Abstract
Abstract 1553
Most pts with AML will achieve complete remission (CR) following therapy with cytarabine and an anthracycline. Early clearance of blasts in peripheral blood (PB) has been shown to be an important prognostic factor in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. We explored the dynamics of PB blasts in pts with AML undergoing induction chemotherapy with AI (ara-C 1.5g/m2x3d and idarubicin 12mg/m2x3d) at our institution and their impact in long-term outcomes.
We reviewed the dynamics of PB blasts (i.e. PB blasts=0%) or WBC (i.e. WBC≤0.1×109/dL) clearance in pts with AML receiving AI (n=486). Patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia were excluded. Pt characteristics were as follows: median age 55 yrs (range, 19–73), pts <60 yrs 44 (30%), diploid cytogenetics (n=54, 36%), poor cytogenetics (n=57, 38%), median WBC 4.9 (range, 0.3–97.4), platelets 39 (range, 2–581), hemoglobin 8.4g/dL (range, 3.3–13.2), PB blasts (15% (range, 1–96), BM blasts 45% (1–96).
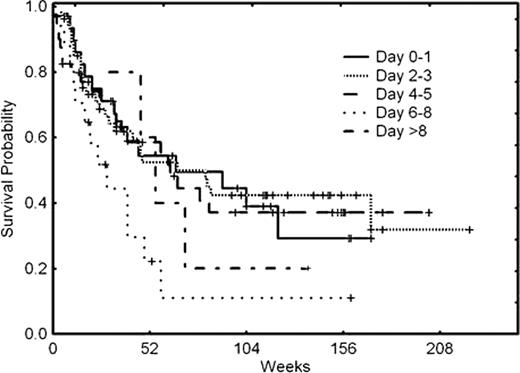
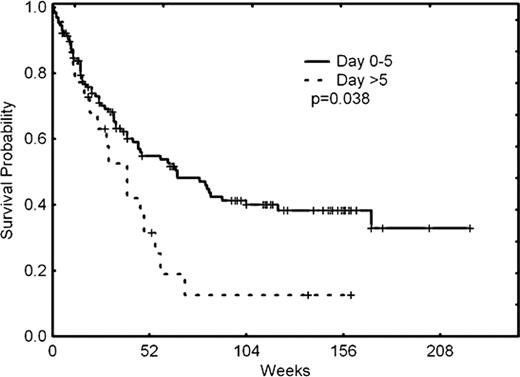
The overall response rate (ORR=CR+CRp) was 65% (58%+7%). Forty-four (30%) pts were resistant to induction therapy. To evaluate the dynamics of PB WBC and PB blast clearance, we divided all pts in 5 groups depending on the day they cleared their WBC or blasts from PB: group 1 (0–1 days), 2 (2–3 days), 3 (4–5 days), 4 (6–8 days), and 5 (beyond day 8). A total of 21, 34, 25, 4, and 3 pts were included in groups 1 through 5. No differences in CR rates were observed across all 5 groups according to the time of clearance of PB WBC (p=0.653). Likewise, similar median overall survival (OS) rates were observed in all 5 groups regardless of the timing of PB WBC clearance (0.2). However, the timing of PB blast clearance was associated with a distinct probability of achieving CR, being 73%, 74%, 65%, 24%, AND 60% for groups 1 through 5 (p=0.003). This translated into distinctly different median OS for the 5 groups (p=0.03) (Figure 1A). When groups 1, 2, and 3 were merged and compared with the merge of groups 4 and 5, the ORR for the resulting two new groups was 71% and 32% (p<0.001) and the corresponding median OS was 40 weeks and 75 weeks (p=0.038) (Figure 1B), suggesting that early PB clearance predicts long-term outcomes.
Overall survival according to timing of PB blast clearance (A & B)
We have shown in a large cohort of uniformly treated pts with AML that early clearance of PB blasts (but not WBC) is an important risk factor for achievement of CR and for OS. Clearance of PB blasts should be considered in prognostication schemas for pts with AML.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.