 3 cohorts revealed significant differences only for Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status score, which was higher in those with R/R disease. All 70 patients achieved CR after first-line therapy and were treated with R-CHOP–like (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, Oncovin [vincristine], and prednisone) regimens. At data cutoff, 8 of 70 patients had a subsequent relapse, and the median follow-up including all patients, alive (n = 66) and dead (n = 4), was 15.5 months (5.4-31.3).
Patient characteristics of the DLBCL cohorts
| . | HCs (N = 60) . | CR after DLBCL (N = 70) . | ND DLBCL (N = 67) . | R/R DLBCL (N = 32) . | P value∗ . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | .25 | ||||
| Male | 30 (50) | 40 (57) | 39 (58) | 23 (72) | |
| Female | 30 (50) | 30 (43) | 28 (42) | 9 (28) | |
| Median age (95% CI), y | 65.4 (51.2-94.2) | 70.8 (21.0-88.7) | 70.1 (23.0-90.5) | 72.1 (34.6-85.4) | .43 |
| Disease type, n (%) | .43 | ||||
| DLBCL | 62 (89) | 59 (88) | 25 (78) | ||
| tFL | 7 (10) | 7 (10) | 5 (16) | ||
| tMZL | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | 2 (6) | ||
| Cell of origin, n (%) | .73 | ||||
| GCB | 31 (58) | 31 (60) | 11 (50) | ||
| Non-GCB | 22 (42) | 21 (40) | 11 (50) | ||
| No data | 17 | 15 | 10 | ||
| Genetic risk stratifiers, n (%) | .60 | ||||
| No/single expressor | 22 (43) | 23 (47) | 8 (38) | ||
| Double expressor | 21 (41) | 19 (39) | 11 (52) | ||
| Triple expressor | 7 (14) | 3 (6) | 1 (5) | ||
| Double hit | 1 (2) | 4 (8) | 1 (5) | ||
| Triple hit | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| No data | 19 | 18 | 11 | ||
| R-IPI, n (%) | .40 | ||||
| Low (0-2) | 32 (46) | 24 (41) | 9 (31) | ||
| High (3-5) | 38 (54) | 35 (59) | 20 (69) | ||
| No data | 0 | 8 | 3 | ||
| IPI factors n (%) | |||||
| Stage ≥III | 54 (77) | 41 (61) | 25 (78) | .38 | |
| LDH >ULN | 46 (66) | 42 (63) | 23 (72) | .17 | |
| Age >60 years | 50 (71) | 54 (81) | 26 (81) | .30 | |
| ECOG PS ≥2 | 8 (11) | 7 (10) | 8 (25) | .04 | |
| Extranodal sites ≥2 | 30 (43) | 30 (45) | 7 (22) | .18 | |
| B-symptoms | 16 (23) | 8 (12) | 9 (28) | .11 | |
| Tumor bulk | 12 (17) | 7 (10) | 4 (13) | .60 |
| . | HCs (N = 60) . | CR after DLBCL (N = 70) . | ND DLBCL (N = 67) . | R/R DLBCL (N = 32) . | P value∗ . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | .25 | ||||
| Male | 30 (50) | 40 (57) | 39 (58) | 23 (72) | |
| Female | 30 (50) | 30 (43) | 28 (42) | 9 (28) | |
| Median age (95% CI), y | 65.4 (51.2-94.2) | 70.8 (21.0-88.7) | 70.1 (23.0-90.5) | 72.1 (34.6-85.4) | .43 |
| Disease type, n (%) | .43 | ||||
| DLBCL | 62 (89) | 59 (88) | 25 (78) | ||
| tFL | 7 (10) | 7 (10) | 5 (16) | ||
| tMZL | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | 2 (6) | ||
| Cell of origin, n (%) | .73 | ||||
| GCB | 31 (58) | 31 (60) | 11 (50) | ||
| Non-GCB | 22 (42) | 21 (40) | 11 (50) | ||
| No data | 17 | 15 | 10 | ||
| Genetic risk stratifiers, n (%) | .60 | ||||
| No/single expressor | 22 (43) | 23 (47) | 8 (38) | ||
| Double expressor | 21 (41) | 19 (39) | 11 (52) | ||
| Triple expressor | 7 (14) | 3 (6) | 1 (5) | ||
| Double hit | 1 (2) | 4 (8) | 1 (5) | ||
| Triple hit | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| No data | 19 | 18 | 11 | ||
| R-IPI, n (%) | .40 | ||||
| Low (0-2) | 32 (46) | 24 (41) | 9 (31) | ||
| High (3-5) | 38 (54) | 35 (59) | 20 (69) | ||
| No data | 0 | 8 | 3 | ||
| IPI factors n (%) | |||||
| Stage ≥III | 54 (77) | 41 (61) | 25 (78) | .38 | |
| LDH >ULN | 46 (66) | 42 (63) | 23 (72) | .17 | |
| Age >60 years | 50 (71) | 54 (81) | 26 (81) | .30 | |
| ECOG PS ≥2 | 8 (11) | 7 (10) | 8 (25) | .04 | |
| Extranodal sites ≥2 | 30 (43) | 30 (45) | 7 (22) | .18 | |
| B-symptoms | 16 (23) | 8 (12) | 9 (28) | .11 | |
| Tumor bulk | 12 (17) | 7 (10) | 4 (13) | .60 |
CI, confidence interval; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; GCB, germinal center B cell; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; tFL, transformed FL; tMZL, transformed marginal zone lymphoma; ULN, upper limit of normal.
P value by the χ2 test or the Fisher exact test for nominal and categorial variables. The analysis of variance was used for metric variables. Boldface P values are statistically significant.
