Abstract
We have studied the expression of gelatinase A, gelatinase B, interstitial collagenase, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2 in reactive lymphoid cells, as well as in a series of cell lines derived from neoplasms of B- and T-cell lineage. Using both Northern blot analysis and zymography, gelatinase B activity was detected by zymography in two Burkitt cell lines and in a tonsillar cell suspension, while gelatinase A and interstitial collagenase activities were not detected by either method. TIMP-1 expression was demonstrated by Northern blot analysis in the multipotential neoplastic K-562 cell line, the high grade Burkitt's B-cell lymphoma lines, isolated tonsillar B cells and at low levels in peripheral blood T cells, but was not expressed in any of the neoplastic T-cell lines or isolated peripheral blood B cells. In contrast, TIMP-2 expression was restricted to tissues containing cells of T-cell lineage with high levels being observed in the neoplastic T-cell lines and lower levels in normal peripheral blood T cells and hyperplastic tonsil. Expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 was confirmed at the protein level by reverse zymography and immunofluorescence assays using antihuman TIMP polyclonal antibodies. Expression of gelatinase B by the high grade B-cell Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines is consistent with previous findings in large cell immunoblastic lymphomas and indicates that this enzyme may play an important role in high grade non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. TIMP expression correlated with cell lineage in that TIMP-1 was primarily observed in B cells and TIMP-2 was restricted to T cells.
THE MATRIX metalloproteinase (MMP) family of enzymes are a group of structurally related zinc metallo-enzymes, which characteristically degrade components of the extracellular matrix.1-6 The elevated activity of these MMP enzymes has been associated with a variety of physiologic and pathologic conditions, including ovulation, blastocyst implantation, as well as invasion and metastasis in solid tumors.7-10 The activity of these enzymes appears dependent on a balance between the production of latent enzyme, activation of latent enzyme, and production of the naturally occurring inhibitors, most notably the tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs).11-13 It is now apparent that this balance of MMP activity and TIMP's expression is a critical determinant of the invasive potential of many solid tumors.
In addition to their role in blocking MMP activity, TIMPs may have additional growth factor-like properties. Both TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 have been demonstrated to have erythroid-potentiating activity, as measured in the in vitro erythroid burst formation assay.14,15 In the pluripotential hematopoietic cell line K562, induction of differentiation by phorbol esters results in TIMP-1 expression.16 In addition, TIMP-1 has a demonstrated growth-promoting action in this cell line,17 and thus may function as an autocrine growth factor for these cells. TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 are reported to have a growth promoting activity in a wide range of cell lines.17-19 In cell lines, growth ceased in serum-free media, but was stimulated after supplementation of the media with 100 ng/mL of TIMP-118 or as little as 10 ng/mL TIMP-2.19 Recently, we have shown that TIMP-2 stimulates fibroblast growth via a cAMP-dependent mechanism.20 Conversely, TIMP-2, but not TIMP-1, specifically inhibits the basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF )-stimulated proliferation of human microvascular endothelial cells by a mechanism independent of TIMP-2 protease inhibition.21 Therefore, in addition to their matrix metalloproteinase inhibiting activity, TIMPs may regulate growth of a variety of cells, including hematopoietic lineage cells.
Lymphoid neoplasms differ fundamentally from solid tumor neoplasms. Due to their role in immunosurveillance, lymphocytes are normally found throughout the organs and connective tissues of the body,22 and as such, have a normally invasive phenotype. Recent evidence suggests that matrix metalloproteinase activity may be involved in the transmigration of lymphocytes from the vascular compartment.23,24 Aggressive lymphoid neoplasms can be observed “invading” through the lymph node capsule and, in some cases, extensively involving the surrounding soft tissue.25 In addition, invasive behavior has been documented in neoplastic lymphoid cell lines using the membrane invasive culture system. This invasive behavior directly correlated with the expression of gelatinase A and associated metastatic behavior in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice was observed in cell lines expressing high levels of gelatinase A.26 Studies by Kossakowska et al27 demonstrate TIMP-1, but not TIMP-2 expression, in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. TIMP-1 expression was localized to the stromal and endothelial cells by in situ hybridization. However, low level expression of TIMP-1 by the tumor cells could not be excluded. The expression of TIMP-1 did not correlate with gelatinase A or interstitial collagenase expression (gelatinase B expression was not studied in this report). Paradoxically, increased TIMP-1 expression was observed in high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and in advanced stage disease, leading the investigators to postulate that TIMP-1 may have lymphoid growth factor activity.27 Further studies by this group demonstrated an association between survival and gelatinase B, but not TIMP-1 expression in high-grade, large cell immunoblastic lymphomas.28 Uchijima et al29 recently observed that human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-2–infected cell lines express elevated levels of TIMP-1. They have proposed that TIMP-1 may be an autocrine growth factor produced by the infected cells and may actually modulate the clinical course in patients with adult T-cell leukemia. These studies suggest that gelatinases and TIMPs may be of importance in lymphomas. We have studied the expression of gelatinase A, gelatinase B, and interstitial collagenase, as well as TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in reactive lymphoid cells and a series of cell lines derived from neoplasms of B-cell and T-cell lineage. These studies using cell lines and isolated lymphoid cells were performed to elucidate the possible involvement of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs in lymphoid neoplasms without the confounding influence of stromal and endothelial cells present in lymphoma tissue specimens.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell samples.Cell lines used in this study include those developed from Burkitt's lymphoma, follicular center cell neoplasms, and T-cell malignancies. The Burkitt cell lines, Jijoye, AG876, DW6, and PA682 were kindly provided by Dr Ian Magrath (Chief, Lymphoma Biology Section, Pediatric Branch, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). The follicular center cell lymphoma-derived lines, SUDHL 6 and SUDHL 4, contain the t(14; 18) translocation characteristic of these neoplasms. The cell lines derived from T-cell neoplasms include Jurkat, Molt-4, and Peer-1. K562, a cell line derived from a patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) in blast crisis, is a poorly differentiated multipotential line that can differentiate into progenitors of erythrocytic, granulocytic, and monocytic series (obtained from American Tissue Culture Collection, Rockville, MD).
