Abstract
Although bone resorption and osteoclast numbers are reduced in osteopetrotic (op/op) mice, osteoclasts are nevertheless present and functional, despite the absence of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF). This suggests that alternative factors can partly compensate for the crucial actions of M-CSF in osteoclast induction. It was found that when nonadherent bone marrow cells were incubated in RANKL with Flt3 ligand (FL) without exogenous M-CSF, tartrate-resistance acid phosphatase (TRAP)–positive cells were formed, and bone resorption occurred. Without FL, only macrophagelike TRAP-negative cells were present. Granulocyte-macrophage CSF, stem cell factor, interleukin-3, and vascular endothelial growth factor could not similarly replace the need for M-CSF. TRAP-positive cell induction in FL was not due to synergy with M-CSF produced by the bone marrow cells themselves because FL also enabled their formation from the hemopoietic cells of op/op mice, which lack any M-CSF. FL appeared to substitute for M-CSF by supporting the differentiation of adherent cells that express mRNA for RANK and responsiveness to RANKL. To determine whether FL can account for the compensation for M-CSF deficiency that occurs in vivo, FL signaling was blockaded in op/op mice by the injection of soluble recombinant Flt3. It was found that the soluble receptor induced a substantial decrease in osteoclast number, strongly suggesting that FL is responsible for the partial compensation for M-CSF deficiency that occurs in these mice.
Introduction
The osteoclast is the cell that resorbs bone. Excessive activity by this cell is responsible for the development of postmenopausal osteoporosis and for the destruction of bone that accompanies inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Although it has been known for some time that the osteoclast derives from the mononuclear phagocyte system and that it shares some cell-surface markers with macrophages (see 1), it is also distinctly different from any other known mononuclear phagocyte derivative (see 2,3). Thus, osteoclasts lack many of the antigens that are characteristic of macrophages, and they express high levels of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), vitronectin receptors, and calcitonin receptors, which are absent from macrophages.1-3 Most distinctively, osteoclasts ex vivo excavate bone within hours, but macrophages show no excavation whatsoever, even after extended incubation on bone surfaces.4-6
It was recently found that osteoclastic differentiation is induced in mononuclear phagocyte precursors by receptor activator of NF-κB ligand RANKL (also known as TRANCE, ODF, OPGL, and TNFSF11), which was originally identified as a T cell-derived product that stimulates dendritic cells.7-9 RANKL is also expressed by osteoblastic and bone marrow stromal cells, and soluble recombinant RANKL with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) substitutes for stromal cells in osteoclast formation and activation.10-13 Deletion of the gene for TRANCE or its receptor is associated with failure of osteoclast formation and osteopetrosis.14 15
The osteoclast derives from a bipotential, M-CSF–dependent precursor shared with the macrophage. In the presence of RANKL and M-CSF, this precursor differentiates into osteoclasts, but in M-CSF alone it differentiates—with increasing resistance to osteoclast-induction—into macrophages by default.16-19 RANKL and M-CSF make distinct contributions to osteoclast formation: M-CSF provides precursors through induction of survival, proliferation, and expression of RANK (TRANCER, TNF receptor superfamily 11A [TNFRSF11A]), the receptor for RANKL, whereas RANKL induces osteoclastic differentiation in these precursors.
The role of M-CSF in osteoclast formation was established by the discovery that M-CSF is absent in osteopetrotic (op/op) mice,20,21 a mutant characterized by deficient bone resorption caused by low numbers of osteoclasts. However, although osteoclasts are reduced in number in these mutants, they are nevertheless present, and most or all of the excess bone is eventually resorbed.22 This suggests that other molecules can substitute for the actions of M-CSF. In this context, controversial data have been reported that granulocyte-macrophage CSF (GM-CSF) can23 and cannot24 cure osteopetrosis in op/op mice. In vitro, continuous incubation of murine hemopoietic cells in GM-CSF strongly suppresses murine osteoclastic differentiation,25-28 though GM-CSF does support the proliferation and survival of precursors that can form osteoclasts in its absence.29,30 Recently, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was reported to support osteoclast formation in op/op mice and in vitro, in the absence of exogenous M-CSF.31
Because M-CSF has several roles in osteoclast formation, we reasoned that compensation might occur through a single factor or that each role might be separately substituted by a different factor. We therefore tested candidate factors, not only alone but also in combination, for their ability to replace the need for M-CSF in osteoclast induction. We were particularly interested in the ability of stem cell factor (SCF) and Flt3 ligand (FL) to substitute for components of the action of M-CSF, because these agents have actions on early precursors of the mononuclear phagocyte lineage (see 32 33). In particular, FL favors the induction of macrophagic versus other lineages and supports the survival of immature mononuclear phagocytes. We found that FL enabled the differentiation of functional osteoclasts by RANKL from hemopoietic cells in the absence of M-CSF. Moreover, blockade of FL by soluble receptors (Flt3-Fc) substantially reduced osteoclast numbers in op/op mice. The mechanism by which FL partially substituted for M-CSF appeared to be through supporting the differentiation of adherent cells that express mRNA for RANK and responsiveness to RANKL.