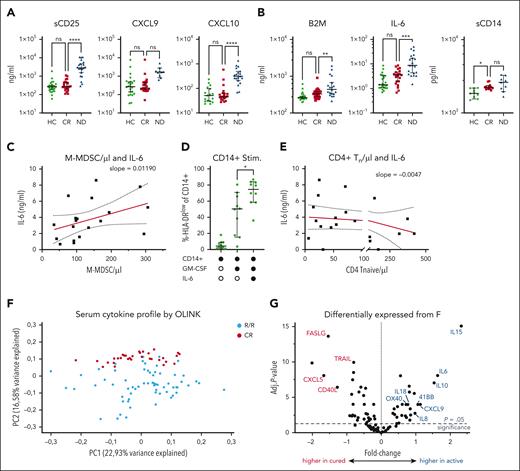
Elevated MDSCs persist years after achieving CR
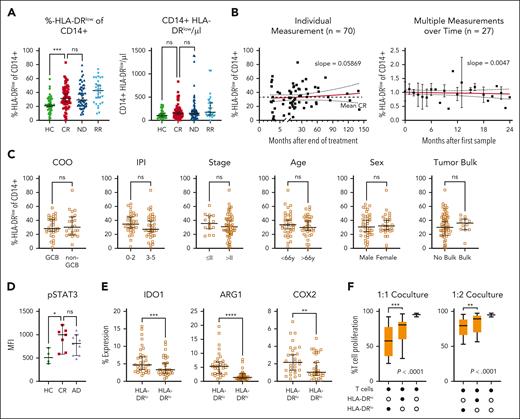
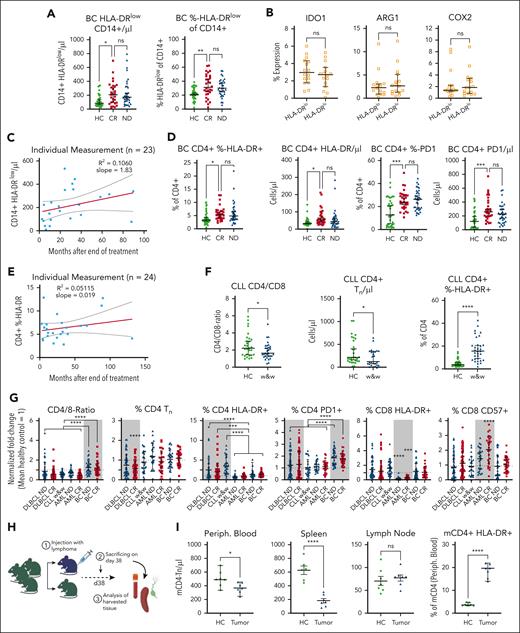
Because of various reports of elevated M-MDSCs at first diagnosis and in relapse of DLBCL, we characterized MDSCs in lasting remission. Both frequency and absolute number of CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes were higher in the peripheral blood of patients with ND and those with R/R DLBCL than HCs (Figure 1A). Comparing patients with DLBCL in CR after therapy with HCs, CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes remained significantly elevated for at least 5 years with no downward trend (Figure 1B; supplemental Figure 2). We also monitored 27 patients in remission longitudinally for up to 2 years and did not find a relevant intrapatient decrease of CD14+/HLA-DRlow cells. This suggested persistently high CD14+/HLA-DRlow cells to be a lasting phenomenon after presumably curative DLBCL treatment. There were no significant differences in CD14+/HLA-DRlow frequency in patients in CR subcategorized regarding cell of origin (P = .6), R-IPI (P = .09), Ann Arbor stage (P = .7), age (P = .28), sex (P = .79), or tumor bulk (0.84) (Figure 1C). In line with the inhibitory function of these CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes, we found a significantly higher intracellular STAT3 phosphorylation in the CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes of patients in CR and those with active disease (AD = ND + R/R) than HCs (Figure 1D). Furthermore, HLA-DRlow monocytes in CR had higher expression levels of arginase-1, indoldioxygenase 1, and cyclooxygenase 2 than HLA-DRhigh monocytes (Figure 1E). Lastly, MDSCs of patients in CR highly significantly suppressed the proliferation of activated autologous T cells in vitro by 80% more efficiently than CD14+/HLA-DRhigh cells (Figure 1F). Thus, immunosuppressive MDSCs remain elevated over years despite lasting remission.
Elevated HLA-DRlow CD14+ myeloid cells persist in patients with DLBCL after achieving CR and show characteristic features of MDSCs. (A) CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes were measured by flow cytometry from fresh peripheral whole blood from HCs, patients with DLBCL in CR, when ND, or when R/R. Symbols indicate individual patients, median is indicated. P values determined by the ordinary 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) including 2-group comparison using the Šidák multiple comparison when indicated. (B) Time point of individual CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes shown in panel A. In addition, 27 patients were measured longitudinally and normalized to the first measurement. The red lines indicate linear regression over time including 95% confidence interval (CI) and slope. (C) Rate of CD14+/HLA-DRlow cells at CR in subgroups of cell of origin (COO), R-IPI, Ann Arbor stage, age, sex, or tumor bulk, significance determined by the unpaired t test. (D) Intracellular phosphrylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (pSTAT3) by flow cytometry in CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes compared with HCs, P value determined by ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (E) Intracellular staining of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), arginase-1 (Arg1), and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) in CD14+/HLA-DRlow and respective DRhigh cells of patients with CR, P value determined by the paired t test. (F) Proliferation of activated T cells alone or in coculture with indicated CD14+ cell population from n = 15 patients in CR with indicated ratios of myeloid cells to T cells; P values determined by the ordinary 1-way ANOVA. For all panels, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. GCB, germinal center B cell; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen type DR; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; ns, not significant.
Elevated HLA-DRlow CD14+ myeloid cells persist in patients with DLBCL after achieving CR and show characteristic features of MDSCs. (A) CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes were measured by flow cytometry from fresh peripheral whole blood from HCs, patients with DLBCL in CR, when ND, or when R/R. Symbols indicate individual patients, median is indicated. P values determined by the ordinary 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) including 2-group comparison using the Šidák multiple comparison when indicated. (B) Time point of individual CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes shown in panel A. In addition, 27 patients were measured longitudinally and normalized to the first measurement. The red lines indicate linear regression over time including 95% confidence interval (CI) and slope. (C) Rate of CD14+/HLA-DRlow cells at CR in subgroups of cell of origin (COO), R-IPI, Ann Arbor stage, age, sex, or tumor bulk, significance determined by the unpaired t test. (D) Intracellular phosphrylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (pSTAT3) by flow cytometry in CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes compared with HCs, P value determined by ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (E) Intracellular staining of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), arginase-1 (Arg1), and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) in CD14+/HLA-DRlow and respective DRhigh cells of patients with CR, P value determined by the paired t test. (F) Proliferation of activated T cells alone or in coculture with indicated CD14+ cell population from n = 15 patients in CR with indicated ratios of myeloid cells to T cells; P values determined by the ordinary 1-way ANOVA. For all panels, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. GCB, germinal center B cell; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen type DR; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; ns, not significant.