Cell suspensions were prepared from hyperplastic tonsilar tissue obtained from patients less than 15 years of age. Unprocessed tonsilar tissue contained 62% B cells and 19% T cells with the remainder of the population being comprised primarily of monocytic lineage cells. Tonsillar B cells30 were isolated as described. Tonsillar B cells were stimulated with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan strain I and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate with cell samples collected at 0, 4, and 24 hours of stimulation. Peripheral blood B cells were isolated as described,31 with the addition of magnetic beads conjugated to anti-CD19 (MACS, Miltenyi Biotec Inc, Auburn, CA).32
T cells were separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells as previously described.33 Briefly, monocytes were allowed to adhere to plastic tissue culture plates followed by B-cell removal using a nylon wool column. Immunophenotypic analysis by flow cytometry showed greater than 90% T cells, less than 1% B cells, and natural killer cells comprising the remaining cell population. No monocytes were detected. T cells were stimulated with interleukin-2 (IL-2) plus phytohemaglutinin (PHA) for up to 9 days.
Conditioned media.The cell lines Jijoye, AG876, DW6, PA682, SUDHL-6, SUDHL-4, Jurkat, Molt-4, and Peer-1 were grown to 1.2 × 106 cells/mL at 37°C and 10% CO2 in AIM V media (GIBCO, Gaithersburg, MD) and conditioned media was collected after 48 hours. Tonsillar cell suspension and isolated peripheral blood T cells were cultured at 1.2 × 106 cells/mL at 37°C and 10% CO2 and conditioned media collected after 12 hours. AIM V media supports lymphoid cell line growth, but does not contain gelatinolytic activity (personal observation, M. Stetler-Stevenson, August 1992). Conditioned media was centrifuged at less than 1,000g for 8 minutes (Sorval centrifuge model RT6000; Dupont, Wilmington, DE) at 4°C to remove cells and then stored at −20°C.
Northern blot analysis.A total of 7.5 μg of total RNA, extracted from cell suspensions using RNAzol (Cinna/Biotecx Laboratories International, Inc, Friendswood, TX), was electrophoresed on 1% wt/vol agarose-formaldehyde gels before transfer onto nylon filters (Gene Screen Plus, Dupont, NEN Products, Boston, MA). The RNA was UV cross-linked to the filter and hybridized using standard conditions. Blots were hybridized with TIMP-1,34 TIMP-2,34 the 72-kD gelatinase A,7 interstitial collagenase,35 and GAPDH36 probes prepared as previously described. The cDNA probe for the 92-kD gelatinase B was prepared by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using HT1080 cell cDNA and the following primers: 5′ primer- GGGGGTACCAGACACCTCTGCCGTCACCAT; 3′ primer-CCCGGTACCGCACAGCTCCCCCGCCGAGTT. These DNA probes were labeled with α[32P] dCTP using a random primer labeling kit (Bethesda Research Laboratories, Gaithersburg, MD). Filters were autoradiographed at −80°C.
Reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR.c-DNA was prepared from isolated peripheral blood B cells and PA682 using 2 μg of RNA and the Superscriptase Preamplification system for first-strand cDNA synthesis (GIBCO-BRL, Gaithersburg, MD). cDNA was prepared from PA682 and the isolated tonsillar B cells using 2 μg of RNA as previously discribed.30 One tenth of the cDNA was used for each PCR reaction. A total of 2.5 U of Taq polymerase (GIBCO-BRL) and 0.8 μmol/L of each primer was used. The following TIMP-1 primers were used: ATAGTCGACATGGCCCCCTTTGAGCCCCTG (5′); GGAATTCCTCAGGCTATCTGGGACCGCAGGGA (3′). β2 -Microglobulin was amplified using previously discribed primers.37 The cDNA was denatured for 5 minutes at 94°C and then 20 cycles of PCR were performed as follows: 1 minute denaturation at 94°C, 1 minute annealing at 55°C, and 1 minute extension at 72°C with the exception of the last cycle in which extension was for 5 minutes. Peripheral blood B-cell cDNA was also amplified for 30 cycles. Products were analyzed by electrophoresis in 1.5% agarose gels and Southern blotting onto nylon membranes (Dupont, NEN Research, Boston, MA) before probing with 32P-labeled TIMP-1 cDNA probe.
