Abstract
Reduced intensity regimens (RIR) have largely replaced conventional myeloablative regimens (CMR) for patients with NHL undergoing allogeneic transplant. However, the impact of dose reduction on relapse has not been extensively studied. We performed a retrospective analysis of 88 patients conditioned with CMR (n=48) and a RIR (n=40) of fludarabine 125mg/m2 and melphalan 140mg/m2. GVHD prophylaxis was with cyclosporine + MTX +/− prednisone for CMR and cyclosporine + MMF +/− MTX for the RIR.
| . | CMR . | RIR . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 48 | 40 | |
| Low grade B-cell | 18 | 16 | NS |
| Intermediate grade B-cell | 16 | 12 | NS |
| Mantle cell | 10 | 5 | NS |
| T cell | 4 | 7 | NS |
| Age (years, median, range) | 44 (18–54) | 51 (20–67) | 0.0002 |
| No of prior regimens (median) | 3 | 2 | 0.02 |
| Previous autologous transplant | 5 | 16 | 0.002 |
| Chemosensitivity at transplant | 24 | 31 | 0.007 |
| FTBI regimen | 41 | 0 | <0.0001 |
| MUD | 8 | 17 | 0.009 |
| PBSC | 16 | 36 | 0.0001 |
| Median follow-up (months,range) | 65 (33-95) | 20 (6-42) |
| . | CMR . | RIR . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 48 | 40 | |
| Low grade B-cell | 18 | 16 | NS |
| Intermediate grade B-cell | 16 | 12 | NS |
| Mantle cell | 10 | 5 | NS |
| T cell | 4 | 7 | NS |
| Age (years, median, range) | 44 (18–54) | 51 (20–67) | 0.0002 |
| No of prior regimens (median) | 3 | 2 | 0.02 |
| Previous autologous transplant | 5 | 16 | 0.002 |
| Chemosensitivity at transplant | 24 | 31 | 0.007 |
| FTBI regimen | 41 | 0 | <0.0001 |
| MUD | 8 | 17 | 0.009 |
| PBSC | 16 | 36 | 0.0001 |
| Median follow-up (months,range) | 65 (33-95) | 20 (6-42) |
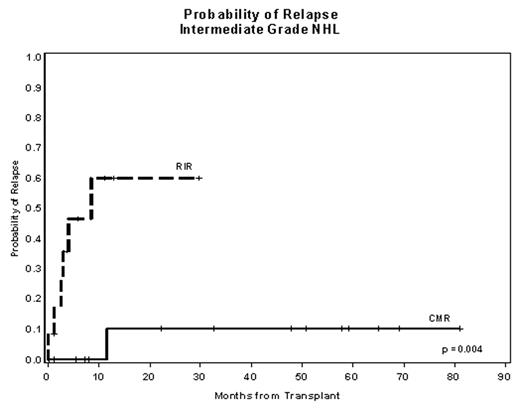
CMR were significantly associated with a lower rate of relapse (RR) of 15% versus 38% after RIR (p=0.017). The 1-year TRM was 38% for CMR and 24% for RIR (p=NS). Kaplan-Meier 2-year OS/PFS for CMR is 52%/48% versus 57%/48% for RIR (p=NS). When analyzed by diagnosis, CMR were significantly associated with decreased RR (10% vs 60%, p=0.004) for intermediate grade B-cell (figure 1). Univariate analysis of patient and treatment-related prognostic factors showed improved survival with chemosensitive disease; treatment intensity was the single predictor of relapse for the entire group, but, when stratified by diagnosis, for intermediate grade B-cell only. In conclusion, CMR provide better disease control for intermediate grade B-cell NHL.
Author notes
Corresponding author