Functionally relevant T-cell alterations at first diagnosis persist in CR
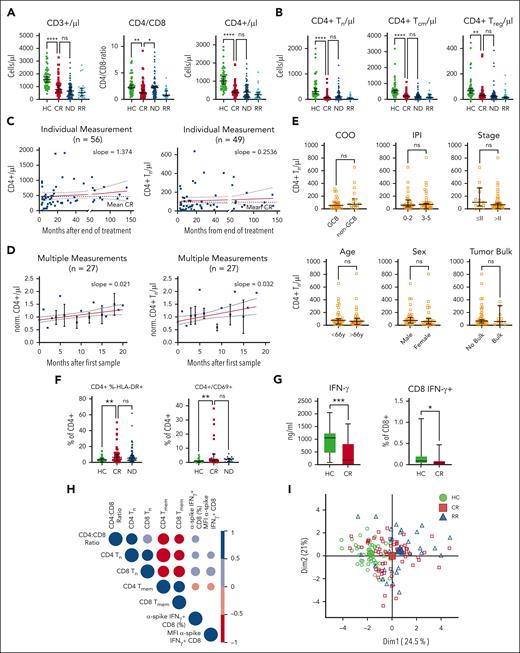
Next, we characterized the T-cell phenotype. The absolute numbers of CD3+ and especially of CD3+/CD4+ T cells were reduced already at ND disease and remained low in CR and at R/R disease compared with in HCs (Figure 2A). Low CD4+ T cells were attributable to a reduced number of naïve T (Tn) cells, central memory T (Tcm) cells, and regulatory T (Treg) cells, whereas terminal effector memory T cells remained comparable in absolute numbers among HCs and those in CR and those with AD (Figure 2B; supplemental Figure 3A-C). Longer time after last treatment did not influence the average total number of peripheral CD4+ T cells or of CD4+ Tn cells in CR (Figure 2C). Measuring individual patients sequentially over 20 months showed a small but steady increase of total CD4+ T cells and of Tn cells over time (Figure 2D). Similar to MDSCs, the low CD4+ Tn cell count in CR did not correlate with cell of origin (P = .25), R-IPI at first diagnosis (P = .84), Ann Arbor stage (P = .076), patient age (P = .59), sex (P = .99), or tumor bulk (P = .76; Figure 2E). Similar findings in patients ND or R/R disease were present to a lesser extent also for CD8+ T cells (supplemental Figure 3D-E). The total CD4+ T cells displayed a chronically activated phenotype characterized by overexpression of HLA-DR and CD69 (Figure 2F). Because chronic activation of T cells as well as reduced levels of Tn cells are known to reduce T-cell function, we assessed antigen-specific responses using vaccine recall assays. Age-, vaccine type–, and number-matched SARS-CoV-2–vaccinated patients with DLBCL in CR were compared with HCs. Both interferon gamma (IFN-γ) levels in the culture supernatant and frequencies of IFN-γ–positive CD8+ T cells of patients in CR were significantly reduced compared with HCs (Figure 2G). The lower vaccine responses correlated with low CD4:CD8 T-cell ratio and with reduced frequencies of naïve T cells (Figure 2H). Because the high fraction of activated CD4+ T cells could be a consequence of antigen-driven expansion, we analyzed the TCR composition of HLA-DR+/CD4+ T-cells of 6 patients in CR compared with 6 HCs and found similar distribution of the top 20 clone sizes and a similar TCR diversity by the Shannon Index between the 2 groups (supplemental Figure 4). In line, V-gene usage of both groups was comparable and polyclonal, suggesting polyclonal unbiased expansion in activated T cells of patients in CR. To understand how the immune phenotype of patients in remission relates to HCs or to those with R/R disease, we created a PCA based on only those multivariate measurements from flow cytometry that were significantly different by univariate analyses between CR and ND or HCs, respectively (Figure 2I) with respective PCA contributors shown in supplemental Figure 5. The average patient with R/R disease or in CR clustered closer together, suggesting that the immune phenotype in CR resembles the immunophenotype of AD and not that of HCs. To more broadly comprehend the status of the immune system, we analyzed natural killer (NK) cell activation and function in patients in remission compared with HCs (supplemental Figure 6). Neither at baseline nor 24 hours after activation, were there any differences between HCs and patients in CR, suggesting that the NK cell population was similar in activation state at baseline and in their capacity to react to HLA-Ineg. K562. In summary, patients in CR presented with reduced counts of total CD4+, Tn, Tcm, and Treg cells, relative higher polyclonal and activated Tem and terminal effector memory T cells, and correlated with impaired T-cell functionality, which is in line with persisting chronic inflammation in patients with DLBCL in remission.
Altered T-cell phenotype correlates with impaired adaptive vaccine response in patients in CR after DLBCL. (A-B) Analysis of total counts and fractions of indicated T-cell subpopulation measured by flow cytometry in HCs and patients with DLBCL in CR, when ND, or when R/R. Each symbol represents an individual patient, P values determined by ordinary 1-way ANOVA including 2-group comparison using Šidák multiple comparison when indicated. (C) Time point of individual CD4+ T-cell or of Tn cell measurement from panels A and B, respectively. The red lines indicate linear regression over time including 95% CI and slope. (D) CD4+ T cells or Tn cells of 27 patients were measured longitudinally and normalized to the first measurement. The red lines indicate linear regression over time including 95% CI and slope. (E) Rate of peripheral CD4+ Tn cell counts in regard to cell of origin (COO), revised international prognostic index (R-IPI), Ann Arbor stage, age, sex, or tumor bulk. Each symbol represents a single patient, P values determined by unpaired t tests. (F) Flow cytometry–based measurements of activated HLA-DR+/CD4+ or CD69+/CD4+ T cells. Each symbol represents individual patients, 2 group comparison by ordinary 1-way ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (G) After antigen-specific stimulation (SARS-CoV-2 peptides) of T cells from HCs or patients in CR, interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in the supernatant and intracellular IFN-γ in CD8+ T cells were compared. Significance was determined by unpaired t tests. (H) Correlogram of the ratio of cell subsets frequencies and anti-spike SARS-CoV-2 T-cell responses across vaccinated HCs and patients in CR. Colored circles represent correlations with P ≤ .05 as determined by the Spearman analysis. Blue and red circles indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively. Color intensity and the size of the circle are proportional to the correlation coefficients. (I) A PCA was performed among patients with DLBCL in CR combining all phenotypic myeloid and T-cell parameters from flow cytometry with HCs and patients with R/R disease mapped using a fixed parameter distribution. Although patients in CR show a diffuse pattern, indicating no clear separation among those patients, the respective HC and R/R clusters separate within the map. Large symbols indicate the centroids of the corresponding groups. For all panels, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. Dim, dimension; GCB, germinal center B cell; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; ns, not significant.
Altered T-cell phenotype correlates with impaired adaptive vaccine response in patients in CR after DLBCL. (A-B) Analysis of total counts and fractions of indicated T-cell subpopulation measured by flow cytometry in HCs and patients with DLBCL in CR, when ND, or when R/R. Each symbol represents an individual patient, P values determined by ordinary 1-way ANOVA including 2-group comparison using Šidák multiple comparison when indicated. (C) Time point of individual CD4+ T-cell or of Tn cell measurement from panels A and B, respectively. The red lines indicate linear regression over time including 95% CI and slope. (D) CD4+ T cells or Tn cells of 27 patients were measured longitudinally and normalized to the first measurement. The red lines indicate linear regression over time including 95% CI and slope. (E) Rate of peripheral CD4+ Tn cell counts in regard to cell of origin (COO), revised international prognostic index (R-IPI), Ann Arbor stage, age, sex, or tumor bulk. Each symbol represents a single patient, P values determined by unpaired t tests. (F) Flow cytometry–based measurements of activated HLA-DR+/CD4+ or CD69+/CD4+ T cells. Each symbol represents individual patients, 2 group comparison by ordinary 1-way ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (G) After antigen-specific stimulation (SARS-CoV-2 peptides) of T cells from HCs or patients in CR, interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in the supernatant and intracellular IFN-γ in CD8+ T cells were compared. Significance was determined by unpaired t tests. (H) Correlogram of the ratio of cell subsets frequencies and anti-spike SARS-CoV-2 T-cell responses across vaccinated HCs and patients in CR. Colored circles represent correlations with P ≤ .05 as determined by the Spearman analysis. Blue and red circles indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively. Color intensity and the size of the circle are proportional to the correlation coefficients. (I) A PCA was performed among patients with DLBCL in CR combining all phenotypic myeloid and T-cell parameters from flow cytometry with HCs and patients with R/R disease mapped using a fixed parameter distribution. Although patients in CR show a diffuse pattern, indicating no clear separation among those patients, the respective HC and R/R clusters separate within the map. Large symbols indicate the centroids of the corresponding groups. For all panels, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. Dim, dimension; GCB, germinal center B cell; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; ns, not significant.