Zymogram analysis.Gelatinolytic activity was assayed by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and gelatin as described by Heussen and Dowdle.38 Gelatin zymography is an exquisitely sensitive technique that is capable of detecting 10 pg of gelatinase enzyme.39 Briefly, 16-μL aliquots of conditioned media were suspended in sample buffer (50 mmol/L Tris-HCL, 2% SDS, 0.1% bromophenol blue, 10% glycerol, pH 6.8) and applied to 10% (wt/vol) acrylamide gels containing 1 mg/mL of gelatin (Novex, San Diego, CA) followed by electrophoresis at 20 mA/gel. Gels were then incubated in 2.5% (vol/vol) Triton X-100 for 60 minutes to remove SDS followed by overnight incubation in developing buffer (50 mmol/L Tris-HCl, 0.2 mol/L NaCl, 5 mmol/L CaCl2 , 0.02% (wt/vol) Brij-35, adjusted to pH 7.6). Gels were stained for 3 hours in 30% methanol, 10% glacial acetic acid, 0.5% Coomassie Blue G-250 (Bio-Rad, Richmond, CA), destained for 1.5 to 2 hours in 30% methanol, 10% glacial acetic acid, and dried overnight.
Reverse zymogram analysis.Metalloproteinase inhibitory activity was assayed by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin as matrix metalloproteinase substrate and HT1080 fibroblast culture-conditioned media as a source of matrix metalloproteinase as previously described.40 Briefly, 12% or 15% polyacrylamide gels (PAGE) were prepared with Tris-HCl containing 0.1% SDS, 2.5 mg/mL gelatin, and 10% (vol) HT1080 fibroblast culture-conditioned media. Aliquots of conditioned media (15 μL) were suspended in sample buffer (50 mol/L Tris-HCL, 2% SDS, 0.1% bromophenol blue, 10% glycerol, pH 6.8) and applied to gels followed by electrophoresis at 20 mA/gel. Gels were then incubated in 2.5% (vol/vol) Triton X-100 for 60 minutes to remove SDS followed by overnight incubation in developing buffer (50 mol/L Tris-HCl, 0.2 mol/L NaCl, 5 mmol/L CaCl2 , 0.02% (wt/vol) Brij-35, adjusted to pH 7.6). This restores the matrix metalloproteinase activity resulting in gelatin degradation. Gels were stained for 3 hours in 30% methanol, 10% glacial acetic acid, 0.5% Coomassie Blue G-250 (Bio-Rad, Richmond, CA), destained for 1.5 to 2 hours in 30% methanol, 10% glacial acetic acid, and dried overnight. TIMPs were visualized as bands of nondegraded gelatin staining positive with Coomassie Blue.
Immunofluorescence staining.Expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 at the protein level was assessed by immunofluorescence analysis. For detection of TIMP-1 protein expression, fresh cytocentrifuge preparations fixed in 10% formalin and permeabilized in 0.01% Triton-X (Research Products Int, Elkgrove Village, IL), were subjected to affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal anti-TIMP–1 antibodies or preimmune rabbit serum for 30 minutes at 37°C followed by a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated goat antirabbit Ig antiserum. The immunofluorescence assay slides were analyzed on a Optihot-2 fluorescence microscope (Nikon Inc, Garden City, NJ) equipped with phase-contrast facilities. In addition, cells in suspension were stained for TIMP-1 and TIMP-2. Briefly, cells were fixed in 3.7% formalin, permeabilized in 0.1% saponin (Sigma, St Louis, MO) and stained with affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal anti-TIMP–1 or anti-TIMP2 antibodies