Abstract
Mastocytosis is characterized by abnormal expansion and accumulation of neoplastic mast cells in one or more organ systems. Traditionally, mastocytosis is divided into cutaneous mastocytosis (CM) and systemic mastocytosis (SM). In most patients with SM, the transforming somatic mutation KIT D816V is detected. However, only few studies have quantified the KIT D816V allele burden in CM and SM. The aim of the present study was to quantify KIT D816V in various forms of mastocytosis and to correlate the allele burden of KIT D816V with the disease category, serum tryptase levels and clinical outcomes. KIT D816V was quantified in bone marrow (BM) and peripheral blood (PB) cells by a real-time PCR (qPCR) assay based on allele-specific primers. In addition, BM and PB cells were also examined for the presence of KIT D816V by melting curve analysis after PCR clamping in all patients. Overall, 225 DNA samples (BM, n=112; PB, n=113) from 107 patients with mastocytosis (females: n=57; males, n=50; median age 49 years; range 18-73 years) were analyzed. Based on WHO criteria, 14 patients had CM, 3 the provisional diagnosis of mastocytosis in the skin (MIS), 66 indolent SM (ISM), 6 smouldering SM (SSM), 7 aggressive SM (ASM), one mast cell leukemia (MCL) and 10 patients SM with an associated hematologic non-mast cell lineage disorder (SM-AHNMD). KIT D816V was found in in 76/107 patients (71%) by melting curve analysis after PCR clamping, and in 92/107 patients (86%) by qPCR (p<0.005). In paired BM and PB samples of 43 patients an excellent correlation of the KIT D816V burden with almost identical results was found (r=0.98, p<0.001). When examining the KIT D816V allele burden in KIT D816V+ patients (n=92) in various categories of the disease, significant differences were found between CM (median KIT D816V allele fraction: 0.042%), MIS (median: 0.084%), ISM (median: 0.286%), SSM (median: 3.012%), ASM (median: 9.346%) and SM-AHNMD (median: 3.761%) (p<0.001). Moreover, we found that the KIT D816V allele burden correlates significantly with the serum tryptase level in our patients (r=0.50, p<0.005). Consecutive studies revealed that the KIT D816V allele fraction is of prognostic significance concerning survival as determined by Cox regression (p=0.015). As assessed by Kaplan Meier estimates and log rank testing, patients with a KIT D816V allele burden of ≥2% were found to have a significantly shorter survival than those with an allele burden of less than 2% (p=0.001) (Figure 1). Thirty patients were evaluated at diagnosis and during the follow up. In untreated patients with stable disease, the KIT D816V allele burden remained within a constant range. By contrast, in patients with disease progression, an increase in the KIT D816V burden over time was detectable. In patients responding to cytoreductive agents (cladribine n=4; hydroxyurea n=1) a significant decrease in the median KIT D816V allele burden (by 91.6%) after therapy compared to pre-therapeutic samples was observed (p=0.027). In summary, our data show that qPCR is a highly sensitive approach for the detection and quantification of KIT D816V in patients with mastocytosis and that the KIT D816V mutation burden differs significantly among patients in different WHO subtypes. Moreover, the KIT D816V allele burden correlates with serum tryptase levels and is of prognostic significance concerning survival in patients with mastocytosis. Finally, quantification of KIT D816V may serve as follow up parameter useful for determining the natural course and treatment responses in patients with mastocytosis. We recommend that the KIT D816V mutation burden is included as a novel parameter in daily practice and clinical trials in advanced SM. Close modal
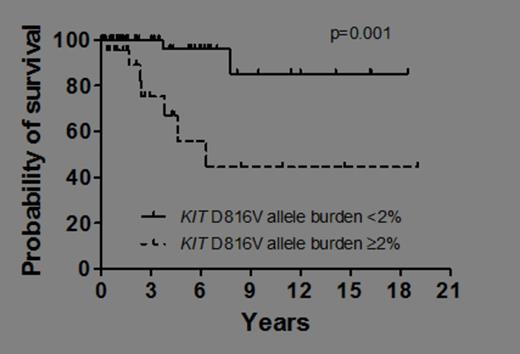
Figure 1
Overall survival of patients with KIT D816V+ mastocytosis. Patients were split into those with a KIT D816V allele burden of<2% and those with an allelic burden of ≥2%. Survival was estimated by the method of Kaplan and Meier (p=0.001).
Figure 1
Overall survival of patients with KIT D816V+ mastocytosis. Patients were split into those with a KIT D816V allele burden of<2% and those with an allelic burden of ≥2%. Survival was estimated by the method of Kaplan and Meier (p=0.001).
Disclosures:
Valent:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
*
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
© 2013 by The American Society of Hematology
2013