Gene expression profile confirms disease-like immune changes in CR
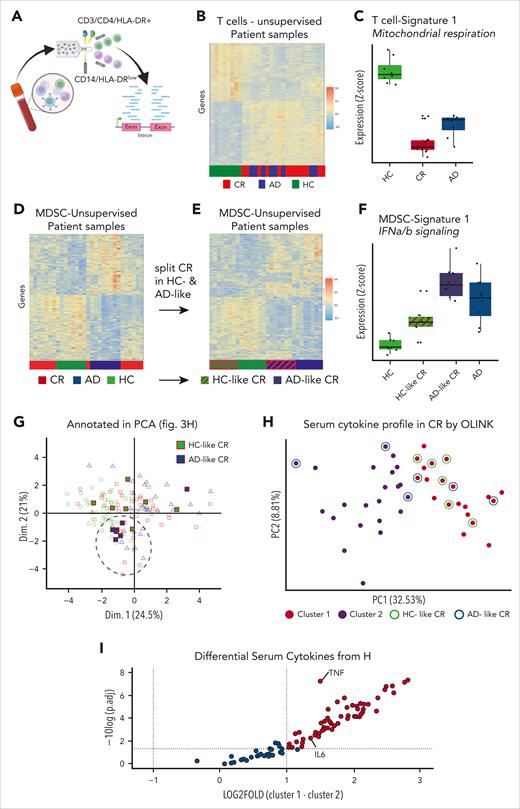
To characterize the immune changes in T and myeloid cells on a molecular level, we sorted CD3+/CD4+/HLA-DR+ T cells and CD14+/HLA-DRlow myeloid cells of HCs, of patients in CR, and of those with AD and analyzed their bulk gene expression profile (Figure 3A). Unsupervised clustering of activated CD4+/HLA-DR+ T cells clearly separated the HCs from patients in CR and with AD. In contrast, patients in CR and with AD were mixed, suggesting a higher level of similarity between their gene expression signatures than with HCs (Figure 3B). Among the most significantly altered pathways, we identified a reduction of mitochondrial respiration, electron transport, and adenosine triphosphate synthesis that functionally suggested a decrease of oxidative phosphorylation in the activated T cells of AD and CR compared with HCs (Figure 3C; supplemental Figure 7A). Unlike the clear distinction in gene expression profiles of T cells, MDSCs showed a more complex landscape. Half of patients with CR clustered with HCs whereas the other half clustered with AD (Figure 3D). There was no significant differentially expressed genes among the 3 groups.
Molecular analyses confirm similar inflammation in CR and AD compared with HCs. (A) CD14+ HLA-DRlow monocytes and activated (HLA-DR+) T cells were sorted from fresh peripheral blood PBMCs for bulk RNA sequencing. (B) The transcription profile of activated (HLA-DR+) T cells of CR DLBCL was compared with those from patients with AD and HCs in an unsupervised clustering. (C) Pathway analysis of the significantly differentially expressed genes of activated (HLA-DR+) T cells highlights signature 1 with reduction of mitochondrial respiration and electron transport in AD and CR compared with HCs. Changes of gene expression levels were determined by Z values. (D) Transcription profiles of CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes from HCs and patients in CR or with AD were unsupervised clustered. (E) CR samples from panel D were manually annotated to either HC-like CR or AD-like CR and unsupervised clustering repeated with the 4 distinct subgroups. (F) Exemplary signature of the 4-group analysis with upregulation of the IFN-α/β signature. Changes of gene expression levels were determined by Z values. (G) Visualizing of the patients HC- and AD-like profiles in the previously shown immunophenotypic pattern PCA from Figure 2H. (H) Cytokine profile of 92 cytokines Olink analysis from serum of patients in CR was clustered by K-means in 2 subgroups by the Elbow method. HC- (green circle) and AD-like samples (blue circles) from the RNA sequencing are indicated. (I) The differentially expressed cytokines of cluster 1 were subtracted by cluster 2 and plotted against their significance levels given by the logarithm of the adjusted P value, that is, −log10 (adj.p). AD., active disease; Dim., dimension; fig., figure; HLA-DR., human leukocyte antigen type DR; IFNa/b, interferon alpha or beta; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Molecular analyses confirm similar inflammation in CR and AD compared with HCs. (A) CD14+ HLA-DRlow monocytes and activated (HLA-DR+) T cells were sorted from fresh peripheral blood PBMCs for bulk RNA sequencing. (B) The transcription profile of activated (HLA-DR+) T cells of CR DLBCL was compared with those from patients with AD and HCs in an unsupervised clustering. (C) Pathway analysis of the significantly differentially expressed genes of activated (HLA-DR+) T cells highlights signature 1 with reduction of mitochondrial respiration and electron transport in AD and CR compared with HCs. Changes of gene expression levels were determined by Z values. (D) Transcription profiles of CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes from HCs and patients in CR or with AD were unsupervised clustered. (E) CR samples from panel D were manually annotated to either HC-like CR or AD-like CR and unsupervised clustering repeated with the 4 distinct subgroups. (F) Exemplary signature of the 4-group analysis with upregulation of the IFN-α/β signature. Changes of gene expression levels were determined by Z values. (G) Visualizing of the patients HC- and AD-like profiles in the previously shown immunophenotypic pattern PCA from Figure 2H. (H) Cytokine profile of 92 cytokines Olink analysis from serum of patients in CR was clustered by K-means in 2 subgroups by the Elbow method. HC- (green circle) and AD-like samples (blue circles) from the RNA sequencing are indicated. (I) The differentially expressed cytokines of cluster 1 were subtracted by cluster 2 and plotted against their significance levels given by the logarithm of the adjusted P value, that is, −log10 (adj.p). AD., active disease; Dim., dimension; fig., figure; HLA-DR., human leukocyte antigen type DR; IFNa/b, interferon alpha or beta; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
We then reannotated MDSCs from patients with CR according to their unsupervised clustering as either “HC-like” or “AD-like.” The now 4 groups separated in 100% of cases (Figure 3E). Corresponding pathway signatures highlighted upregulation of type 1 interferon signaling in the MDSCs of AD and AD-like (Figure 3F; supplemental Figure 7B). With this separation of MDSCs in healthy-like and disease-like groups based on distinct IFN-α signature, we superimposed the respective patients in CR on the immunophenotypic PCA obtained by multivariate flow cytometry discussed earlier, that is, Figure 2I. Intriguingly, all but 1 of the AD-like samples very closely clustered and were separated from the HC-like samples predominantly by PCA dimension 2 (Figure 3G). Next, we interrogated whether serum cytokine profiles of patients in CR may further distinguish the 2 groups. Using the Olink Target 96 Immuno-Oncology cytokine array, we analyzed serum proteomic profiles of 43 patients with DLBCL in remission. However, the cytokine profiles showed a continuum of all samples with no obvious pattern or separation in PCA (Figure 3H). We then applied a separation algorithm using k-means and relying on the elbow method. Within the 2 identified clusters, we annotated HC-like and AD-like samples that did not relate to the 2 clusters, arguing against a separation of the interferon signature by the measured serum cytokines (Figure 3H). Analysis of the cytokine levels that differentiated the clusters 1 and 2 showed that all cytokines were generally upregulated in cluster 1 and no cytokine was significantly downregulated (Figure 3I). This suggests that all patients in CR exhibit significant inflammation, which can be more (cluster 1) or less (cluster 2) severe. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) showed a highly significant increase by 1.3-fold in cluster 1 over cluster 2, suggesting relevance of this cytokine in the inflammatory state of patients in CR.
IL-6–driven chronic inflammation in CR is distinct from AD
Next, we measured serum inflammation markers to approach the nature of chronic inflammation despite absence of active lymphoma. Patients in CR showed HC-like levels of soluble CD25, CXCL9, and CXCL10, which were increased at first diagnosis (Figure 4A). In contrast, interleukin-6 (IL-6), β2-microglobulin, and soluble CD14 were high in ND disease and still remained significantly higher in CR than in HCs (Figure 4B). IL-6 levels correlated with total M-MDSCs in patients in CR (Figure 4C). Vice versa, IL-6 was not found expressed in the gene expression profile of the deep sequencing analysis or by real-time polymerase chain reaction from sorted MDSCs (supplemental Figure 8). Establishing causality of high IL-6 levels and higher MDSCs, differentiation of monocytes of HCs in presence of IL-6 resulted in marked downregulation of HLA-DR in otherwise healthy monocytes (Figure 4C). Furthermore, we found an inverse correlation between the absolute numbers of CD4+ Tn cells and IL-6 levels in CR, further highlighting the relevance of IL-6 (Figure 4D).
Persisting systemic inflammation in CR is distinct from AD. (A) Serum levels of soluble CD25 (sCD25), CXCL9, and CXCL10 or (B) of proinflammatory IL-6, beta-2-microglobuline (B2M), and soluble CD14 (sCD14) were determined from serum samples of HCs and patients in CR, ND patients or patients with R/R disease by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Each symbol indicates individual patients, P values were determined by ANOVA including 2-group comparison using the Šidák multiple comparison when indicated. (C) Serum IL-6 concentration was correlated with absolute M-MDSCs per μL from the peripheral blood of patients in CR, R2 of matching is indicated. (D) Monocytes of HCs were differentiated using GM-CSF with or without IL-6 in vitro, and rate of HLA-DRlow monocytes was determined by flow cytometry. Each symbol represents an individual HC, P values were determined by the matched-pair ordinary ANOVA. (E) Absolute counts of CD4+ Tn cells were correlated with serum levels of IL-6. (F) Cytokine profiles of 72 patients with DLBCL in relapse were compared with profiles of 43 patients with DLBCL in remission to assess the different inflammation profile between the 2 groups. Each circle corresponds to an individual patient with R/R disease (blue) or CR (red). (G) Volcano plot showing the fold change and significance level of significantly upregulated or downregulated serum cytokines in R/R compared with CR. For all panels, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. adj., adjusted; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; FASLG, fas ligand; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ns, not significant; OX40, TNF receptor superfamily member 4; Stim., stimulated; Tn, naive T cells; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
Persisting systemic inflammation in CR is distinct from AD. (A) Serum levels of soluble CD25 (sCD25), CXCL9, and CXCL10 or (B) of proinflammatory IL-6, beta-2-microglobuline (B2M), and soluble CD14 (sCD14) were determined from serum samples of HCs and patients in CR, ND patients or patients with R/R disease by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Each symbol indicates individual patients, P values were determined by ANOVA including 2-group comparison using the Šidák multiple comparison when indicated. (C) Serum IL-6 concentration was correlated with absolute M-MDSCs per μL from the peripheral blood of patients in CR, R2 of matching is indicated. (D) Monocytes of HCs were differentiated using GM-CSF with or without IL-6 in vitro, and rate of HLA-DRlow monocytes was determined by flow cytometry. Each symbol represents an individual HC, P values were determined by the matched-pair ordinary ANOVA. (E) Absolute counts of CD4+ Tn cells were correlated with serum levels of IL-6. (F) Cytokine profiles of 72 patients with DLBCL in relapse were compared with profiles of 43 patients with DLBCL in remission to assess the different inflammation profile between the 2 groups. Each circle corresponds to an individual patient with R/R disease (blue) or CR (red). (G) Volcano plot showing the fold change and significance level of significantly upregulated or downregulated serum cytokines in R/R compared with CR. For all panels, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. adj., adjusted; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; FASLG, fas ligand; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ns, not significant; OX40, TNF receptor superfamily member 4; Stim., stimulated; Tn, naive T cells; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
To more comprehensively discriminate the inflammation in remission from an actual relapse, we used broad serum cytokine and chemokine profiles to screen for differences between patients in CR and with R/R disease. The serum cytokine profiles of 43 patients in CR separated from the profiles of 72 patients with R/R disease in a PCA (Figure 4F). Evaluation of the most differentially expressed cytokines in the serum showed a higher level of lymphoma-produced cytokines (eg, IL-10 and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 [CXCL9]), of monocyte-derived inflammation (IL-6, IL-8, and IL-18), and a high degree of T-cell activation (IL-15, TNF Receptor Superfamily Member 9 [TNFRSF9 or 4-1BB], TNF Receptor Superfamily Member 4 [TNFRSF4 or OX40]) in R/R disease compared with CR. In contrast, mediators of innate immunity were predominantly upregulated in CR including the neutrophil activating cytokines CXCL5 and effector molecules of the TNF superfamily including tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and Fas ligand (FASLG), suggesting activation of innate immune cells in CR compared to R/R disease (Figure 4F).
Patients with BC, B-CLL, or AML, and mice with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) show distinct immune changes
To better understand the relationship between reduced Tn and inflammation, we analyzed survivors of BC at first diagnosis and in CR for immune cell changes and compared the results with matched HCs (patient characteristics in supplemental Table 1). The cohort of survivors of BC was enrolled on median 24.3 months (2.8-131.3) after last treatment. Resembling DLBCL, patients with BC at first diagnosis and in CR showed a persisting elevation of CD14+/HLA-DRlow monocytes (Figure 5A). Distinct from DLBCL, the CD14+/HLA-DRlow cells showed similar levels of indoldioxygenase 1, cyclooxygenase 2, and arginase-1, compared with their HLA-DRhigh counterpart (Figure 5B). Plotting the individual CD14+/HLA-DRlow data points over time showed that their average number did not drop below the average value of HCs, years after the end of treatment (Figure 5C). Mirroring DLBCL, the T cells of patients with BC in CR remained altered (Figure 5D). ND and CR were associated with similarly high numbers of activated (HLA-DR+) and, different from DLBCL, exhausted (programmed cell death protein 1–positive) CD4+ T cells when compared with HCs. The CD4+/HLA-DR+ T cells also remained elevated for years, showing, in line with DLBCL, that the disease-inflicted immune changes did not revert to a status found in HCs (Figure 5E). Interestingly, survivors of BC did not show changes in absolute CD4+ Tcm or Tn cells (supplemental Figure 9). Thus, we asked if the decrease of T-cell subsets could be a lymphoma-specific finding and analyzed patients with untreated CLL in watch-and-wait before therapy (supplemental Table 2). As in DLBCL, the CD4:CD8 ratio as well as the absolute CD4+ Tn cell counts were reduced. The CD4+/HLA-DR+ T cells were on average 16.9% in watch-and-wait as compared with 4.8% in matched HCs (Figure 5F). We then determined immune alterations of 26 matched sample pairs of patients with AML from first diagnosis and later follow-up in CR (patient characteristics shown in supplemental Table 3). From these frozen samples only T cells but not MDSCs were measured for comparability reasons (supplemental Figure 10). Altered already at first diagnosis, several phenotypes persisted including an expanded, less activated but more exhausted and senescent CD8+ T-cell compartment. We then normalized the identified T-cell phenotypes of all analyzed entities to their disease-specific, matched HC cohort and found distinct patterns of changes in line with a disease-specific immune imprint that persisted in remission for years in all diseases studied (Figure 5G).
