Abstract
Abstract 2941
MDS is a spectrum of abnormalities in the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells that result in peripheral cytopenias, bone marrow dysplasia and increased risk of transformation to acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Cytogenetic abnormalities occur in more than 50% of patients (pts) and have an impact on survival and risk of transformation to AML. CE, or acquisition of additional clonal chromosomal abnormalities, has been reported to occur in 30 to 50% of primary MDS pts. Their impact on prognosis and transformation into AML among pts with low and intermediate risk MDS is not known. In this study, we analyzed the impact of CE on prognosis in lower risk MDS.
we reviewed 722 pts clinic records of low and intermediate risk MDS pts at MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) from 2000–2010 and conducted a retrospective analysis of all MDS pts with at least two consecutive cytogenetic analysis (365 patients, 50.6%) and compared the cytogenetic evolution group (CE group) with the group without cytogenetic changes (no CE group). Cytogenetic analysis was performed in the Cytogenetics Laboratory at MDACC.
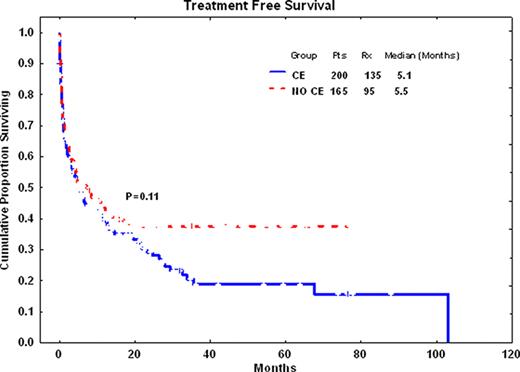
CE was detected in 200 pts (55%). Characteristics of patients with CE are: median age 65 years (23-91), IPSS int-1 79%, diploid CG 42%, excess blasts 25%. Pts with CE were more frequently female (p=0.005), and had more frequently abnormalities of chromosome 5 and 7 (p<0.001) at baseline. There were no statistically significant difference between these two groups (p>0.05) regarding age, WBC, platelet, hgb, ANC, BM blasts percent, diagnosis (RA or RAEB), and IPSS score. There were more chr.-5/-7, insufficient metaphases, and other abnormalities, but less diploid cases in CE group compared with no CE group (p<0.001). History of malignancy (p=0.001) and prior chemotherapy exposure were also associated with CE (p=0.001), but this was not as strong for radiation exposure (p=0.066). Also, more CE patients required therapy for MDS compared to no CE patients (p=0.039). Progression free survival was significantly extended in no CE patients (p=0.02). Overall survival was a longer in no CE (34.1months), compared with CE group (26.2 months), although this was not statistically significant.
CE is more commonly observed among pts with high-risk features, and is usually associated with disease progression and resistance. Also, prior malignancy and chemotherapy exposure were associated with CE in this study. This data indicates that genomic instability has a role in disease progression in MDS. Further analysis of CE in MDS is needed.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.