Materials and methods
Mice
Six- to 8-week-old male MF-1 mice were from the St George's Hospital Medical School colony. Op/op mice (6- to 8-week-old, male) were from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME).
Media and reagents
Cells were incubated in minimum essential medium (MEM) with Earle salts, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 2 mM glutamine, 100 IU/mL benzylpenicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (all Imperial Laboratories, Andover, United Kingdom). Recombinant human (rh) M-CSF was provided by the Chiron Corporation (Emeryville, CA)55; soluble recombinant murine (rm) RANKL and recombinant rat SCF were provided by Amgen (Thousand Oaks, CA). R&D Systems (Abingdon, United Kingdom) supplied rm interleukin-3 (IL-3), rmGM-CSF, rhVEGF, rmFL, rhFlt3-Fc, and neutralizing anti–murine GM-CSF antibody. All other materials were from Sigma Chemical (Poole, United Kingdom) unless otherwise stated. All incubations were performed at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air.
Preparation of hemopoietic cells
Bone marrow cells were isolated from MF1 mice as previously described.18 Mice were killed by cervical dislocation. Femora and tibiae were aseptically removed and dissected free of adherent soft tissue. The bone ends were cut, and the marrow cavity was flushed into a Petri dish by slowly injecting phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at one end of the bone using a sterile 21-gauge needle. Bone marrow cells were carefully agitated through a 21-gauge needle to obtain a single cell suspension. Mononuclear cells were isolated by centrifugation of the bone marrow cell suspension on Histopaque (Sigma). The mononuclear cell fraction was resuspended in MEM-FBS, and incubated with cytokines as stated, at a density of 3 × 105 cells/mL in a 75-cm2 flask (Helena Biosciences, Sunderland, United Kingdom). After 6 to 24 hours, nonadherent cells were harvested, washed, and resuspended in MEM-FBS for further use.
Hemopoietic cells were obtained from the spleens of op/op mice.34 Spleens were aseptically removed. The capsule was cut open, and spleen cells were squeezed from it into suspension. The suspension was disaggregated, and the mononuclear fraction was separated as above using Histopaque. Spleen cells were then washed, resuspended in MEM-FBS, and incubated with or without cytokines at 3 × 105 cells/mL in 75-cm2 flasks. After 6 to 24 hours, nonadherent cells were harvested, washed, and resuspended in MEM-FBS for further use.
Osteoclast formation assay
Nonadherent hemopoietic cells (3 × 104), prepared as above, were added to the wells of 96-well plates (Helena Biosciences) containing a 6-mm thermanox coverslip (Gibco BRL, Paisley, United Kingdom) or a slice of bovine cortical bone35 and incubated in a total volume of 200 μL MEM-FBS with cytokines and antibodies as stated. All cultures were fed every 2 to 3 days by replacing 100 μL culture medium with an equal volume of fresh medium and cytokines. Coverslips and bone slices were assessed for TRAP positivity or bone resorption, respectively, as described below.
Assessment of TRAP expression and bone resorption by hemopoietic cells
TRAP expression assessment and bone resorption by hemopoietic cells were performed as previously described.18 35 After aspiration of medium, cells on coverslips were washed in PBS, fixed in 10% formalin for 10 minutes, and stained for acid phosphatase in the presence of 0.05 M sodium tartrate. The substrate used was naphthol AS-BI phosphate.
For bone resorption, bone slices were prepared as previously described.35 After incubation with hemopoietic cells, cells were removed from the surfaces of the bone slices to enable visualization of excavations. This was achieved by immersion of the bone slices in 10% (vol/vol) sodium hypochlorite (Lutterworth, Leicestershire, United Kingdom) for 10 minutes, followed by washing in water and dehydration in 70% ethanol. Bone slices were then mounted on stubs, sputter-coated with gold, and inspected in a Cambridge S90 scanning electron microscope (Cambridge Instruments, Cambridge, United Kingdom).
Reverse-transcription–polymerase chain reaction analysis
Bone marrow or spleen cells prepared as above were washed, resuspended, and incubated at 2 × 105/mL in 6-well plates (Helena Biosciences) with or without the stated cytokines for 3 days. Wells were then washed twice to remove nonadherent cells. RNA was extracted using an RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Crawley, United Kingdom) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Total RNA was reverse transcribed using MMLV (Gibco) using random hexamers (100 pmol) (Pharmacia, St Albans, United Kingdom) according to manufacturer's instructions. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers were as follows: actin, 5′-GTTACCAACTGGCACGATATGG-3′ (forward) and 5′-GATCTTGATCTTCATGGTGC-3′ (reverse); RANK, 5′GAGGCATTATGAGCATCTCGG-3′ (forward) and 5′-TTTCTTTTGTCAGGTGCTTTTCAG-3′ (reverse).
cDNAs were amplified for 25 to 38 cycles using Platinum Taq (2.5 U) (Gibco), 0.2 mM of each dNTP, 1.5 mM MgCl2, and 0.2 μM each primer. Each cycle consisted of 45-second denaturation at 94°C, 45-second denaturation at 60°C, and 60-second denaturation at 72°C. Product was measured during the exponential phase and checked for size by Southern blot analysis using internal oligos (actin, 481-531 nt; RANK, 721-770 nt).
Effect of Flt3 ligand on osteoclasts isolated from rat bone
Osteoclasts were isolated from 2-day-old rats as previously described.35 Briefly, femora were removed from 2-day-old Wistar rats, cleaned of adherent soft tissue, and curetted with a scalpel into medium 199 (Imperial). Curetting was agitated with a Pasteur pipette. Larger fragments were allowed to sediment for 30 seconds, and the resultant suspension was sedimented onto plastic coverslips or bone slices for 20 minutes. Substrates were washed vigorously to remove nonadherent cells and were incubated for 2 hours or 24 hours in MEM with 1 ng/mL bovine serum albumin with cytokines as described above. Coverslips and bone slices were then processed for assessment of TRAP positivity or bone resorption, respectively, as described above.
Effect of Flt3-Fc in vivo
Op/op mice were administered subcutaneous injections of Flt3-Fc (5 μg) or vehicle on each of 3 days. Two mice were given vehicle on each of the 3 days. Three mice were given Flt3-Fc on the first day, 2 were given it on the second, and 1 of these 2 was injected on the third day. Mice were killed 24 hours after the last injection. Femurs were removed and fixed in 10% formalin for 24 hours and were decalcified in 10% EDTA (pH 7.0) for 7 days. Decalcified bones were embedded in paraffin, and sections were cut and processed for histochemical localization of TRAP by a modification of the method of Burstone.36 The number of TRAP-positive cells lining bone surfaces was assessed by a modification of the method previously described.37 Data for bone perimeter and TRAP-positive cells were input into a computer and analyzed using histomorphometry software (Osteomeasure, Osteometrics, Atlanta, GA). The portion of bone between epiphyseal plates was selected for examination. The number of TRAP-positive cells per centimeter endosteal surface was counted “blind” in the diaphysis and metaphysis. TRAP-positive mononuclear cells were discriminated from TRAP-positive multinuclear (including binuclear) cells and then counted.
Statistics
The significance of differences between means was evaluated by the Student t test. Linear regression analysis with number of injections versus TRAP-positive cells was performed using Statview 5.0 (Abacus, Berkeley, CA). P < .05 was considered significant.
Results
We initially tested the ability of agents known to be able to support some or all stages of development of the mononuclear phagocytic lineage to replace M-CSF in osteoclast-induction by RANKL. To do this, these factors, alone or in combination, were substituted for M-CSF in an assay in which osteoclast formation is dependent on exogenous M-CSF. In this assay, bone marrow cells are depleted of stromal cells by incubation for 24 hours in M-CSF, followed by incubation of the nonadherent bone marrow cells for 6 days in M-CSF with RANKL. M-CSF is present in both phases to support precursors. Thus, to test the ability of cytokines to compensate for the M-CSF deficiency, the candidates replaced M-CSF in both preincubation and osteoclast-inductive phases. We found that all cultures containing FL developed strongly TRAP-positive cells (Table 1). GM-CSF, interleukin-3, and SCF were unable to support the differentiation of TRAP-positive cells by RANKL. VEGF alone (with RANKL) did not induce TRAP-positive cells (data not shown) and did not synergize with FL (Table 1).
Ability of hemopoietic cytokines to replace M-CSF in the induction of osteoclastic differentiation
| Preincubation . | Combinations of cytokines with RANKL . | TRAP-positive cells/coverslip . |
|---|---|---|
| GM-CSF (5 ng/mL) | GM-CSF (50 ng/mL) | 0 |
| IL-3 (1 ng/mL) | IL-3 (1 ng/mL) | 0 |
| IL-3 (1 ng/mL) | IL-3 (1 ng/mL) + GM-CSF (50 ng/mL) | 0 |
| SCF (5 ng/mL) | SCF (100 ng/mL) | 0 |
| SCF (5 ng/mL) | SCF (100 ng/mL) + FL (100 ng/mL) | 18 ± 7 |
| SCF (5 ng/mL) | SCF (100 ng/mL) + VEGF (100 ng/mL) | 0 |
| FL (5 ng/mL) | FL (100 ng/mL) | 39 ± 14 |
| FL (5 ng/mL) | FL (100 ng/mL) + SCF (100 ng/mL) | 43 ± 23 |
| FL (5 ng/mL) | FL (100 ng/mL) + IL-3 (1 ng/mL) | 31 ± 12 |
| FL (5 ng/mL) | FL (100 ng/mL) + VEGF (100 ng/mL) | 41 ± 14 |
| Preincubation . | Combinations of cytokines with RANKL . | TRAP-positive cells/coverslip . |
|---|---|---|
| GM-CSF (5 ng/mL) | GM-CSF (50 ng/mL) | 0 |
| IL-3 (1 ng/mL) | IL-3 (1 ng/mL) | 0 |
| IL-3 (1 ng/mL) | IL-3 (1 ng/mL) + GM-CSF (50 ng/mL) | 0 |
| SCF (5 ng/mL) | SCF (100 ng/mL) | 0 |
| SCF (5 ng/mL) | SCF (100 ng/mL) + FL (100 ng/mL) | 18 ± 7 |
| SCF (5 ng/mL) | SCF (100 ng/mL) + VEGF (100 ng/mL) | 0 |
| FL (5 ng/mL) | FL (100 ng/mL) | 39 ± 14 |
| FL (5 ng/mL) | FL (100 ng/mL) + SCF (100 ng/mL) | 43 ± 23 |
| FL (5 ng/mL) | FL (100 ng/mL) + IL-3 (1 ng/mL) | 31 ± 12 |
| FL (5 ng/mL) | FL (100 ng/mL) + VEGF (100 ng/mL) | 41 ± 14 |
Bone marrow cells were preincubated for 24 hours to remove stromal cells. Normally during this phase, the survival of osteoclastic precursors is supported by M-CSF, which was replaced in these experiments by a variety of cytokines. After 24 hours, nonadherent cells were removed, washed, and resuspended in the cytokines shown, together with RANKL (30 ng/mL). TRAP-positive cells were enumerated after 6 days of incubation and expressed as mean ± SEM (6 cultures per variable).
Two distinct populations of cells were present: TRAP-negative macrophagelike cells and strongly TRAP-positive cells (Figure1). The absolute number of TRAP-positive cells that formed when bone marrow cells were incubated with FL was small but similar, as a proportion of total cells present, to that observed in the presence of M-CSF (Figure 1). This is consistent with a model in which FL shares with M-CSF the capacity to support osteoclastic differentiation, but it lacks its proliferative action so that both in vitro and in vivo the total number of osteoclastic cells formed was small.
Induction of TRAP-positive cells by RANKL in the presence of FL.
Bone marrow cells were incubated for 6 hours at 3 × 105cells/mL. Nonadherent cells (3 × 104/well) were then incubated in RANKL (100 ng/mL) and FL for 6 days before the assessment of (A) TRAP-positive cell numbers and (B) total cell numbers. Figures are mean ± SEM of 6 cultures per variable. Cultures in which M-CSF (50 ng/mL) replaced FL were included for comparison. No TRAP cells developed in cultures to which RANKL had not been added. *P < .05 versus no FL/M-CSF. (C, D) Formation of TRAP-positive cells capable of bone resorption by RANKL and FL. Nonadherent bone marrow cells were incubated with RANKL (100 ng/mL) and FL (100 ng/mL) for 6 days (for TRAP staining) or 10 days for bone resorption. (C) Two strongly TRAP-positive mononuclear cells, and several TRAP-negative cells (no counterstain). (D) Three small excavations (arrows) produced by cells incubated in RANKL and FL. Excavations were never seen in cultures from which RANKL was omitted.
Induction of TRAP-positive cells by RANKL in the presence of FL.
Bone marrow cells were incubated for 6 hours at 3 × 105cells/mL. Nonadherent cells (3 × 104/well) were then incubated in RANKL (100 ng/mL) and FL for 6 days before the assessment of (A) TRAP-positive cell numbers and (B) total cell numbers. Figures are mean ± SEM of 6 cultures per variable. Cultures in which M-CSF (50 ng/mL) replaced FL were included for comparison. No TRAP cells developed in cultures to which RANKL had not been added. *P < .05 versus no FL/M-CSF. (C, D) Formation of TRAP-positive cells capable of bone resorption by RANKL and FL. Nonadherent bone marrow cells were incubated with RANKL (100 ng/mL) and FL (100 ng/mL) for 6 days (for TRAP staining) or 10 days for bone resorption. (C) Two strongly TRAP-positive mononuclear cells, and several TRAP-negative cells (no counterstain). (D) Three small excavations (arrows) produced by cells incubated in RANKL and FL. Excavations were never seen in cultures from which RANKL was omitted.
Although FL induced cells that were strongly TRAP positive (Figure 1), they were almost all mononuclear. However, the cells made excavations when they were incubated on bone slices (Figure 1). Most of the osteoclasts in op/op mice are mononuclear.23 This propensity for mononuclearity in vivo and in vitro may reflect an inability of FL to compensate for M-CSF in the induction of fusion. An alternative explanation is that fusion, which requires cells to make contact, is less common at the low cell densities achieved without M-CSF. It has been noted that, especially at low densities in vitro, some osteoclastic cells remain mononuclear but are nevertheless capable of bone resorption.38-40
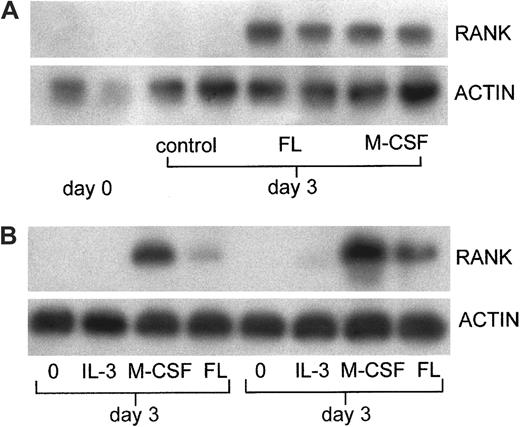
Like M-CSF, FL showed a capacity to support the expression of mRNA for RANK in the adherent cells that develop from nonadherent bone marrow cells in culture (Figure 2A). No RANK mRNA was detected in cultures incubated with VEGF (100 ng/mL) or IL-3 (1 ng/mL) (data not shown). To determine whether TRAP-positive cell differentiation and RANK expression in the cultures of cells from normal mice was attributable to FL alone or whether it represented synergy with endogenous M-CSF, the experiments were repeated using hemopoietic cells from op/op mice, which do not express M-CSF. As observed using cells from normal mice, mRNA for RANK was detected only after incubation in M-CSF or FL (Figure 2B). In addition, similar to cultures of cells from normal mice, FL supported the differentiation of TRAP-positive cells indistinguishable from those seen in normal animals in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 3). The total number of cells induced by FL was greater from op/op hemopoietic cells than from wild-type cells. Although the populations of cells from spleen (op/op) and marrow (wild-type) are not readily comparable, a similar 3-fold increase in M-CSF–derived colonies was noted in op/op spleen versus wild-type bone marrow, possibly reflecting an attempted hemopoietic compensation for the deficiency of mature cells.41 TRAP-positive cell formation was not inhibited by neutralizing antibody to GM-CSF. However, proliferation was inhibited, suggesting that GM-CSF is present in these cultures. GM-CSF has complex effects on osteoclast precursors—it increases the provision of uncommitted precursors but inhibits osteoclast differentiation25-30 (see “Discussion”). Presumably, the lack of effect of anti–GM-CSF on TRAP-positive cell formation reflects the net result of these 2 actions. VEGF did not significantly increase TRAP-positive cells (Figure 3).
Induction of expression of mRNA for RANK in hemopoietic cells by FL.
(A) Expression of mRNA for RANK in bone marrow cells incubated with FL. Expression of RANK mRNA was analyzed by RT-PCR. Bone marrow cells nonadherent after 6 hours without cytokine were incubated for 3 days with and without FL (100 ng/mL) or M-CSF (50 ng/mL) before extraction of RNA from adherent cells. (B) Expression of mRNA for RANK in op/op spleen cells incubated with FL. Spleen cells were incubated with and without IL-3 (1 ng/mL), M-CSF (50 ng/mL), or FL (100 ng/mL) for 3 days. RNA was extracted from adherent cells and analyzed by RT-PCR. Results are from 2 separate experiments.
Induction of expression of mRNA for RANK in hemopoietic cells by FL.
(A) Expression of mRNA for RANK in bone marrow cells incubated with FL. Expression of RANK mRNA was analyzed by RT-PCR. Bone marrow cells nonadherent after 6 hours without cytokine were incubated for 3 days with and without FL (100 ng/mL) or M-CSF (50 ng/mL) before extraction of RNA from adherent cells. (B) Expression of mRNA for RANK in op/op spleen cells incubated with FL. Spleen cells were incubated with and without IL-3 (1 ng/mL), M-CSF (50 ng/mL), or FL (100 ng/mL) for 3 days. RNA was extracted from adherent cells and analyzed by RT-PCR. Results are from 2 separate experiments.
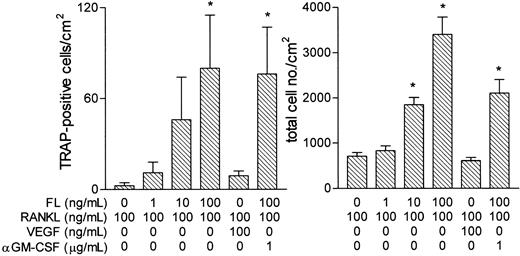
Induction of TRAP-positive cells by RANKL and FL in spleen cells from op/op mice.
Spleen cells were incubated for 24 hours in FL (10 ng/mL). Nonadherent cells were then incubated as shown for 6 days, and the cells formed were assessed for expression of TRAP. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of 12 cultures per variable. *P < .05 versus cultures containing no FL.
Induction of TRAP-positive cells by RANKL and FL in spleen cells from op/op mice.
Spleen cells were incubated for 24 hours in FL (10 ng/mL). Nonadherent cells were then incubated as shown for 6 days, and the cells formed were assessed for expression of TRAP. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of 12 cultures per variable. *P < .05 versus cultures containing no FL.
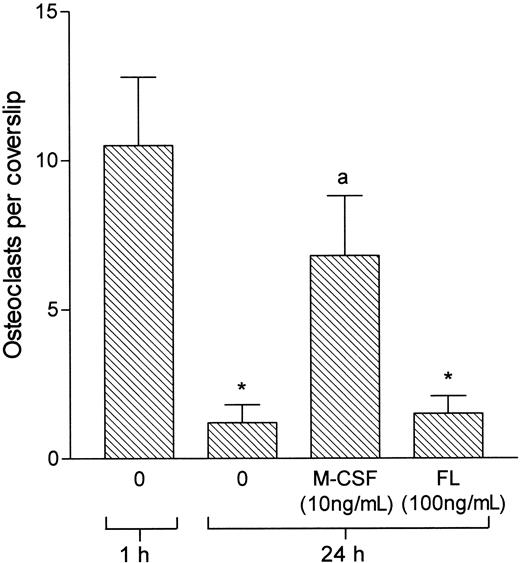
M-CSF supports not only osteoclastic differentiation but also the survival of mature osteoclasts.13 42 Therefore, we tested the effects of FL on osteoclasts isolated from neonatal rat long bones. FL showed no significant effect on the survival of isolated osteoclasts (Figure 4) and did not influence the number or plan area of bone surface resorbed by these cells (data not shown).
FL does not support the survival of osteoclasts isolated from rat bone.
Osteoclasts were extracted from the long bones of 2-day-old rats and sedimented onto coverslips for 20 minutes. Nonadherent cells were then washed off, and incubation continued for 1 hour or 24 hours with and without M-CSF or FL. *P < .05 versus 1 hour; a,P < .05 versus 24-hour control.
FL does not support the survival of osteoclasts isolated from rat bone.
Osteoclasts were extracted from the long bones of 2-day-old rats and sedimented onto coverslips for 20 minutes. Nonadherent cells were then washed off, and incubation continued for 1 hour or 24 hours with and without M-CSF or FL. *P < .05 versus 1 hour; a,P < .05 versus 24-hour control.
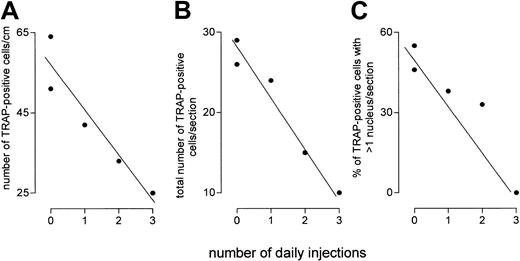
A critical prediction of the notion that FL compensates for lack of M-CSF in op/op mice is that blockade of FL signaling in these mice should reduce osteoclast number. To blockade FL signaling, op/op mice were injected with 5 μg soluble receptor for FL (Flt3-Fc) or vehicle daily for up to 3 days. We found (Figure5) a highly significant inverse correlation between the number of daily injections of Flt3-Fc and the number of osteoclasts per centimeter of bone surface (P < .02) or per section (P = .003). We also confirmed that many osteoclasts in op/op mice showed only one nucleus, and we found that the proportion of such osteoclasts was increased by soluble receptor (Figure 5). This suggests that the reduction in osteoclast number understates the reduction in osteoclast cell bulk brought about by blockade of FL.
Flt3-Fc administration to op/op mice reduces the number or osteoclasts and the number of nuclei per osteoclast section in vivo.
Flt3-Fc (5 μg) or vehicle was injected daily. On the first day, 2 animals were given vehicle, and the other 3 were injected with Flt3-Fc. On the second day, 2 of the latter were given Flt3-Fc; and one of these was also given a third dose on the third day. Animals were killed 24 hours after the last injection. The number of TRAP-positive cells per centimeter (A) correlates inversely (r = 0.94;P = .016) with the duration of injections, as does the number of TRAP cells per section (B) (r = 0.98;P = .003) and the proportion of such cells showing more than one nucleus per cell (C) (r = 0.937;P = .019).
Flt3-Fc administration to op/op mice reduces the number or osteoclasts and the number of nuclei per osteoclast section in vivo.
Flt3-Fc (5 μg) or vehicle was injected daily. On the first day, 2 animals were given vehicle, and the other 3 were injected with Flt3-Fc. On the second day, 2 of the latter were given Flt3-Fc; and one of these was also given a third dose on the third day. Animals were killed 24 hours after the last injection. The number of TRAP-positive cells per centimeter (A) correlates inversely (r = 0.94;P = .016) with the duration of injections, as does the number of TRAP cells per section (B) (r = 0.98;P = .003) and the proportion of such cells showing more than one nucleus per cell (C) (r = 0.937;P = .019).
Discussion
Osteoclast formation and bone resorption occur, albeit at reduced levels, in the op/op mouse, which lacks any M-CSF.20-22This suggests that factors exist in vivo that can partially compensate for M-CSF deficiency. We tested several putative or potential M-CSF surrogates, including SCF, FL, VEGF, GM-CSF, and IL-3, for their ability to substitute for M-CSF in osteoclast formation. Only FL was able to support RANKL-induced differentiation of TRAP-positive cells from hemopoietic cells. Such cells were also formed from the hemopoietic cells of op/op mice. Although only small numbers of TRAP-positive cells formed in the presence of FL, the proportion of adherent cells that were TRAP positive was similar to the proportion seen after incubation in M-CSF. This pattern suggests that FL can replace M-CSF for RANKL responsiveness but not for proliferation, and it is consistent with both the presence and the scarcity of osteoclasts in op/op mice. Also consistent with this role for FL, we found that the injection of soluble decoy receptors for FL into op/op mice dramatically reduced osteoclast number, suggesting that FL compensates in vivo for the absence of M-CSF.
There have been no previous reports of osteoclastic differentiation in vitro in the absence of M-CSF. It has been reported that GM-CSF can23 and cannot24 increase bone resorption in op/op mice. In vitro, GM-CSF strongly inhibits osteoclast formation from murine hemopoietic cells,25-28 and GM-CSF is unable to support osteoclast formation in cultures of op/op cells.34 However, GM-CSF can support osteoclast formation in vitro if precursors are incubated in GM-CSF and then transferred to RANKL/M-CSF–expressing cultures of stromal cells.29 Thus, if osteoclast formation is enhanced by GM-CSF in op/op mice, this is likely to occur through an increase by GM-CSF in the provision of hemopoietic precursors available for osteoclast-induction by RANKL/FL. Recently, it was shown that GM-CSF induces the expression of RANK in precursors, but then, in the presence of RANKL, it induces dendritic cell rather than osteoclastic differentiation.43Hence, it appears that GM-CSF and M-CSF direct differentiation induction by RANKL into the alternative destinies of dendritic cells and osteoclasts, respectively. This makes it unlikely that GM-CSF compensates directly for M-CSF deficiency in op/op mice.
It has also been suggested that VEGF compensates for the lack of M-CSF in vivo and in vitro.31 However, we found that VEGF did not induce osteoclastic differentiation or mRNA for RANK. This makes it unlikely that VEGF substitutes directly for M-CSF. In fact, the experiments31 reporting osteoclast induction by VEGF in vitro used not op/op but wild-type bone marrow cells and, moreover, did not include VEGF-free control cultures. Thus, the induction of osteoclastic differentiation by M-CSF produced by contaminating stromal cells or macrophages was not excluded and indeed was especially likely to have occurred because VEGF supports bone marrow endothelial stromal cells, which express M-CSF and FL.44 In vivo, bone resorption has been shown to be dependent on VEGF-mediated angiogenesis,45 and this dependency might account for the inhibition of bone resorption by the blockade of VEGF in vivo in those31 experiments. Alternatively, because enhancement of the survival of hematogenous osteoclastic precursors augments bone resorption in op/op mice,46 VEGF blockade might impair osteoclast function in op/op mice by interfering with endothelial cell-mediated transit of hematogenous precursors to bone surfaces.
Flt3 is widely expressed by hemopoietic cells and, consistent with our observation that FL enables TRAP cell induction, is expressed by hemopoietic cells known to be precursors of osteoclasts.32,33,47,48 Its ligand, FL, is widely expressed in bone and many other tissues and exerts effects on hemopoietic cells in synergy with other cytokines (see32,33,48). FL shares several characteristics with SCF, but though SCF favors the differentiation of granulocytes, eosinophils, and red blood cells, FL enhances the production of mononuclear phagocytes, including likely precursors of osteoclasts and dendritic cells.32,33 48 The ability of FL but not SCF to restore RANKL responsiveness in vitro suggests that osteoclasts are part of the spectrum of differentiation in hemopoietic cells facilitated by FL.
Recently, it was shown that nonadherent hemopoietic precursors do not express RANK in the absence of M-CSF and that RANK is induced simultaneously with adhesion receptors.19 Therefore, because our cultures were derived from nonadherent cells, our results suggest that FL similarly induces the expression of mRNA for RANK and RANKL responsiveness in such RANK-negative nonadherent cells. This is strongly supported by the similar results using spleen cells from op/op animals in which endogenous M-CSF cannot be responsible for the induction of mRNA for RANK. Thus, FL might substitute for M-CSF in op/op mice primarily through the induction of responsiveness to RANKL.
We found that although FL facilitated osteoclast formation, it had no effect on the survival or function of mature cells in vitro. This pattern of decreasing responsiveness to FL with maturation is also observed in other lineages. However, osteoclast numbers were reduced rapidly in vivo by soluble Flt3. We found that FL does not augment the survival of existing osteoclasts; presumably FL blockade reduces the supply of replacement osteoclasts. This mechanism is also consistent with the greater proportion of mononuclear cells in Flt3-Fc–treated mice: if osteoclasts are scarce, there are fewer opportunities for fusion.
It is possible that FL participates in the maintenance of osteoclastic precursors on bone surfaces in normal animals. Recent evidence suggests that although osteoclasts have their origin in hematogenous cells and can be supplied from the circulation during development or in conditions of physiological stress, they derive under physiological conditions from a self-sustaining precursor that becomes established on the bone surface49 (and see 50). If this is so, FL might be more suited to the long-term support of such cells than is M-CSF: precursors rapidly become refractory to osteoclast induction in M-CSF,16-19 whereas FL can maintain the responsiveness of precursors to cytokines.51 Because the circulation can supply osteoclast precursors, such a role is unlikely to be essential (a nonessential role is also consistent with the lack of reports of an osteopetrotic phenotype in mice deleted of the gene for FL).52 53 Nevertheless, local osteoclast precursors might facilitate rapid resorptive responses. The role of FL in the physiology of normal bone is being addressed.
We found that the blockade of FL signaling by the administration of Flt3-Fc dramatically reduced the number of osteoclasts in the bones of op/op mice. This suggests that FL accounts for the presence of osteoclasts in these mice, despite the absence of M-CSF. Although we have not tested the ability of FL to also increase osteoclast formation in vivo, this result is anticipated from experiments in which it was shown that the systemic administration of FL increases the number of osteoclast precursors,48 consistent with our in vivo and in vitro observations. Our results also suggest that, in addition to providing precursors, FL induces the expression of RANK in osteoclast precursors.
It has been shown that osteopetrosis in op/op mice resolves with age. Although FL appears to partially compensate for the absence of M-CSF in these mice and might explain the presence of osteoclasts, we do not know whether this is related to the spontaneous resolution of osteopetrosis that occurs in these mice later in life. As growth rate slows with age, the rate of bone formation decreases and with it the resorptive burden, so that spontaneous cure might reflect the ability of suboptimal osteoclast function to catch up when formation rates decline. Alternatively, the ability of FL to support osteoclast precursors might be enhanced once these become established on bone surfaces, as discussed above; or spontaneous cure might occur through an age-related increase in expression of FL or through the expression of other, as-yet-unidentified compensatory agents.
Injection of FL has been shown to increase dendritic cell numbers in vivo.54 Because RANKL can induce dendritic cell differentiation in vitro,43 our observation that FL induces RANKL responsiveness provides a mechanism for osteoclast induction and dendritic cell induction by FL. Indeed, the induction of RANKL responsiveness may reflect a more general mechanism by which FL favors the differentiation of certain hemopoietic lineages—not only through the synergistic induction of proliferation but also through the induction of lineage-specific receptors in the precursors so formed, which facilitate maturation of the precursors in an appropriate ligand environment.
Supported by The Wellcome Trust.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
T. J. Chambers, Department of Cellular Pathology, St George's Hospital Medical School, Cranmer Terrace, London, United Kingdom; e-mail: t.chambers@sghms.ac.uk.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal