Abstract
The combination of bortezomib, doxorubicin and dexamethasone (BDD) is well tolerated and induces a high overall response rate (ORR). Preclinical studies have demonstrated that vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, is synergistic with bortezomib and doxorubicin. The aim of this phase I/II study was to determine the tolerability and activity of the combination of BDD with vorinostat (VBDD) in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (MM).
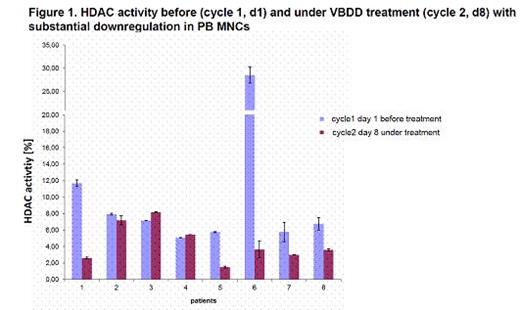
Patients received escalated vorinostat-doses (provided by MSD) at 100mg (dose level 0), 200mg (dose level +1) and 300mg (dose level+2) on days 1-4, 8-11, 15-18, combined with bortezomib 1.3mg/m2 day 1,8,15 (provided by Janssen), dexamethasone 40mg day 1,8,15,22 and doxorubicin on 9mg/m2 day 1+8. The primary objective was the maximum tolerated dose (MTD; 3+3 dose escalation design). Secondary objectives were safety, response assessed by EBMT and IMWG criteria, progression-free survival and overall survival. Correlative endpoints include prognostic MM-parameters, organ function, QoL-, comorbidity-assessments and translational studies (e.g. HDAC-activity in PB MNCs, Figure 1). Dose limiting toxicities (DLTs) were defined as any possibly drug related adverse events (AEs) ≥grade 3 (CTCAE) within the 1st cycle. After completion of 6 cycles, patients could continue with bortezomib maintenance therapy or proceed to (most often 2nd) ASCT.
To date, 18/30 patients have been enrolled (median age 63 years [range 54-75], 55% men). The median Karnofsky Performance Status was 90% (range 70-100%). Median prior therapy lines were substantial with 3 (range 1-8): bortezomib, thalidomide or lenalidomide were given in 88% and 24% each, respectively; 94% of patients had undergone prior SCTs. Cytogenetic abnormalities included del(17p) (n=2), t(4;14) (n=2), gain(1q) (n=2), t(11;14) (n=4) and hyperdiploidy (n=7). No DLTs have been observed to date; with 3 patients each being included in dose level 0 and dose level +1 and the following patients safely proceeding to dose level +2. Six SAEs occurred in 4/18 patients (22%): bacteraemia (n=1) and herpes zoster reactivation (n=1) were suspected to be related to all VBDD-drugs. No causal relationship to study drugs was suspected for pneumonia (n=2), 1 syncope and 1 death due to PD with persisting plasma cell leukemia. The ORR (>PR) and clinical benefit rate (SD, PR, CR) was 65% and 89%, respectively. At a median follow-up of 8 months (range 3-23), there have been only 2 patients with PD (refractory MM + plasma cell leukemia). The analysis of HDAC activity after VBDD initiation demonstrated downregulation in 6/8 (75%) patients (Figure 1). Further analyses will determine, whether HDAC activity and treatment response may correlate and whether this HDAC downregulation may precede and/or indicate depth of response
VBDD is a well tolerated and effective regimen in heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory MM patients. There have been no observed DLT and the MTD of vorinostat was set at 300mg, with all reported SAEs being in line with the known safety profile of the investigated drugs. Our alternative vorinostat-schedule (dosing of 4 days on and 4 days off) induced excellent tolerability and seems to enhance the antimyeloma response, warranting completion of this study.
Kleber: MSD, Janssen-Cilag: Research Funding. Off Label Use: Preclinical studies have demonstrated that vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, is synergistic with bortezomib and doxorubicin. The aim of this phase I/II study was to determine the tolerability and activity of the combination of BDD with vorinostat (VBDD) in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Vorinostat is off-label use for MM patients, all other drugs are in label use. Waesch:MSD, Janssen-Cilag: Research Funding. Engelhardt:MSD, Janssen-Cilag: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.