followed by an FITC-conjugated goat antirabbit Ig antiserum. Preimmune rabbit serum followed by FITC-conjugated secondary, as well as secondary antibody alone, was used as negative controls. Analyses were performed on a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA) as previously described.41 The TIMP-1 antibodies were kindly provided by Dr Benta Birkedahl-Hansen (Extracellular Matrix Pathology Section, Laboratory of Pathology, Division of Clinical Sciences, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). The TIMP-2 antibodies have been previously characterized.34
RESULTS
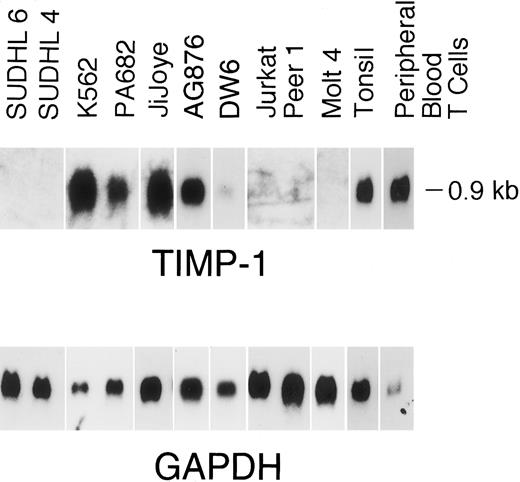
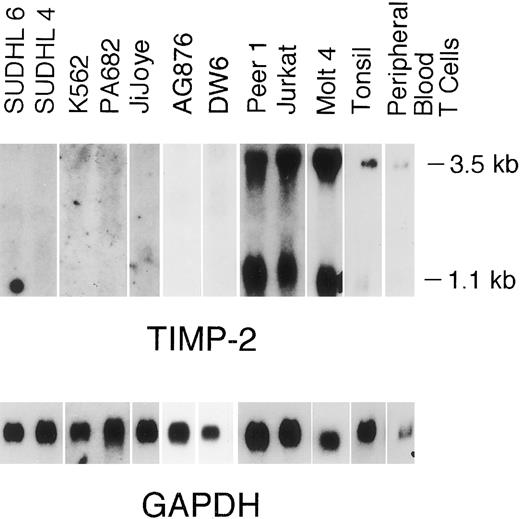
Neoplastic lymphoid cell lines.TIMP-1 transcripts (0.9 kb MW) were detected in all four Burkitt cell lines (Jijoye, AG876, DW6, and PA682) and in the multipotential neoplastic K562 line, but were not detected in the low-grade follicular center cell lymphoma cell lines (SUDHL-4 and SUDHL-6) or neoplastic T-cell lines (Fig 1). TIMP-1 protein expression was demonstrated by reverse zymography (Fig 2) and immunofluorescence assays (Fig 3). Although the expression of TIMP-1 was not definitively quantitated by these methods, a semiquantitative assessment of the levels of expression correlated well with the Northern blot data. Cytopreparations showed a globular cytoplasmic localization of the TIMP-1 (Fig 3A and B), consistent with cellular packaging for secretion. This is further supported by the demonstration that secreted and functional TIMP-1 is found in the conditioned media from these cell lines (Fig 2).
Northern blot analysis of TIMP-1 expression. A total of 7.5 μg of total RNA was electrophoresed on 1% wt/vol agarose-formaldehyde, transfered onto nylon filters, and hybridized with TIMP-1 and GAPDH. Filters were autoradiographed at −80°C. Radiographs were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner.
Northern blot analysis of TIMP-1 expression. A total of 7.5 μg of total RNA was electrophoresed on 1% wt/vol agarose-formaldehyde, transfered onto nylon filters, and hybridized with TIMP-1 and GAPDH. Filters were autoradiographed at −80°C. Radiographs were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner.
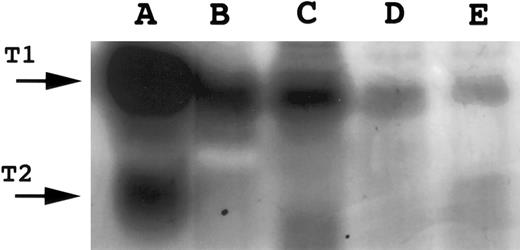
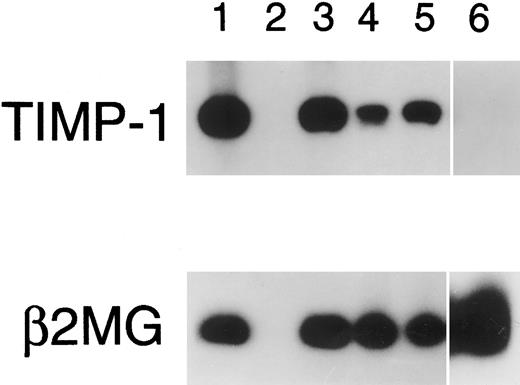
Reverse zymography for TIMP-1. A total of 15 μL of conditioned media was electrophoresed on 15% SDS polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin and HT1080 fibroblast culture-conditioned media. SDS was removed following electrophoresis and gels incubated to restore gelatinase activity. Gels were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner. Lane A, HT1080-conditioned media (positive control containing both TIMP-1 and TIMP-2); lane B, AG876; lane C, Jijoye; lane D, PA682; lane E, DW6.
Reverse zymography for TIMP-1. A total of 15 μL of conditioned media was electrophoresed on 15% SDS polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin and HT1080 fibroblast culture-conditioned media. SDS was removed following electrophoresis and gels incubated to restore gelatinase activity. Gels were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner. Lane A, HT1080-conditioned media (positive control containing both TIMP-1 and TIMP-2); lane B, AG876; lane C, Jijoye; lane D, PA682; lane E, DW6.
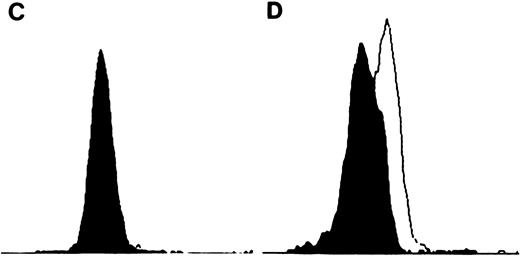
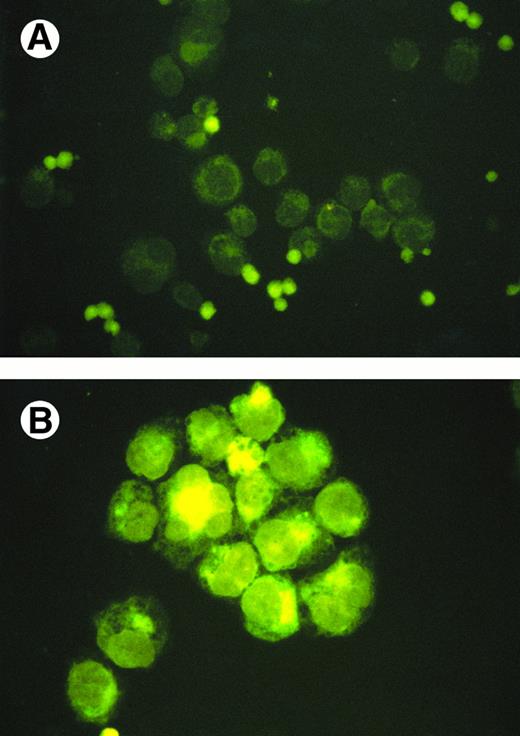
TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 protein expression. (A) Molt-4 cytocentrifuge preparations stained with rabbit polyclonal anti-TIMP–1 followed by FITC-conjugated goat antirabbit antibodies. Excitation wavelength 490 nm. Original magnification × 630. Small intensely fluorescent structures are debris (too small for cells and no nuclear content on light microscopy). (B) K562 cytocentrifuge preparations stained with rabbit polyclonal anti-TIMP–1 followed by FITC-conjugated goat antirabbit antibodies. Excitation wavelenght 490 nm. Original magnification × 630. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of TIMP-2 expression in K562 cells. Cell number represented on Y-axis and fluorescence intensity on X-axis. Filled in histogram staining with nonimmunized rabbit serum (negative control), clear histogram staining with TIMP-2. Histograms overlap. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of TIMP-2 expression in Jurkat cells. Cell number represented on Y-axis and fluorescence intensity on X-axis. Filled in histogram staining with nonimmunized rabbit serum (negative control), clear histogram staining with TIMP-2.
TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 protein expression. (A) Molt-4 cytocentrifuge preparations stained with rabbit polyclonal anti-TIMP–1 followed by FITC-conjugated goat antirabbit antibodies. Excitation wavelength 490 nm. Original magnification × 630. Small intensely fluorescent structures are debris (too small for cells and no nuclear content on light microscopy). (B) K562 cytocentrifuge preparations stained with rabbit polyclonal anti-TIMP–1 followed by FITC-conjugated goat antirabbit antibodies. Excitation wavelenght 490 nm. Original magnification × 630. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of TIMP-2 expression in K562 cells. Cell number represented on Y-axis and fluorescence intensity on X-axis. Filled in histogram staining with nonimmunized rabbit serum (negative control), clear histogram staining with TIMP-2. Histograms overlap. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of TIMP-2 expression in Jurkat cells. Cell number represented on Y-axis and fluorescence intensity on X-axis. Filled in histogram staining with nonimmunized rabbit serum (negative control), clear histogram staining with TIMP-2.
TIMP-2 transcripts (1.0 and 3.5 kb) were detected at high levels in the neoplastic T-cell lines (Fig 4). Cellular TIMP-2 protein expression was detected in the neoplastic T-cell lines and isolated peripheral blood T cells by flow cytometric analysis (Fig 3C and D). Although the number of molecules of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 expressed on the cell surface was not definitively quantitated by flow cytometric analysis, relative levels of expression were determined (fluorescent intensity) and again correlated well with the Northern blot data.
Northern blot analysis of TIMP-2. A total of 7.5 μg of total RNA was electrophoresed on 1% wt/vol agarose-formaldehyde, transfered onto nylon filters, and hybridized with TIMP-2 and GAPDH. Filters were autoradiographed at −80°C. Radiographs were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner.
Northern blot analysis of TIMP-2. A total of 7.5 μg of total RNA was electrophoresed on 1% wt/vol agarose-formaldehyde, transfered onto nylon filters, and hybridized with TIMP-2 and GAPDH. Filters were autoradiographed at −80°C. Radiographs were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner.
Transcripts for gelatinase A, gelatinase B, and interstitial collagenase were not detected for any of the neoplastic cell lines or tissues studied, although they were readily detectable in control RNA preparations. Zymography, a more sensitive method to detect gelatinase activity, failed to demonstrate gelatinase A or interstitial collagenase in any cell lines studied. A 92-kD gelatinase activity consistent with gelatinase B was observed (Fig 5) in the Burkitt cell lines Jijoye and PA682, but was absent from the follicular center cell lines (SUDHL-4 and SUDHL-6) and the T-cell lines (Molt-4, Jurkat, and Peer 1).
Gelatin zymography for Gelatinase B. A total of 16 μL of conditioned media was electrophoresed on 10% SDS polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin. SDS was removed following electrophoresis and gels incubated to restore gelatinase activity. Gels were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner. Lane A, Gelatinase A; lane B, SUDHL-6; lane C, Molt-4; lane D, Jijoye; lane E, PA682; lane F, tonsil; lane G, HT1080-conditioned media (positive control for Gelatinase A and Gelatinase B.
Gelatin zymography for Gelatinase B. A total of 16 μL of conditioned media was electrophoresed on 10% SDS polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin. SDS was removed following electrophoresis and gels incubated to restore gelatinase activity. Gels were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner. Lane A, Gelatinase A; lane B, SUDHL-6; lane C, Molt-4; lane D, Jijoye; lane E, PA682; lane F, tonsil; lane G, HT1080-conditioned media (positive control for Gelatinase A and Gelatinase B.
Normal B and T cells.Having detected a differential pattern of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 expression in neoplastic B- and T-cell lines, respectively, we undertook the examination of these protease inhibitors and associated MMPs in nonneoplastic B- and T-cell populations. Hyperplastic tonsils, isolated tonsillar B cells, and isolated peripheral blood B cells were studied. Unprocessed tonsillar tissue contained 62% B cells and 19% T cells with the remainder of the population being comprised primarily of monocytic lineage cells. TIMP-1 expression was detected in hyperplastic tonsils (Fig 1) and isolated tonsillar B cells, although it decreased under in vitro conditions, even with stimulation by Staphylococcus aureus Cowan strain I and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate for 24 hours (Fig 6). Unexpectedly, TIMP-1 transcripts could not be detected in isolated peripheral blood B cells using RT-PCR with high numbers of cycles (Fig 6). TIMP-2 transcripts (1.0 and 3.5 kb) were detected at low levels in tonsillar tissue (Fig 4). A 92-kD gelatinase activity consistent with gelatinase B was observed in the tonsillar cell suspension by gelatin zymography (Fig 5), although no signal for this protease was detected by Northern blot analysis. Gelatinase A and interstitial collagenase were not detected.
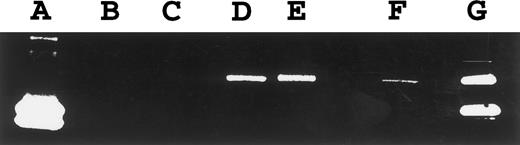
RT-PCR for TIMP-1. PCR amplification of TIMP-1 cDNA was performed for 20 cycles (except isolated peripheral blood B cells, 30 cycles shown). Lane 1, PA682 (positive control); lane 2, water (negative control); lanes 3 to 5, isolated tonsillar B cells at 0 hours (lane 3), 4 hours (lane 4), and 24 hours (lane 5) stimulation with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan strain I and phorbal 12-myristate 13-acetate; lane 6, isolated peripheral blood B cells.
RT-PCR for TIMP-1. PCR amplification of TIMP-1 cDNA was performed for 20 cycles (except isolated peripheral blood B cells, 30 cycles shown). Lane 1, PA682 (positive control); lane 2, water (negative control); lanes 3 to 5, isolated tonsillar B cells at 0 hours (lane 3), 4 hours (lane 4), and 24 hours (lane 5) stimulation with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan strain I and phorbal 12-myristate 13-acetate; lane 6, isolated peripheral blood B cells.
Peripheral blood T cells expressed TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 (Figs 1 and 4). In vitro, peripheral blood T cells cultured without mitogens did not secrete TIMP-2 activity, as assessed by reverse zymography (Fig 7A). However, on stimulation with IL-2 plus PHA, active TIMP-2 could be detected in the media within 24 hours (Fig 7A). Peripheral blood T cells secreted active TIMP-1 at a basal rate that did not increase with activation (Fig 7A). Gelatinase B activity was observed in peripheral blood T cells and increased poststimulation with activated forms being detected (Fig 7B). Gelatinase A and interstitial collagenase were not detected.
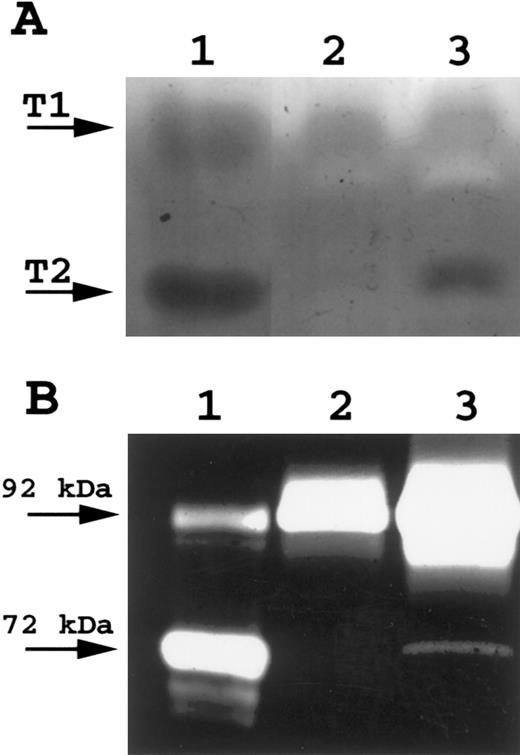
(A) Reverse zymography of peripheral blood T cells. A total of 15 μL of conditioned media was electrophoresed on 15% SDS polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin and HT1080 fibroblast culture-conditioned media. SDS was removed following electrophoresis and gels incubated to restore gelatinase activity. Gels were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner. Lane A, HT1080 cell-conditioned media (positive control for both TIMP-1 and TIMP-2); lane B, unstimulated peripheral blood T-cell–conditioned media; lane C, IL-2/PHA-stimulated peripheral blood T-cell–conditioned media. (B) Gelatin zymography of peripheral blood T cells. A total of 16 μL of conditioned media was electrophoresed on 10% SDS polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin. SDS was removed following electrophoresis and gels incubated to restore gelatinase activity. Gels were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner. Lane A, HT1080 cell-conditioned media (positive control for both TIMP-1 and TIMP-2); lane B, unstimulated peripheral blood T-cell–conditioned media; lane C, IL-2/PHA-stimulated peripheral blood T-cell–conditioned media.
(A) Reverse zymography of peripheral blood T cells. A total of 15 μL of conditioned media was electrophoresed on 15% SDS polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin and HT1080 fibroblast culture-conditioned media. SDS was removed following electrophoresis and gels incubated to restore gelatinase activity. Gels were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner. Lane A, HT1080 cell-conditioned media (positive control for both TIMP-1 and TIMP-2); lane B, unstimulated peripheral blood T-cell–conditioned media; lane C, IL-2/PHA-stimulated peripheral blood T-cell–conditioned media. (B) Gelatin zymography of peripheral blood T cells. A total of 16 μL of conditioned media was electrophoresed on 10% SDS polyacrylamide gels containing gelatin. SDS was removed following electrophoresis and gels incubated to restore gelatinase activity. Gels were scanned by an AGFA Arcus flatbed scanner. Lane A, HT1080 cell-conditioned media (positive control for both TIMP-1 and TIMP-2); lane B, unstimulated peripheral blood T-cell–conditioned media; lane C, IL-2/PHA-stimulated peripheral blood T-cell–conditioned media.
DISCUSSION
The involvement of the MMPS in development of the metastatic phenotype in solid tumors and the ability of the TIMPS to inhibit tumor cell invasion and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo is now well established.1-13 Previous studies indicate these gene products may also be involved in the progression of hematopoietic neoplasms.14-18,26-28 Our study of eight hematopoietic cell lines, peripheral blood T cells, and tonsillar cell suspensions did not demonstrate the expression of gelatinase A, gelatinase B, or interstitial collagenase at the RNA level. Using the sensitive zymogram technique, a 92-kD gelatinase activity consistent with gelatinase B was only detected in the two Burkitt cell lines, Jijoye, and PA 682, peripheral blood T cells and in the tonsillar cell suspension. Gelatinase A or interstitial collagenase activity was not detected by either method. Elevated gelatinase B expression, as assayed by in situ hybridization, has previously been observed in high-grade, large cell immunoblastic lymphomas and was associated with decreased survival.28 Zymogram detection of gelatinase B expression by the high-grade B-cell Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines is consistent with these findings and indicates that this enzyme may play an important role in high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
Gelatinase B was expressed by the highly reactive hyperplastic tonsils and peripheral blood T cells. The actual tonsillar cell population producing gelatinase B may be B or T cells, although granulocytes and monocytes cannot be excluded. Although granulocytes and monocytes are known to express this enzyme,5,42 the 135- and 220-kD forms of gelatinase, which are typically expressed by these cells were not present, indicating they are unlikely sources for gelatinase B. Upon activation of peripheral blood T cells with IL-2 and PHA, we observed an increase in Gelatinase B expression as well as the presence of activated forms of the 92-kD gelatinase, a finding consistent with findings in several other laboratories.24,43 Gelatinase B is reported to be expressed basally in cultures containing normal peripheral blood B cells and T cells (monocyte-depleted) and increases upon activation with PHA or IL-2.24 Tumor specific T cells have been shown in vitro to secrete Gelatinase B at low levels basally with increased expression upon stimulation with IL-2 or tumor cells. The ability of conditioned media from the tumor specific T cells to degrade basement membrane correlated with Gelatinase B levels.23 Our studies support the concept that Gelatinase B may play an important role in lymphoid degradation of basement membrane components. These findings support the role of this protease in normal lymphocyte migration from the vascular compartment to sites of inflammation, as well as invasion of structures by lymphoma cells.
The lack of gelatinase A expression is interesting in that expression of human Gelatinase A by stimulated T cells has been previously reported.24 However, in this previous study of normal donor T cells, the B cells were not removed. The B cells could stimulate T cells to produce Gelatinase A or they could be the actual source of this matrix metalloproteinase. In another study where T cells were isolated by fluorescence activated sorting and the purity of the T-cell population determined at 98%, the results were identical to ours in that Gelatinase A was not detected, although Gelatinase B was present basally and increased with stimulation (interstitial collagenase was not studied).23 We, therefore, are of the opinion that Gelatinase A is not produced in isolated T-cell cultures, although the observed lack of expression may be due to other undefined differences in culture conditions. Gelatinase A expression has been observed in some lymphoblastoid cell lines,26 but we did not detect expression in our series of neoplastic lymphoid cell lines. This may reflect differences in the cell lines studied. Other enzymes not detected by zymography under conditions used in these studies, such as plasminogen activators, may play an important role in basement membrane degradation during lymphoid cell invasion. Alternatively, lymphoid cells may produce MMPs upon interaction with basement membrane components, such as laminin, type IV collagen, or heparan sulfate proteoglycan, or in response to other tissue-specific interactions (eg, interaction with endothelial cells) that are not present under in vitro tissue culture conditions. In fact, specific induction of T-cell Gelatinase A has been observed in murine T cells that was mediated by vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1)–dependent adhesion to endothelial cells.44 Human T-cell synthesis and secretion of Gelatinase A and Gelatinase B have been shown to be influenced by integrin-mediated adherence to basement membrane matrix.43 45 These findings suggest that these proteases may contribute significantly to events associated with T-cell transmigration across the subendothelial basement membrane. The lack of Gelatinase A expression by T cells in the present study is at least, in part, due to the suspension culture technique used. The influence of VCAM-1 and other integrin-mediated adhesion events on TIMP-1 expression in lymphoid cells awaits further investigations. Thus, although Gelatinase A and interstitial collagenase are not observed in the peripheral blood T cells and all of the cell lines studied under the culture conditions used, they may be produced by lymphomas and normal lymphocytes in vivo. This aspect will be examined in ongoing studies.
In this study, TIMP-1 RNA transcripts and protein were expressed by the multipotential K-562 cell line, the high-grade Burkitt's B-cell lymphoma lines, tonsillar cells, and peripheral blood T cells. TIMP-1 was not expressed in any of the neoplastic T-cell lines. Expression of TIMP-1 by K562 has been previously reported and has been shown to possibly promote growth in these cells.16,17 Although TIMP-1 expression by Burkitt cell lines has not been previously studied, it was observed in high-grade, large cell immunoblastic lymphomas and was associated with advanced stage disease.27 The expression of TIMP-1 in the large cell immunoblastic lymphomas was localized to the stromal and endothelial cells by in situ hybridization, although the method was not sufficiently sensitive to exclude lower levels of expression in the tumor cell.27 We have demonstrated that TIMP-1 is expressed not only by stromal cells, but also by high-grade neoplastic lymphoid cells of B lineage. This suggests that TIMP-1 may be of importance in high-grade B-cell lymphomas. Expression of TIMP-1 by tonsillar cells and peripheral blood T cells may indicate an association with the “activated” lymphoid phenotype or another role in normal lymphoid function. High levels of TIMP-2 RNA transcript and protein expression were observed in the neoplastic T-cell lines with lower levels of expression in normal peripheral blood T cells and hyperplastic tonsils. TIMP-2 expression occurred in response to activation with IL-2 and PHA in the peripheral blood T cells.
We find the presence of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in the absence of Gelatinase expression an interesting observation. Although the gelatinases studied may be expressed under different culture conditions, one would expect the regulation of expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 might mirror that of the Gelatinases A and B if the action of the TIMPs is merely inhibition of gelatinase activity. Therefore, the constitutive expression of the TIMPs without gelatinase suggests that they may have a growth factor activity, similar to that observed for TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in the erythroid burst formation assay14 and for TIMP-1 in K562 cells.15-17 This is further supported by the work of Hayakawa et al,18 19 who observed that both TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 promoted growth in serum-free media for a number of human cell lines, including the following: the Burkitt cell lines Raji, Daudi, and Ramos; the human myelogenous leukemia line HL60; human lymphoblast line WIL2-NS; human breast adenocarcinoma line MCF7; human gingival fibroblasts; human skin epithelial cells; and human aortic smooth muscle cells. The increased levels of TIMP-2 expression in neoplastic T-cell lines compared with normal T cells is also consistent with an autocrine growth factor activity, such as is observed in K562 cells and is currently being investigated. Alternatively, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 may be coexpressed with and modulate the activity of other metalloproteinases that were not studied or may be coupled with gelatinase expression in vivo.
In conclusion, we have studied the expression of TIMP-1, TIMP-2, Gelatinase A, Gelatinase B, and interstitial collagenase in a variety of low-grade and high-grade hematopoietic cell lines, as well as normal T and B cells. Gelatinase B production was demonstrated in the two Burkitt cell lines, tonsillar cell suspension, and normal peripheral blood T cells and may play an important role in lymphoid cell migration. We do not detect gelatinase production in the other lymphoid cell lines. This may be due to a requirement by lymphoid cells for interaction with components of the extracellular matrix or endothelial cells to induce or initiate gelatinase transcriptional activity. However, our results do demonstrate differential expression of the tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2. TIMP-1 is expressed in the high-grade B-cell Burkitt lymphoma lines, the multipotential K562 cells, tonsillar tissue, and activated T cells, while TIMP-2 expression is apparently restricted to T-cell lymphoma lines and tissues containing T cells.
Address reprint requests to Maryalice Stetler-Stevenson, MD, PhD, Laboratory of Pathology, NIH, Bldg 10, Room 2A-33, Bethesda, MD 20892.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal