Abstract
Abstract 3712
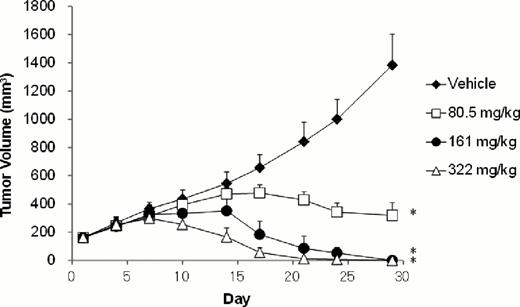
The coupled enzymatic activity of wild-type and mutant EZH2 results in hyper-trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27), which drives lymphomagenesis in heterozygous patients bearing the EZH2 mutations. Our group has previously reported that selective inhibition of EZH2 in cell culture results in selective killing of lymphoma cells bearing EZH2 mutations, with minimal effect on non-mutant lymphoma cells, suggesting that EZH2 enzymatic activity is a required driver of proliferation in the mutant-bearing cells [Knutson et al. (2012) Nature Chemical Biology, in press]. Through iterative medicinal chemistry we have developed a selective inhibitor of EZH2 with good pharmacological properties, E7438. E7438 binds to the enzyme in a manner competitive with S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) and a Ki for wild-type EZH2 of 2.5 ± 0.5 nM. The compound potently inhibits all known mutants of EZH2 that have been identified in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patient samples. E7438 displays about 35-fold less activity against the closely related enzyme EZH1, and is >4500-fold selective with respect to all other protein methyltransferases tested. Lymphoma cells treated with E7438 display concentration- and time-dependent loss of H3K27 methylation with no effect on the methylation status of any other histone sites. The loss of H3K27 methylation results in selective killing of EZH2 mutant-bearing lymphoma cell lines. E7438 displays good oral bioavailability and pharmacokinetic properties. Various EZH2 mutant-bearing human lymphoma tumors were subcutaneously implanted in nude, SCID or NSG mice. Oral administration of E7438 to tumor bearing mice resulted in significant anti-tumor activity. The responses ranged from dose-dependent tumor growth inhibition to complete and sustained regressions. For example, KARPAS422 tumors in nude mice showed complete tumor elimination after 28 days of dosing, with mice remaining tumor free for up to 90 days after treatment cessation.
E7438 causes complete and sustained tumor regression in a KARPAS422 nude mouse xenograft model of EZH2-mutated NHL. Dosing was on a BID schedule. * P< 0.05, Repeated measures ANOVA, Dunnett's post test vs. vehicle.
E7438 causes complete and sustained tumor regression in a KARPAS422 nude mouse xenograft model of EZH2-mutated NHL. Dosing was on a BID schedule. * P< 0.05, Repeated measures ANOVA, Dunnett's post test vs. vehicle.
Mice and rats tolerated E7438 administration well at doses representing high multiples of doses that show antitumor activity in mice. Activity against the EZH2 target in both species was demonstrated by dose-dependent diminution of H3K27me3 levels, assessed by ELISA, in samples of tumor, bone marrow, skin and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Highly sensitive detection of existing H3K27me3 signal could also be observed with this ELISA assay in drug-naïve samples of human PBMCs. The ability to measure dose-dependent changes in H3K27me3 levels in skin and PBMCs portends the use of signal from these surrogate tissues as a non-invasive pharmacodynamics biomarker in human clinical trials.
Keilhack:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Yokoi:Eisai Co., Ltd.: Employment. Knutson:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Wigle:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Warholic:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kawano:Eisai Co., Ltd.: Employment. Minoshima:Eisai Co., Ltd.: Employment. Huang:Eisai Inc.: Employment. Kuznetsov:Eisai Inc.: Employment. Kumar:Eisai Inc.: Employment. Klaus:Epizyme, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Allain:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Raimondi:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Porter Scott:Epizyme: Employment, Equity Ownership. Chesworth:Epizyme: Employment, Equity Ownership. Moyer:Epizyme: Employment, Equity Ownership. Uenaka:Eisai Co., Ltd.: Employment. Copeland:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Richon:Epizyme, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Pollock:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kuntz:Epizyme Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.