Specific immune changes in patients with BC, patients with CLL, AML, and lymphoma-bearing mice. (A) Determination of CD14+ HLA-DRlow monocytes by flow cytometry in patients with BC when ND and in CR compared with matched HCs. Each symbol represents an individual patient. Significance determined by the ordinary 1-way ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (B) Staining for intracellular enzymes that correlate with inhibitory function IDO1, Arg1, and COX2 in CD14+/HLA-DRlow compared with respective in-patient control of DRhigh myeloid cells of patients in CR. Each symbol represents an individual patient, significance determined by the paired t tests. (C) The count of CD14+/HLA-DRhigh is blotted against the time point of the individual blood draw. Each symbol indicates a single patient. Red line indicates linear regression. (D) Relative and absolute CD4+ T-cell activation (HLA-DR) and exhaustion (PD1) in survivors of BC was measured by flow cytometry compared with HCs. Each symbol represents an individual patient, P values were determined by ordinary 1-way ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (E) The rate of activated (HLA-DR) CD4+ T-cells was blotted against the time point of the individual blood draw. Each symbol indicates a single patient. Red line indicates linear regression. (F) Indicated T-cell subsets were measured by flow cytometry from untreated CLL in watch-and-wait. Each symbol represents an individual patient. Two-group comparison was done using the ordinary 1-way ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (G) Indicated T-cell subset changes of respective disease entities including AML were normalized to the mean of their own HC group as 1 and allow for data comparison between the groups as indicated using the ANOVA group comparisons. Gray boxes indicate disease-specific significant alterations. (H) Scheme of the BL6 systemic BCL mouse model. (I) Indicated organs were analyzed for alterations in the indicated T-cell populations including respective markers after tumor injection compared with tumor-free mice by flow cytometry. Each symbol indicates values from an individual mouse, P values were determined by unpaired t tests. For all panels, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. Arg1, arginase-1; BL6, black 6; COX2, cyclooxygenase 2; IDO-1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; mCD4, murine CD4; ns, not significant; PD1, programmed cell death protein 1; periph., peripheral; Tn, naive T cells; w&w, watch-and-wait.
Specific immune changes in patients with BC, patients with CLL, AML, and lymphoma-bearing mice. (A) Determination of CD14+ HLA-DRlow monocytes by flow cytometry in patients with BC when ND and in CR compared with matched HCs. Each symbol represents an individual patient. Significance determined by the ordinary 1-way ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (B) Staining for intracellular enzymes that correlate with inhibitory function IDO1, Arg1, and COX2 in CD14+/HLA-DRlow compared with respective in-patient control of DRhigh myeloid cells of patients in CR. Each symbol represents an individual patient, significance determined by the paired t tests. (C) The count of CD14+/HLA-DRhigh is blotted against the time point of the individual blood draw. Each symbol indicates a single patient. Red line indicates linear regression. (D) Relative and absolute CD4+ T-cell activation (HLA-DR) and exhaustion (PD1) in survivors of BC was measured by flow cytometry compared with HCs. Each symbol represents an individual patient, P values were determined by ordinary 1-way ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (E) The rate of activated (HLA-DR) CD4+ T-cells was blotted against the time point of the individual blood draw. Each symbol indicates a single patient. Red line indicates linear regression. (F) Indicated T-cell subsets were measured by flow cytometry from untreated CLL in watch-and-wait. Each symbol represents an individual patient. Two-group comparison was done using the ordinary 1-way ANOVA using the Šidák multiple comparison. (G) Indicated T-cell subset changes of respective disease entities including AML were normalized to the mean of their own HC group as 1 and allow for data comparison between the groups as indicated using the ANOVA group comparisons. Gray boxes indicate disease-specific significant alterations. (H) Scheme of the BL6 systemic BCL mouse model. (I) Indicated organs were analyzed for alterations in the indicated T-cell populations including respective markers after tumor injection compared with tumor-free mice by flow cytometry. Each symbol indicates values from an individual mouse, P values were determined by unpaired t tests. For all panels, ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. Arg1, arginase-1; BL6, black 6; COX2, cyclooxygenase 2; IDO-1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; mCD4, murine CD4; ns, not significant; PD1, programmed cell death protein 1; periph., peripheral; Tn, naive T cells; w&w, watch-and-wait.
To elucidate whether the lymphoma induces the observed T-cell changes, we studied an immune competent, myc-driven C57BL/6 lymphoma mouse model (Figure 5G; supplemental Figure 11).29 Thirty-eight days after systemic injection of the lymphoma cells, lymph nodes were infiltrated on average by 66.9% and the spleen by 14.8% lymphoma cells and, as previously published, by lymphoma-induced, functionally relevant MDSCs.29 In line with reduced Tn cells in humans, lymphoma-challenged mice presented with a decrease of CD4+ Tn cells in the peripheral blood and in the spleen but not in lymph nodes compared with healthy C57BL/6 mice (Figure 5H). Furthermore, the rate of activated CD4+ T cells was higher in lymphoma-challenged mice than in HCs. Taken together, we find persisting alterations of immune cells in various malignant disease settings whereas reduced Tn cells are B-NHL specific and likely caused by the malignant B cells.
Discussion
We identified a functionally relevant signature of chronic inflammation in survivors of DLBCL, including persisting inhibitory MDSCs and chronic activation and depletion of T cells as summarized in the visual abstract. This inflammatory signature persists years after the end of therapy. Our mouse data suggest that these changes are likely initiated by the DLBCL itself and, in humans, aggravated after therapy. Inflammatory cytokines elevated at first diagnosis such as IL-6 remain high in CR and inversely correlate with the number of Tn cells and positively with the number of MDSCs. Compared with BC or AML, survivors of DLBCL show a distinct reduction of Tn and Tcm cells suggesting disease-specific, persisting immune alterations in CR, which may explain increased rates of long-term complications of survivors of DLBCL.
The hyperactivated and functionally impaired T cells, the elevated MDSCs, and the increased proinflammatory cytokines including IL-6 represent hallmarks of chronic and unresolved inflammation similar to changes found in HIV or autoimmune diseases.30-34 Remarkably, these hallmarks are present in survivors of DLBCL even years after achieving CR. Supporting our findings, several reports on immune alterations in DLBCL have shown an incomplete resolution of inflammation shortly after the last treatment with elevated β2-microglobulin, IL-6, or M-MDSCs.35,36 However, no longitudinal studies late after the end of therapy have been conducted. We provide strong evidence that the alterations do not revert to the status of healthy individuals despite the absence of DLBCL. Intriguingly, the immunological scar in remission closely mirrored the immunological changes at first diagnosis in DLBCL but also in AML and BC. However, the phenotypes of inflammation of the 3 diseases were remarkably distinct, suggesting disease-specific immune imprints already before therapy. Specific for DLBCL were the marked reduction of Tn and Tcm cells already present at first diagnosis. Both were further aggravated by treatment as previously shown.37 Supporting a B-cell malignancy–induced reduction, Tn cells were lower also in treatment naïve CLL but not in BC or AML. In line with BCL as cause of reduced Tn cells, they are also decreased in FL at first diagnosis.38 Determined only by fraction but not by number, rituximab maintenance led to a relative increase of Tn cells although data on longer follow-up in FL are missing.38 In HL up to 30 years after achieving remission, Tn cells remain numerically reduced.39 Activation and/or exhaustion of the T-cell compartment with high HLA-DR+ and high programmed cell death protein 1–positive CD4+ T cells is a more commonly described finding among indolent NHL, DLBCL, and HL. Distinct from DLBCL, patients with CLL, indolent NHL, or HL present with elevated Treg cells.38,40,41 Although we established causality of reduced Tn cells and NHL in mice, the details of this BCL-induced depletion are not understood. Because B cells modulate T cells and, for example, deplete autoreactive T-cell clones,42 a B-NHL–derived depletion of T cells seems a possible explanation. Why distinct alterations persist, however, in the 3 disease entities remains unclear. We speculate that disease-specific microenvironments introduce lasting changes such as in the immune compartment or the microbiome, which then leads to perpetuated inflammation and immune imprints.43 Vice versa, such distinct immune imprints could align with disease-specific microbiome modulation.44
The reduced number of immature T cells, the T-cell dysfunction and the chronic inflammation could potentially explain the increased rates of fungal, viral, and bacterial infections in survivors of DLBCL compared with survivors of BC7 and also provides a possible explanation for an increased rate of infections already 1 year before first diagnosis of DLBCL.45 That T-cell alterations and not therapy-induced B-cell impairment is relevant for higher rates of infections after therapy is underscored because reported infectious complications were similar in the pre- and post-rituximab eras7 and are further supported by normalization of the B-cell compartment 2 years after completing chemotherapy, whereas chronic inflammation and increased infections persist well beyond 5 years.46 As postulated in autoimmune disease and HIV infection, a sustained T-cell dysfunction in survivors of DLBCL with possibly reduced immune surveillance may furthermore explain a higher rate of SPM compared with survivors of other cancers,10 with a generally elevated risk of melanoma and of lung cancer >10 years after treatment.47,48
As shown by our data, the dysfunctional T-cell compartment bears importance for vaccine-induced immunity.49-51 High Tn cells correlate with higher antigen-specific T-cell responses in survivors of DLBCL vaccinated for SARS-CoV-2, highlighting their importance for a protective adaptive T-cell responses.52 In contrast, dysfunctional T-cell composition at administration of BsAbs or CAR T cells has been associated with therapy failure,53,54 and high numbers of activated T cells and low numbers of Tn and Tcm cells at apheresis result in less active CAR T-cell products.37,55 Lastly, elevated inflammation as well as IFN-α–expressing MDSCs may serve as poor risk markers.19,56,57 Taken together, the chronic inflammation likely translates into dysfunctional T cells at first diagnosis and correlates with reduced T-cell responses to vaccines in survivors. Whether our findings translate to an impairment of T-cell engaging therapies is a question of ongoing research.
The source of the lymphoma-independent, IL-6–mediated systemic inflammation remains incompletely understood but is not a direct consequence of lymphoma cells because it persists in CR. IL-6 is a hallmark of acute and of chronic inflammation and many cells beyond immune cells can secret IL-6.58,59 Consequently, IL-6 could be cause or consequence of chronic inflammation in survivors of DLBCL. Although the immune activation was confirmed by RNA sequencing, the elevated IL-6 levels could not be traced back to activated T cells or MDSCs. Because low naïve T cells correlated with higher IL-6, we hypothesize that the lack of T cells and the resulting immune dysfunction could be causing chronic immune activation. This notion is further supported by the cytokine profiles that highlighted high TNF, classically elevated in chronic inflammation and associated with autoimmune disease, cancer, and infections.31,60 As part of increased innate activation, MDSCs remain elevated; however, NK cells do not show baseline or functional differences from HCs, arguing against a general immune hyperactivation. It is therefore possible, that a cancer- and/or treatment imprinted immune cell alteration through chronic interaction with, for example, the microbiome43,61 might drive the persisting, distinct inflammation resulting in a state of “high alert” in DLBCL. Therapeutically, this state may be influenced by immune-modulatory therapies including autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplant or more targeted approaches such as blockage of inflammasome with Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors or anti–IL-6 and anti-TNFα, which may also revert the altered phenotypes and subsequently restore immune function.
Although our samples were collected prospectively and in an unbiased manner, a major limitation of our study is the retrospective nature, because patients had achieved cure before being enrolled in this study. The collection time points were unstructured, and samples were acquired during clinical routine visits. In addition, the number of patients is too small to identify multivariate correlation of low Tn cells, inflammation, and clinical parameters such as clinically meaningful evidence of increased infections. Furthermore, research to identify the cause of persisting immune alterations is ongoing. Despite these drawbacks, we show, to our knowledge, for the first time a substantial immune alteration in patients that achieve long-term remission after DLBCL, AML, and BC, with a disease-specific immune imprint. The described immune alterations possibly have broad implications for immune therapies including BsAbs as well as CAR T-cells, for potential immune modulatory adjunct therapies, and lastly for the management of the increasing number of survivors of cancer, including vaccination strategies to prevent serious infections years after achieving remission.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all patients for giving their informed consent and for supporting the study. Furthermore, the authors thank Kristin Mentz, Luisa Albert, Lena Tarantik, Dorothea Gebhard, Florentine Schonath (Core Unit, Cell Sorting and Immunomonitoring Erlangen), and Cedric Smolka for their assistance in handling patient samples; the team of the outpatient unit (Hochschulambulanz); and all supporting doctors of the Department of Hematology and Oncology. The authors thank Stefan Krause, Georg Schett, Benedikt Jakobs, Dimitrios Mougiakakos, and Domenica Saul for helpful discussions; and Arif Ekici of the next-generation sequencing Core Unit (Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Medical Faculty) for technical assistance with the T-cell receptor sequencing. The authors are grateful for the technical support of the Metabolomics and Proteomics Core at Helmholtz Munich. Lastly, the authors thank the biobank team of the German Study Alliance Leukemia for providing valuable samples of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. This work was performed in fulfillment of the requirements of R.J.P. for obtaining the doctor of medicine degree (Dr. med.) This paper is part of the doctoral research of G.B. within the “PhD Advanced Immunomedicine Program” at the Medical Faculty of the Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Germany.
This work was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe (DKH no. 701161123 [F.M.] and no. 70114623 [R.J.P]), Bayerisches Zentrum für Krebsforschung (no. TLG-22 [F.M. and M.S.]), Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (no. 01EO2105 [F.M.]), Gilead (grant no. 20951 [F.M.]), the Deutsche José Carreras Leukämie-Stiftung (02 R/2021 [S.V.]), the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (no. 468571579 [K.N.-M.]), and the Hightech Agenda Bavaria (F.G.). J.K.S. was supported by the NOTICE clinician scientist program of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grant no. 493624887.
Authorship
Contribution: R.J.P., G.B., and F.M. designed the project and wrote the manuscript; R.J.P., G.B., F. Gsottberger, H.Y., K.W., J.K.S., S.K., M. Schmiedeberg, P.K., L.M., S.P., K.R., K.N.-M., and S.V. analyzed patient samples, performed experiments, analyzed the data, and performed statistical analyses; F. Gsottberger designed and performed the mouse experiments; F. Gsottberger, K.W., S.V., and K.N.-M. gave technical support for several assays; J.K.S., M.R., H.A., R.B., S.E., S.H.-G., H.H., C.R., M. Subklewe, L.L., and S.V. were responsible for patient enrollment, sampling, and biobanking; F. Graw performed data modeling and dynamic clustering; A.P. performed Olink measurements and data analyses; G.S. and A.M. provided scientific support and consultation; and S.V., K.N.-M., and F.M. supervised the project.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.K.S reports travel support from BeiGene, AbbVie, and Janssen. K.R. reports research funding, honoraria, and travel support from, and consultancy with, Kite/Gilead; honoraria from Novartis and Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS)/Celgene; served as an consultant to BMS/Celgene; and received travel support from Pierre-Fabre. C.R. has received honoraria from AbbVie, Astellas, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Jazz, Janssen, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, and Servier; and reports institutional research funding from AbbVie, Astellas, Novartis, and Pfizer. M. Subklewe has served on an advisory board for Amgen Inc, BMS/Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Seattle Genetics; served on the speakers bureau for Amgen Inc, BMS/Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Novartis, Pfizer, and Takeda; received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Amgen Inc, BMS/Celgene, and Gilead Sciences; and received research support from Amgen Inc, BMS/Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Miltenyi Biotec, MorphoSys, Novartis, Roche, and Seattle Genetics. G.S. has received speaker honoraria from Novartis, BMS, Kyverna, and Cabaletta. A.M. has received grants from Miltenyi Biomedicine and Kyverna; reports consulting fees from BMS/Celgene, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, BioNTech, Miltenyi Biomedicine, and Century Therapeutics; received speaker honoraria from BMS/Celgene, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, and Miltenyi Biomedicine; and received meeting support from AbbVie and Janssen. F.M. has received research funding from AstraZeneca and Kite/Gilead; served as an advisor to AstraZeneca, ArgoBio, BMS, CRISPR Therapeutics, Janssen, Kite/Gilead, Miltenyi, Novartis, and Sobi; and received honoraria from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, BeiGene, BMS, Janssen, Kite/Gilead, Miltenyi, Novartis, Sobi, and Takeda. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Fabian Müller, University Hospital Erlangen, Ulmenweg 18, 91054 Erlangen, Germany; email: fabian.mueller@uk-erlangen.de.
References
Author notes
R.J.P., G.B., S.V., K.N.-M., and F.M. contributed equally to this study.
The RNA sequencing data generated during this study have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus data repository (accession number GSE277575).
All other data supporting the findings of this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author, Fabian Müller (fabian.mueller@uk-erlangen.de).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

Comments
The Hen and Egg Dilemma
The “hen–egg” dilemma of whether the immune scar is “cause or consequence” cannot be resolved in patients, so we turned to a murine model reproducing the observed alterations (3). While species differences are acknowledged, these data support that lymphoma is the initiating event. Beyond causality, the persistence of systemic immune dysfunction has wide-ranging clinical implications, likely contributing to impaired vaccine responses, recurrent infections, secondary malignancies, and potentially determining the success or failure of T cell–directed therapies which we evaluate in ongoing research (4,5).
1 Lachmann, R. et al. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) seroprevalence in the adult population of Germany. PLoS One 13, e0200267 (2018). https://doi.org:10.1371/journal.pone.0200267
2 Klenerman, P. & Oxenius, A. T cell responses to cytomegalovirus. Nat Rev Immunol 16, 367-377 (2016). https://doi.org:10.1038/nri.2016.38
3 Gsottberger, F. et al. Human CD22-Transgenic, Primary Murine Lymphoma Challenges Immunotherapies in Organ-Specific Tumor Microenvironments. Int J Mol Sci 22 (2021). https://doi.org:10.3390/ijms221910433
4 Friedrich, M. J. et al. The pre-existing T cell landscape determines the response to bispecific T cell engagers in multiple myeloma patients. Cancer Cell 41, 711-725 e716 (2023). https://doi.org:10.1016/j.ccell.2023.02.008
5 Galli, E. et al. The CD4/CD8 ratio of infused CD19-CAR-T is a prognostic factor for efficacy and toxicity. Br J Haematol 203, 564-570 (2023). https://doi.org:10.1111/bjh.19117
Immune scar in DLBCL: EBV and MDSCs?
Literature:
Collins, Paul J. et al. Characterizing EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disease and the role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Blood (2021) 137 (2): 203–215.
Glover A. et al. Deciphering the roles of myeloid derived suppressor cells in viral oncogenesis. Front. Immunol Mar 2023:14:1161848
Immune scar in DLBCL: Cause or Consequence
T-cell characterization as exhausted, activated, or senescent is a multi-faceted and complex process (1) that most of the time, requires supplementary methods such as single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), TCR sequencing, and ATAC-sequencing, yet none of these methods were used here.
The main unanswered question of this work is whether the observed cytokine shifts and T-cell impairment had already existed before the development of lymphoma and hence are its causative factor, or are they simply the outcomes of lymphoma and its treatment. Without a prospective longitudinal study that contains pre-lymphoma samples (which is, admittedly, challenging to conduct), it is almost impossible to tell whether this “immune scar” signature is causative, a result of the malignancy, or a product of our therapy.
Authors applied a murine model to exemplify concept of inflammatory changes; however, such models do not necessarily represent the complex immune system dynamics in vivo of humans (2, 3). Lastly, the study also lacks crucial detailed matching criteria for the comparator cohort. Differences in age, varieties of prior therapy, and comorbidity profiles may act as confounder factors, potentially affecting the interpretation of both cytokine profiles, T-cell function and tendency of the immune system to develop the so called “immune scar”.
Literature:
1.Mogilenko DA et al. Comprehensive Profiling of an Aging Immune System Reveals Clonal GZMK(+) CD8(+) T Cells as Conserved Hallmark of Inflammaging. Immunity. 2021 Jan 12;54(1):99-115.e12
2.Seok J et al. Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 26;110(9):3507-12.
3.Mestas J, Hughes CC. Of mice and not men: differences between mouse and human immunology. J Immunol. 2004 Mar 1;172(5):2731-8.