Abstract
Prior to the introduction of modern induction and maintenance regimens, autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) improved outcomes in chemotherapy-sensitive, relapsed follicular lymphoma (FL). We re-evaluated the impact of Rituximab (R) sensitivity on ASCT for relapsed FL in the current Rituximab era.
194 consecutive patients with a confirmed diagnosis of relapsed, grade 1, 2 or 3A FL underwent ASCT at our center from April 1993 to October 2011. They were categorized as R-sensitive, R-refractory, or no R (NoR) if transplanted prior to use of Rituximab. Rituximab refractoriness was defined as failure (at any point in treatment) to achieve at least a PR or documented disease progression within 6 months of receiving the first dose of a full course of single-agent rituximab (³ 4 doses of 375mg/m2 weekly), getting rituximab maintenance (R-maintenance) or completing 2 courses of Rituximab combined with chemotherapy (R-chemotherapy). The statistical significance of differences in event rates was evaluated with the proportional hazards regression model. Two-sided p-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Kaplan-Meier (K-M) curves were used to estimate the probabilities of overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Cumulative incidence of relapse was calculated in a competing risk data analysis considering non-relapse mortality as a competing event.
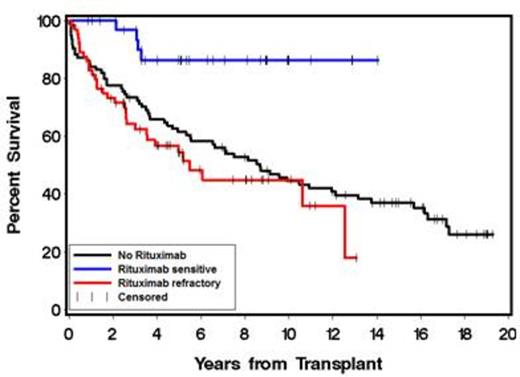
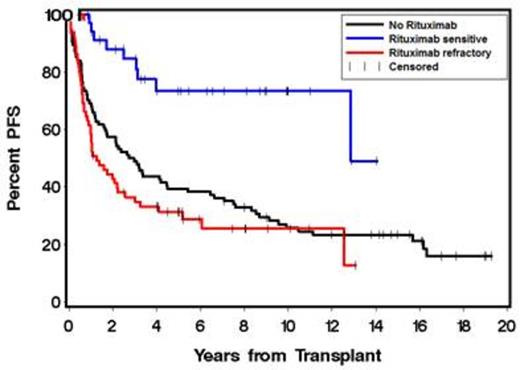
There were 65 rituximab-refractory (RR), 35 rituximab-sensitive (RS) and 94 NoR patients. RS (11%) and RR (12%) patients received R-maintenance. High-risk FL international prognostic index (FLIPI) scores at the time of ASCT was imbalanced between the groups: RS 3%, RR 23% and NoR 26% (P = .009). Baseline characteristics were otherwise comparable between the 3 groups. Median follow-up from ASCT to time of last contact or death was 64 months (range 10-169), 42 months (range 1-157) and 91 months ( range 0.5-231) in the RS, RR and NoR groups, respectively. Univariate analyses showed significantly better OS (P = .003) and PFS (P = .0004) in RS patients with 3-year OS and PFS (Figure 3) of 97% and 85% compared with 63% and 35% in RR and 73.4% and 49% in NoR patients, respectively (Figures 1 & 2). Time to next treatment in relapsing patients was significantly shorter in the RR group compared to the RS and NoR groups. We performed multivariate adjustment for pre-ASCT factors that could affect outcomes i.e. age ≥ 50, FLIPI score ≥ 3, # prior chemotherapy regimens ≥ 3, chemo-resistance, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, prior radiation therapy, bone marrow stem cell source, and remission quotient ≥ 6 (defined as the months from diagnosis to ASCT divided by number of prior therapies). Multivariate adjustment showed OS to be significantly affected only by rituximab sensitivity, with a lower risk of death in RS patients (HR 0.24, P = .01). PFS was also significantly affected by pre-ASCT rituximab sensitivity (HR 0.35, P = .006). Cumulative incidence of relapse was increased in RR patients (HR 2.11, P = .01). The differences in post-ASCT OS, PFS, and relapse rates between the RS and RR patients were maintained independent of transplant conditioning regimen. There were no differences in OS, PFS or relapse whether RR patients were refractory to single-agent rituximab, R-maintenance, or R-chemotherapy.
Pre-transplant rituximab sensitivity in relapsed FL is a strong independent predictor of post-ASCT outcome. For RR FL patients with limited effective options, nearly half were alive and progression-free at 3 years after ASCT.
OS according to whether patients were rituximab sensitive, rituximab refractory or had not received rituximab before ASCT
OS according to whether patients were rituximab sensitive, rituximab refractory or had not received rituximab before ASCT
PFS according to patient groups
Shustov:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Honoraria, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract